Artificial cells act like the real thing
 Cell-like compartments produce proteins and communicate with one another, similar to natural biological systems.
Cell-like compartments produce proteins and communicate with one another, similar to natural biological systems.
Aug 18th, 2014
Read more
 Subscribe to our Biotechnology News feed
Subscribe to our Biotechnology News feed
 Cell-like compartments produce proteins and communicate with one another, similar to natural biological systems.
Cell-like compartments produce proteins and communicate with one another, similar to natural biological systems.
Aug 18th, 2014
Read more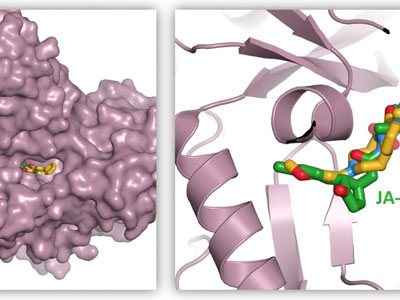 A small molecule inhibits jasmonic acid and helps to explain its effects.
A small molecule inhibits jasmonic acid and helps to explain its effects.
Aug 17th, 2014
Read more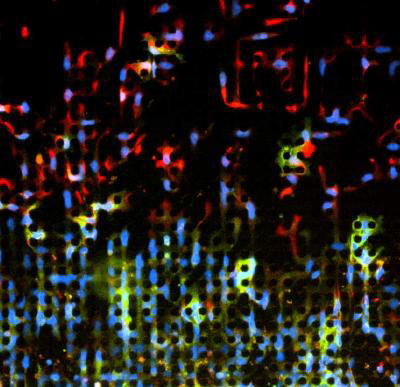 Using a microengineered device that acts as an obstacle course for cells, researchers have shed new light on a cellular metamorphosis thought to play a role in tumor cell invasion throughout the body.
Using a microengineered device that acts as an obstacle course for cells, researchers have shed new light on a cellular metamorphosis thought to play a role in tumor cell invasion throughout the body.
Aug 17th, 2014
Read more Scientists now have a clear picture of the bacterial immune system and say its unique shape is likely why bacteria can so quickly recognize and destroy their assailants.
Scientists now have a clear picture of the bacterial immune system and say its unique shape is likely why bacteria can so quickly recognize and destroy their assailants.
Aug 16th, 2014
Read more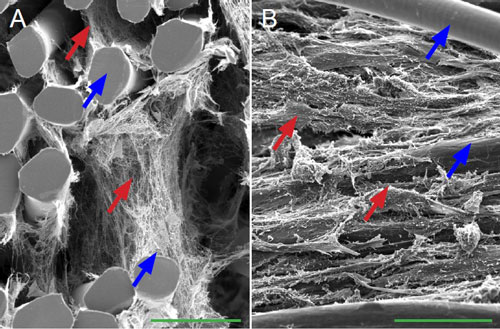 In a new study, a thermosensitive collagen hydrogel remained as a liquid when kept at temperatures below 10C and gelled when the temperature was increased to 37C in an incubator for 30 minutes, which was used as an extracellular matrix and combined with bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells to construct tissue-engineered peripheral nerve composites in vitro.
In a new study, a thermosensitive collagen hydrogel remained as a liquid when kept at temperatures below 10C and gelled when the temperature was increased to 37C in an incubator for 30 minutes, which was used as an extracellular matrix and combined with bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells to construct tissue-engineered peripheral nerve composites in vitro.
Aug 15th, 2014
Read more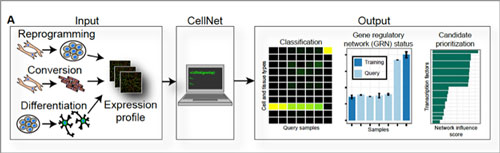 In a boon to stem cell research and regenerative medicine, scientists have created a computer algorithm called CellNet as a 'roadmap' for cell and tissue engineering, to ensure that cells engineered in the lab have the same favorable properties as cells in our own bodies.
In a boon to stem cell research and regenerative medicine, scientists have created a computer algorithm called CellNet as a 'roadmap' for cell and tissue engineering, to ensure that cells engineered in the lab have the same favorable properties as cells in our own bodies.
Aug 14th, 2014
Read moreA new technique has demonstrated for the first time that the size of molecules penetrating the blood-brain barrier can be controlled using acoustic pressure - the pressure of an ultrasound beam - to let specific molecules through.
Aug 14th, 2014
Read more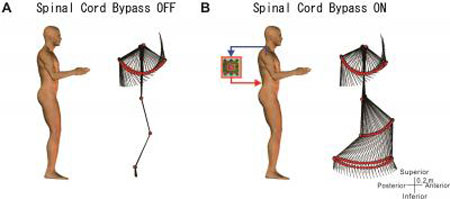 Researchers have successfully made an artificial connection from the brain to the locomotion center in the spinal cord by bypassing with a computer and exercised control over walking.
Researchers have successfully made an artificial connection from the brain to the locomotion center in the spinal cord by bypassing with a computer and exercised control over walking.
