Sscientists have developed geochemical tracers to identify hydraulic fracturing flowback fluids that have been spilled or released into the environment. The tracers have been field-tested at two sites and can distinguish fracking fluids from wastewater versus conventional wells or other sources. They give scientists new forensic tools to detect if fracking fluids are escaping into water supplies and what risks, if any, they might pose.
Oct 20th, 2014
Read more
 Visio.M consortium presents new electric car at the eCarTec 2014 in Munich.
Visio.M consortium presents new electric car at the eCarTec 2014 in Munich.
Oct 20th, 2014
Read more
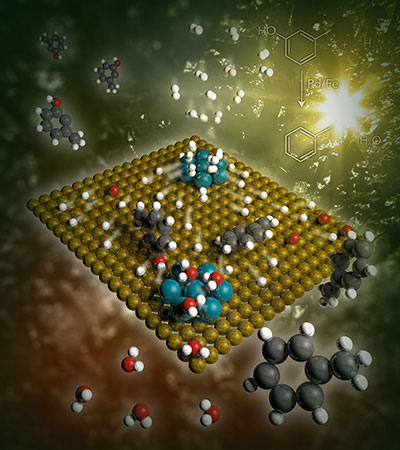 Researchers have developed a new catalyst that could lead to making biofuels cheaply and more efficiently. They mixed inexpensive iron with a tiny amount of rare palladium to make the catalyst.
Researchers have developed a new catalyst that could lead to making biofuels cheaply and more efficiently. They mixed inexpensive iron with a tiny amount of rare palladium to make the catalyst.
Oct 16th, 2014
Read more
 Researchers have developed innovative new materials and contactless techniques for applying ultrafine, homogeneous contact fingers to solar cells. This 'dispensing' technology can be easily integrated into conventional silicon solar cell production lines where it replaces screen printing as the method of applying front side metallization.
Researchers have developed innovative new materials and contactless techniques for applying ultrafine, homogeneous contact fingers to solar cells. This 'dispensing' technology can be easily integrated into conventional silicon solar cell production lines where it replaces screen printing as the method of applying front side metallization.
Oct 16th, 2014
Read more
 A Norwegian researcher has been able to achieve bio-oil yields of 79% from a common kelp. Other researchers working with the same species have yields closer to 20%. The secret is to heat the kelp very quickly and bring it to the right temperature within seconds.
A Norwegian researcher has been able to achieve bio-oil yields of 79% from a common kelp. Other researchers working with the same species have yields closer to 20%. The secret is to heat the kelp very quickly and bring it to the right temperature within seconds.
Oct 16th, 2014
Read more
The recent natural gas boom due to the use of technologies such as fracking will not lead to a reduction of overall greenhouse gas emissions. Burning natural gas produces only half the CO2 emissions as coal per unit of energy. However, as natural gas becomes abundant and therefore cheap, it adds to the total energy supply and only partially replaces coal.
Oct 15th, 2014
Read more
 The phase-out of traditional incandescent bulbs in the U.S. and elsewhere, as well as a growing interest in energy efficiency, has given light-emitting diode lighting a sales boost. However, that trend could be short-lived as key materials known as rare earth elements become more expensive. Scientists have now designed new materials for making household light-emitting diode bulbs without using these ingredients.
The phase-out of traditional incandescent bulbs in the U.S. and elsewhere, as well as a growing interest in energy efficiency, has given light-emitting diode lighting a sales boost. However, that trend could be short-lived as key materials known as rare earth elements become more expensive. Scientists have now designed new materials for making household light-emitting diode bulbs without using these ingredients.
Oct 15th, 2014
Read more
The European Commission has commissioned a study that aims at helping to close the knowledge gap by quantifying the extent of public interventions in energy markets in all 28 Member States.
Oct 13th, 2014
Read more
Simulating the cost of generating a combination of electricity sources provides tools to optimise such energy mix.
Oct 13th, 2014
Read more
Researchers are questioning the received wisdom regarding the promotion of electric vehicles in towns and cities. They suggest that the evidence of benefits in terms of energy usage and emissions points to electric vehicle use in sub-urban and rural settings as being much stronger.
Oct 9th, 2014
Read more
Solar, wind and other alternative sources are easier on the environment but less predictable than coal, gas or oil-fired plants, demanding a more sophisticated distribution and delivery system.
Oct 8th, 2014
Read more
The Global Climate and Energy Project (GCEP) at Stanford University has awarded $10.5 million for seven research projects designed to advance a broad range of renewable energy technologies.
Oct 8th, 2014
Read more
In the race to secure clean energy in the future, engineers are reinventing a piece of technology which has so far only been used in labs to diagnose cancer, detect explosives, and even analyse grand artistic masterpieces.
Oct 8th, 2014
Read more
It has been known for several years that sulfuric acid contributes to the formation of tiny aerosol particles, which play an important role in the formation of clouds. A new study shows that dimethylamine can tremendously enhance new particle formation. The formation of neutral nucleating clusters of sulfuric acid and dimethylamine was observed for the first time.
Oct 8th, 2014
Read more
 New tools will merge urban design with scientific analysis to improve the decision-making process associated with large-scale urban developments. One such tool, called LakeSim, has been prototyped with an initial focus on consumer-driven energy and transportation demand.
New tools will merge urban design with scientific analysis to improve the decision-making process associated with large-scale urban developments. One such tool, called LakeSim, has been prototyped with an initial focus on consumer-driven energy and transportation demand.
Oct 8th, 2014
Read more
Researchers are working on producing more cost-effective gallium nitride LEDs that can have widespread use in homes and offices.
Oct 8th, 2014
Read more
'for the invention of efficient blue light-emitting diodes which has enabled bright and energy-saving white light sources'
Oct 7th, 2014
Read more
A future where electricity comes mostly from low-carbon and renewable resources is not only feasible in terms of material demand, but will significantly reduce air pollution, a new study says.
Oct 6th, 2014
Read more

 Subscribe to our Cleantech News feed
Subscribe to our Cleantech News feed




