Showing Spotlights 81 - 88 of 331 in category All (newest first):
 Researchers report the direct writing of laser-induced graphene on a Kevlar textile. The transformation of Kevlar into graphene can be attributed to the photothermal effect induced by CO2 laser irradiation. Specifically, this resulted in high localized temperature, leading to the ablation and depolymerization of the Kevlar fiber. The remaining carbon atoms are recombined and 'recrystallized' into graphene. Based on this technique, it becomes feasible to prepare various types of flexible electronics on different commercial textiles such as silk and cotton. This will enable the efficient and customized preparation of multi-functional textile electronics.
Researchers report the direct writing of laser-induced graphene on a Kevlar textile. The transformation of Kevlar into graphene can be attributed to the photothermal effect induced by CO2 laser irradiation. Specifically, this resulted in high localized temperature, leading to the ablation and depolymerization of the Kevlar fiber. The remaining carbon atoms are recombined and 'recrystallized' into graphene. Based on this technique, it becomes feasible to prepare various types of flexible electronics on different commercial textiles such as silk and cotton. This will enable the efficient and customized preparation of multi-functional textile electronics.
Mar 11th, 2020
 Nanofluidic membranes based on two-dimensional materials are promising materials for next-generation water desalination and purification. For instance, pristine and chemically modified graphene oxide membranes (GOMs) effectively block organic dyes and nanoparticles as small as 9 �. However, these nanomembranes fail to exclude smaller inorganic salt ions, which would be required to extract pure potable water from unconventional water sources such as, salt water, industrial waste water, and rain water. With a novel approach called planar heterogeneous interface desalination researchers can now achieve a high salt rejection rate close to 97%.
Nanofluidic membranes based on two-dimensional materials are promising materials for next-generation water desalination and purification. For instance, pristine and chemically modified graphene oxide membranes (GOMs) effectively block organic dyes and nanoparticles as small as 9 �. However, these nanomembranes fail to exclude smaller inorganic salt ions, which would be required to extract pure potable water from unconventional water sources such as, salt water, industrial waste water, and rain water. With a novel approach called planar heterogeneous interface desalination researchers can now achieve a high salt rejection rate close to 97%.
Mar 3rd, 2020
 Two-dimensional (2D) materials could offer new building blocks for future technologies, but this requires approaches to control the carrier type in 2D semiconductors. A number of pioneering works have demonstrated different methods to program the carrier type in 2D materials, such as electrostatic doping, chemical doping, ion implantation, charge transfer, and annealing control. Recently, a team of researchers have developed a technique to dope 2D materials for redefinable nanoelectronics using nonvolatile ferroelectric domains.
Two-dimensional (2D) materials could offer new building blocks for future technologies, but this requires approaches to control the carrier type in 2D semiconductors. A number of pioneering works have demonstrated different methods to program the carrier type in 2D materials, such as electrostatic doping, chemical doping, ion implantation, charge transfer, and annealing control. Recently, a team of researchers have developed a technique to dope 2D materials for redefinable nanoelectronics using nonvolatile ferroelectric domains.
Feb 20th, 2020
 Hematite as a magnetic photocatalyst can support the production of oxygen in its magnetic ground state and thereby improve the efficiency of hydrogen production. When hematite is made thinner, another important improvement in the efficiency of the reaction could be accomplished by expectedly more efficient separation of charge carriers upon the absorption of light on the surface. Scientists now elucidate exactly how optical and magnetic properties of hematite change when decreased in thickness to the atomistic scale.
Hematite as a magnetic photocatalyst can support the production of oxygen in its magnetic ground state and thereby improve the efficiency of hydrogen production. When hematite is made thinner, another important improvement in the efficiency of the reaction could be accomplished by expectedly more efficient separation of charge carriers upon the absorption of light on the surface. Scientists now elucidate exactly how optical and magnetic properties of hematite change when decreased in thickness to the atomistic scale.
Feb 14th, 2020
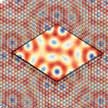 Researchers explain how a higher order periodic modulations due to the encapsulation of graphene between hexagonal boron nitride, called supermoire, affects the electronic and structural properties of graphene, as revealed in three recent independent experiments. High quality graphene samples are of high importance for obtaining and exploiting its theoretically described properties. Utilizing an adequate substrate reduces the corrugation and improves otherwise disorder limited properties of graphene.