Aug 14th, 2014
Read more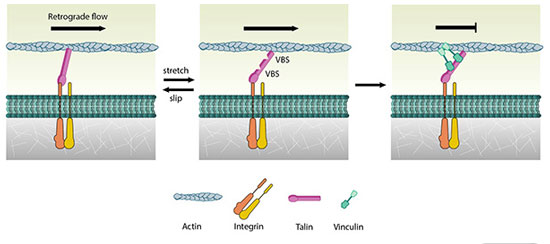 Scientists discovered that living cell migration is regulated by the engagement of a force transmitter composed of vinculin and talin, two types of cytoskeletal protein. The researchers showed that force-dependent vinculin binding to talin plays a critical role in mechanically connecting the actin cytoskeleton to the extracellular substrate to contribute towards cell migration.
Scientists discovered that living cell migration is regulated by the engagement of a force transmitter composed of vinculin and talin, two types of cytoskeletal protein. The researchers showed that force-dependent vinculin binding to talin plays a critical role in mechanically connecting the actin cytoskeleton to the extracellular substrate to contribute towards cell migration.
Aug 14th, 2014
Read moreDeep within most tumors lie areas that remain untouched by chemotherapy and radiation. These troublesome spots lack the blood and oxygen needed for traditional therapies to work, but provide the perfect target for a new cancer treatment using bacteria that thrive in oxygen-poor conditions. Now, researchers have shown that injections of a weakened version of one such anaerobic bacteria can shrink tumors in rats, pet dogs, and a human patient.
Aug 13th, 2014
Read moreRecent advances that allow the precise editing of genomes now raise the possibility that fruit and other crops might be genetically improved without the need to introduce foreign genes.
Aug 13th, 2014
Read more Spider silk is light and delicate, while incredibly resilient and tear-resistant. Understanding the structure and way of construction of these threads is a challenge taken up by a research team of Kiel University.
Spider silk is light and delicate, while incredibly resilient and tear-resistant. Understanding the structure and way of construction of these threads is a challenge taken up by a research team of Kiel University.
Aug 13th, 2014
Read more Researchers have developed a 'self-fitting' material that expands with warm salt water to precisely fill bone defects, and also acts as a scaffold for new bone growth.
Researchers have developed a 'self-fitting' material that expands with warm salt water to precisely fill bone defects, and also acts as a scaffold for new bone growth.
Aug 13th, 2014
Read more A synthetic scaffold with fine-tuned physical properties helps cartilage regrowth at injury sites.
A synthetic scaffold with fine-tuned physical properties helps cartilage regrowth at injury sites.
Aug 13th, 2014
Read moreResearchers have created a molecule that can cause cancer cells to self-destruct by carrying sodium and chloride ions into the cells.
Aug 12th, 2014
Read more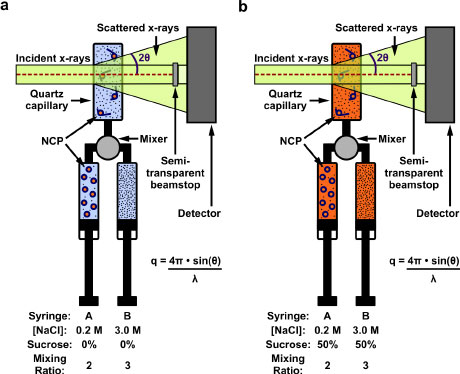 Biophysics is a science of shapes - the shapes of molecules like DNA as they wrap and unwrap around protein cores, for instance. Researchers have unveiled a new method for observing such processes in real time.
Biophysics is a science of shapes - the shapes of molecules like DNA as they wrap and unwrap around protein cores, for instance. Researchers have unveiled a new method for observing such processes in real time.
Aug 12th, 2014
Read more Model shows biochemical and electrophysiological responses; research offers new options for study of brain function, disease and trauma.
Model shows biochemical and electrophysiological responses; research offers new options for study of brain function, disease and trauma.
Aug 11th, 2014
Read more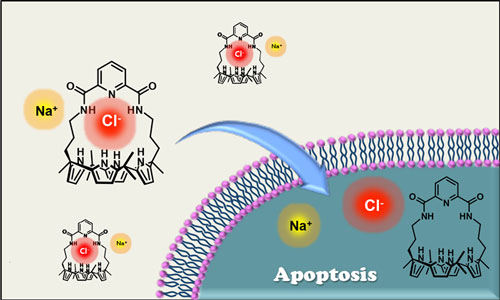 Researchers have created a molecule that can cause cancer cells to self-destruct by ferrying sodium and chloride ions into the cancer cells. These synthetic ion transporters confirm a two-decades-old hypothesis that could point the way to new anticancer drugs while also benefitting patients with cystic fibrosis.
Researchers have created a molecule that can cause cancer cells to self-destruct by ferrying sodium and chloride ions into the cancer cells. These synthetic ion transporters confirm a two-decades-old hypothesis that could point the way to new anticancer drugs while also benefitting patients with cystic fibrosis.
Aug 11th, 2014
Read more