Showing Spotlights 105 - 112 of 544 in category All (newest first):
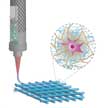 Recent developments in hydrogel chemistries, reinforcement approaches, and crosslinking methods have expanded the applications of 3D bioprinting to pharmaceutics, regenerative medicine, and biomedical devices. A multitude of 3D bioprinting techniques have been developed, but among these different approaches, extrusion-based 3D bioprinting has become a popular technique as it is easy to optimize and all its constituents are economical in price. A recent review elucidates the nuances of 3D bioprinting in a step-by-step guideline format, from its basics to more advanced levels.
Recent developments in hydrogel chemistries, reinforcement approaches, and crosslinking methods have expanded the applications of 3D bioprinting to pharmaceutics, regenerative medicine, and biomedical devices. A multitude of 3D bioprinting techniques have been developed, but among these different approaches, extrusion-based 3D bioprinting has become a popular technique as it is easy to optimize and all its constituents are economical in price. A recent review elucidates the nuances of 3D bioprinting in a step-by-step guideline format, from its basics to more advanced levels.
Apr 10th, 2020
 Nanotechnology offers many benefits that can be leveraged to increase the potency of vaccine formulations. For anticancer vaccination, antigenic material can be collected directly from a patient's resected tumor, formulated into a biomimetic nanoparticle, and then administered back into the patient to promote tumor-specific immunity. For antibacterial vaccination, strain-specific virulence factors or membrane can be immobilized onto nanoparticle substrates, and the resulting complexes can be used to vaccinate patients with an identified risk against the associated pathogen.
Nanotechnology offers many benefits that can be leveraged to increase the potency of vaccine formulations. For anticancer vaccination, antigenic material can be collected directly from a patient's resected tumor, formulated into a biomimetic nanoparticle, and then administered back into the patient to promote tumor-specific immunity. For antibacterial vaccination, strain-specific virulence factors or membrane can be immobilized onto nanoparticle substrates, and the resulting complexes can be used to vaccinate patients with an identified risk against the associated pathogen.
Apr 3rd, 2020
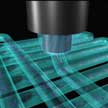 Biofabrication is a revolutionizing toolkit for regenerative medicine that allows cells and other biomaterials to be precisely combined and patterned into three-dimensional (3D) constructs through automated, cell-friendly fabrication methods. With rapid advanced in 3D-printing hardware on one hand and bioink materials on the other, biofabrication techniques have gained significant momentum and provide a powerful approach to tackle major hurdles in the generation of engineered living tissues. While 3D bioprinting is still in its early stages, the remarkable leap it has made in recent years points to the eventual reality of lab-grown, functional organs.
Biofabrication is a revolutionizing toolkit for regenerative medicine that allows cells and other biomaterials to be precisely combined and patterned into three-dimensional (3D) constructs through automated, cell-friendly fabrication methods. With rapid advanced in 3D-printing hardware on one hand and bioink materials on the other, biofabrication techniques have gained significant momentum and provide a powerful approach to tackle major hurdles in the generation of engineered living tissues. While 3D bioprinting is still in its early stages, the remarkable leap it has made in recent years points to the eventual reality of lab-grown, functional organs.
Mar 25th, 2020
 New types of magnetic nanostructures have interesting properties that enhance novel medical applications in diagnosis and allow the exploration of new therapeutic techniques. In a new paper, researchers review promising new nanomaterials that can be used in cancer diagnosis and treatment, namely as magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) contrast agents. One especially interesting advance involves exotic spin configurations, like a vortex state in nanodiscs, where magnetic moments arrange into a curly geometry.
New types of magnetic nanostructures have interesting properties that enhance novel medical applications in diagnosis and allow the exploration of new therapeutic techniques. In a new paper, researchers review promising new nanomaterials that can be used in cancer diagnosis and treatment, namely as magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) contrast agents. One especially interesting advance involves exotic spin configurations, like a vortex state in nanodiscs, where magnetic moments arrange into a curly geometry.
Feb 6th, 2020
 Proteins present in human plasma mirror a person's physiology and the ability to rapidly profile the plasma proteome holds the promise of a revolution in point-of-care disease diagnosis and therapeutic monitoring. New research findings suggest that levitation patterns of human plasma proteins using a magnetic levitation technique may provide useful information about the health spectrum of individual donors. The study reveals that optical images of magnetically levitated plasma proteins carry important information about the health spectrum of plasma donors.
