Showing Spotlights 177 - 184 of 544 in category All (newest first):
 Researchers have demonstrated that nitric-oxide releasing nanoparticles interfere with Staphylococcus aureus (S. aureus) adhesion and prevent biofilm formation on a rat central venous catheters model of infection. Specifically, they demonstrated that a well studied nitric oxide-releasing nanoparticle platform (NO-np) has the potential to reduce the incidence and/or treat central venous catheter infections. The investigators examined the formation of staphylococcal biofilms by confocal and scanning electron microscopy and found that treatment of staphylococcal biofilms with NO-np significantly reduced biofilm thickness and bacterial number compared to control biofilms.
Researchers have demonstrated that nitric-oxide releasing nanoparticles interfere with Staphylococcus aureus (S. aureus) adhesion and prevent biofilm formation on a rat central venous catheters model of infection. Specifically, they demonstrated that a well studied nitric oxide-releasing nanoparticle platform (NO-np) has the potential to reduce the incidence and/or treat central venous catheter infections. The investigators examined the formation of staphylococcal biofilms by confocal and scanning electron microscopy and found that treatment of staphylococcal biofilms with NO-np significantly reduced biofilm thickness and bacterial number compared to control biofilms.
Nov 11th, 2016
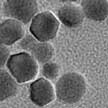 Researchers have, for the first time, used naturally occurring bacterial magnetic nanoparticles (BMPs) - magnetosome extracted from magnetotactic bacteria - to substitute man-made nanoparticles for photothermal cancer therapy. Compared with engineered magnetic nanoparticles, BMPs have specific features such as large-scale production, monodispersity, good biocompatibility, high crystallinity, and close-to-bulk magnetization besides being covered with a lipid bilayer. This layer of biomembrane is particularly useful as it removes the need for a postsynthetic surface modification step for escaping destruction by the body's immune system.
Researchers have, for the first time, used naturally occurring bacterial magnetic nanoparticles (BMPs) - magnetosome extracted from magnetotactic bacteria - to substitute man-made nanoparticles for photothermal cancer therapy. Compared with engineered magnetic nanoparticles, BMPs have specific features such as large-scale production, monodispersity, good biocompatibility, high crystallinity, and close-to-bulk magnetization besides being covered with a lipid bilayer. This layer of biomembrane is particularly useful as it removes the need for a postsynthetic surface modification step for escaping destruction by the body's immune system.
Nov 10th, 2016
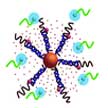 Scientists have designed an advanced type of nanoparticle, which is able to carry drugs directly into cells and release them only in the presence of an appropriate mRNA signature; in other words, the nanoparticle carriers release their payload only in specific - metastatic cancer - cells and remain inactive in healthy cells. The researchers designed nanoparticles that can selectively distinguish healthy cells from model metastatic cells and release their payload - an anticancer drug - only to the model metastatic cells.
Scientists have designed an advanced type of nanoparticle, which is able to carry drugs directly into cells and release them only in the presence of an appropriate mRNA signature; in other words, the nanoparticle carriers release their payload only in specific - metastatic cancer - cells and remain inactive in healthy cells. The researchers designed nanoparticles that can selectively distinguish healthy cells from model metastatic cells and release their payload - an anticancer drug - only to the model metastatic cells.
Oct 31st, 2016
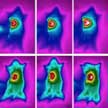 Microwave hyperthermia is one of the most important clinical thermotherapy techniques due to the instinctive advantages of non-intrusive heating model, fair depth of penetration in tissues and ideal potential of killing tumor cells without surgical risks or toxicity of chemotherapy. Scientists have now developed a novel multifunctional nanoplatform to combine the non-thermal and thermal effects of microwave to achieve enhanced thermal/chemo cancer therapy under mild microwave irradiation.