Researchers explain how a higher order periodic modulations due to the encapsulation of graphene between hexagonal boron nitride, called supermoire, affects the electronic and structural properties of graphene, as revealed in three recent independent experiments. High quality graphene samples are of high importance for obtaining and exploiting its theoretically described properties. Utilizing an adequate substrate reduces the corrugation and improves otherwise disorder limited properties of graphene.
Jan 29th, 2020
 Researchers have produced graphene by molten carbonate electrolytic splitting of CO2 to a nano-thin carbon product (carbon nanoplatelets) comprised of 25 to 125 graphene layers, and subsequent electrochemical exfoliation of the nanoplatelets to graphene in a carbonate soluble aqueous solution. The sole products of the carbon dioxide electrolysis are straightforward: high yield carbon nanoplatelets and oxygen. The carbon nanoplatelets provide a thinner starting point than a conventional graphite reactant to facilitate electrochemical exfoliation.
Researchers have produced graphene by molten carbonate electrolytic splitting of CO2 to a nano-thin carbon product (carbon nanoplatelets) comprised of 25 to 125 graphene layers, and subsequent electrochemical exfoliation of the nanoplatelets to graphene in a carbonate soluble aqueous solution. The sole products of the carbon dioxide electrolysis are straightforward: high yield carbon nanoplatelets and oxygen. The carbon nanoplatelets provide a thinner starting point than a conventional graphite reactant to facilitate electrochemical exfoliation.
Dec 2nd, 2019
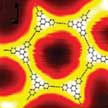 Graphyne is a little known sibling of graphene. Simulations have shown that graphyne's conduction electrons travel extremely fast - as they do in graphene - but in only one direction. That property could help researchers design faster transistors and other electronic components that process one-way current. Graphyne is distinct in being composed of sp and sp2 carbon atoms, which contrasts with graphene containing only sp2 carbon. The coexistence of sp and sp2 carbons in graphyne gives rise to unique physical properties, such as high conductivity and large carrier mobility.
Graphyne is a little known sibling of graphene. Simulations have shown that graphyne's conduction electrons travel extremely fast - as they do in graphene - but in only one direction. That property could help researchers design faster transistors and other electronic components that process one-way current. Graphyne is distinct in being composed of sp and sp2 carbon atoms, which contrasts with graphene containing only sp2 carbon. The coexistence of sp and sp2 carbons in graphyne gives rise to unique physical properties, such as high conductivity and large carrier mobility.
Oct 31st, 2019
 Researchers have developed a method for direct, point-of-use detection of mycotoxins in food. The method is based on the modification of electrolyte operated graphene filed effect transistors that have been specifically functionalized with aptamers by covalent binding. Demonstrating the performance of this method on Ochratoxin A, these sensors show a response time of within 5 minutes with a sensitivity down to 4 pg/ml - that is about three orders of magnitude less than accepted tolerance levels of Ochratoxin A.
Researchers have developed a method for direct, point-of-use detection of mycotoxins in food. The method is based on the modification of electrolyte operated graphene filed effect transistors that have been specifically functionalized with aptamers by covalent binding. Demonstrating the performance of this method on Ochratoxin A, these sensors show a response time of within 5 minutes with a sensitivity down to 4 pg/ml - that is about three orders of magnitude less than accepted tolerance levels of Ochratoxin A.
Oct 4th, 2019
 Researchers report the direct writing of laser-induced graphene on a Kevlar textile. The transformation of Kevlar into graphene can be attributed to the photothermal effect induced by CO2 laser irradiation. Specifically, this resulted in high localized temperature, leading to the ablation and depolymerization of the Kevlar fiber. The remaining carbon atoms are recombined and 'recrystallized' into graphene. Based on this technique, it becomes feasible to prepare various types of flexible electronics on different commercial textiles such as silk and cotton. This will enable the efficient and customized preparation of multi-functional textile electronics.
Researchers report the direct writing of laser-induced graphene on a Kevlar textile. The transformation of Kevlar into graphene can be attributed to the photothermal effect induced by CO2 laser irradiation. Specifically, this resulted in high localized temperature, leading to the ablation and depolymerization of the Kevlar fiber. The remaining carbon atoms are recombined and 'recrystallized' into graphene. Based on this technique, it becomes feasible to prepare various types of flexible electronics on different commercial textiles such as silk and cotton. This will enable the efficient and customized preparation of multi-functional textile electronics. 
 Subscribe to our Nanotechnology Spotlight feed
Subscribe to our Nanotechnology Spotlight feed