Proteins present in human plasma mirror a person's physiology and the ability to rapidly profile the plasma proteome holds the promise of a revolution in point-of-care disease diagnosis and therapeutic monitoring. New research findings suggest that levitation patterns of human plasma proteins using a magnetic levitation technique may provide useful information about the health spectrum of individual donors. The study reveals that optical images of magnetically levitated plasma proteins carry important information about the health spectrum of plasma donors.
Feb 3rd, 2020
 The density of proteins in solution is an important fundamental biophysical quantity that has not been accurately measured yet. This has led to extensive debate in the literature regarding the precise density value of proteins. This rough density metric can often lead to inaccurate estimates on the other physicochemical and composite protein features, especially after their interactions with other materials such as nanoparticles. Researchers have now demonstrated a new technique using superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles for magnetic levitation, which promises a more precisely measurement of the density of proteins in solution.
The density of proteins in solution is an important fundamental biophysical quantity that has not been accurately measured yet. This has led to extensive debate in the literature regarding the precise density value of proteins. This rough density metric can often lead to inaccurate estimates on the other physicochemical and composite protein features, especially after their interactions with other materials such as nanoparticles. Researchers have now demonstrated a new technique using superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles for magnetic levitation, which promises a more precisely measurement of the density of proteins in solution.
Jan 13th, 2020
 The combination of multiple therapeutic modalities with synergetic effects is a promising approach to enhance antibacterial efficiency and possibly decrease the needed concentration of bactericidal reagents. In new work, scientists report a path to achieve efficient localized bacterial eradication and anti-infective therapy by combining the advantages of 2D graphene and metal organic framework (MOF)-derived carbon nanomaterials. This proposed MOF-derived 2D carbon nanosheets (2D-CNs) can form aggregations spontaneously under NIR irradiation and meanwhile exhibit localized triple bactericidal modalities.
The combination of multiple therapeutic modalities with synergetic effects is a promising approach to enhance antibacterial efficiency and possibly decrease the needed concentration of bactericidal reagents. In new work, scientists report a path to achieve efficient localized bacterial eradication and anti-infective therapy by combining the advantages of 2D graphene and metal organic framework (MOF)-derived carbon nanomaterials. This proposed MOF-derived 2D carbon nanosheets (2D-CNs) can form aggregations spontaneously under NIR irradiation and meanwhile exhibit localized triple bactericidal modalities.
Jan 2nd, 2020
 Optical biosensors and micromotors that can sense and actuate biological environments are considered promising theranostic devices because of their high spatial resolution and flexibility.
Advancing the field from synthetic sensors to living materials - which often can be incompatible with biological systems - researchers have assembled living biosensors and micromotors using an in vivo red blood cell (RBC) waveguide for applications in pH sensing and particle transport. This living biosensor can be used for the diagnosis of pH-related disorders of the blood; then, the waveguide can rotate as a micromotor and transport microparticles to the target region.
Optical biosensors and micromotors that can sense and actuate biological environments are considered promising theranostic devices because of their high spatial resolution and flexibility.
Advancing the field from synthetic sensors to living materials - which often can be incompatible with biological systems - researchers have assembled living biosensors and micromotors using an in vivo red blood cell (RBC) waveguide for applications in pH sensing and particle transport. This living biosensor can be used for the diagnosis of pH-related disorders of the blood; then, the waveguide can rotate as a micromotor and transport microparticles to the target region.
Dec 16th, 2019
 Recent developments in hydrogel chemistries, reinforcement approaches, and crosslinking methods have expanded the applications of 3D bioprinting to pharmaceutics, regenerative medicine, and biomedical devices. A multitude of 3D bioprinting techniques have been developed, but among these different approaches, extrusion-based 3D bioprinting has become a popular technique as it is easy to optimize and all its constituents are economical in price. A recent review elucidates the nuances of 3D bioprinting in a step-by-step guideline format, from its basics to more advanced levels.
Recent developments in hydrogel chemistries, reinforcement approaches, and crosslinking methods have expanded the applications of 3D bioprinting to pharmaceutics, regenerative medicine, and biomedical devices. A multitude of 3D bioprinting techniques have been developed, but among these different approaches, extrusion-based 3D bioprinting has become a popular technique as it is easy to optimize and all its constituents are economical in price. A recent review elucidates the nuances of 3D bioprinting in a step-by-step guideline format, from its basics to more advanced levels.
 Subscribe to our Nanotechnology Spotlight feed
Subscribe to our Nanotechnology Spotlight feed