Microwave hyperthermia is one of the most important clinical thermotherapy techniques due to the instinctive advantages of non-intrusive heating model, fair depth of penetration in tissues and ideal potential of killing tumor cells without surgical risks or toxicity of chemotherapy. Scientists have now developed a novel multifunctional nanoplatform to combine the non-thermal and thermal effects of microwave to achieve enhanced thermal/chemo cancer therapy under mild microwave irradiation.
Oct 7th, 2016
 Researchers demonstrate a completely new micro-array design that is looking at capture and detection of circulating tumor cells (CTCs) from an entirely new perspective. As an alternative to invasive biopsies, capturing CTCs is of great interest for evaluating cancer dissemination, predicting patient prognosis, and also for the evaluation of therapeutic treatments, representing a reliable potential alternative to invasive biopsies and subsequent proteomic and functional genetic analysis. The new approach is based on a static isolation in the form of micro-arrays of single-walled carbon nanotubes.
Researchers demonstrate a completely new micro-array design that is looking at capture and detection of circulating tumor cells (CTCs) from an entirely new perspective. As an alternative to invasive biopsies, capturing CTCs is of great interest for evaluating cancer dissemination, predicting patient prognosis, and also for the evaluation of therapeutic treatments, representing a reliable potential alternative to invasive biopsies and subsequent proteomic and functional genetic analysis. The new approach is based on a static isolation in the form of micro-arrays of single-walled carbon nanotubes.
Oct 5th, 2016
 The intravenous iron-replacement product ferumoxytol and other iron oxide nanoparticles are being used for treating iron deficiency, as contrast agents for magnetic resonance imaging, and as drug carriers. In a new study, researchers have shown an intrinsic therapeutic effect of ferumoxytol on the growth of early mammary cancers and lung cancer metastases in liver and lungs. They showed that ferumoxytol can activate the immune system to attack cancer cells. This is the first description of an intrinsic therapeutic effect of iron oxide nanoparticles against cancer.
The intravenous iron-replacement product ferumoxytol and other iron oxide nanoparticles are being used for treating iron deficiency, as contrast agents for magnetic resonance imaging, and as drug carriers. In a new study, researchers have shown an intrinsic therapeutic effect of ferumoxytol on the growth of early mammary cancers and lung cancer metastases in liver and lungs. They showed that ferumoxytol can activate the immune system to attack cancer cells. This is the first description of an intrinsic therapeutic effect of iron oxide nanoparticles against cancer.
Oct 4th, 2016
 Researchers have developed an enteric micromotor consisting of a magnesium-based motor body with an enteric polymer coating. These motors, aimed controlling and enhancing site-specific delivery in the gastrointestinal tract, consist of water-powered magnesium-based tubular micromotors coated with an enteric polymer layer. The microscale robot can deliver payload to particular location via dissolution of their enteric polymeric coating to activate their propulsion at the target site towards localized tissue penetration and retention.
Researchers have developed an enteric micromotor consisting of a magnesium-based motor body with an enteric polymer coating. These motors, aimed controlling and enhancing site-specific delivery in the gastrointestinal tract, consist of water-powered magnesium-based tubular micromotors coated with an enteric polymer layer. The microscale robot can deliver payload to particular location via dissolution of their enteric polymeric coating to activate their propulsion at the target site towards localized tissue penetration and retention.
Sep 27th, 2016
 The optical manipulation of plasmonic nanoparticles has advantages for applications such as nanofabrication, drug delivery and biosensing. To that end, researchers have been developing techniques for the reversible assembly of plasmonic nanoparticles that can be used to modulate their structural, electrical and optical properties. The latest such technique is a low-power assembly that is enabled by thermophoretic migration of nanoparticles due to the plasmon-enhanced photothermal effect and the associated enhanced local electric field over a plasmonic substrate.
The optical manipulation of plasmonic nanoparticles has advantages for applications such as nanofabrication, drug delivery and biosensing. To that end, researchers have been developing techniques for the reversible assembly of plasmonic nanoparticles that can be used to modulate their structural, electrical and optical properties. The latest such technique is a low-power assembly that is enabled by thermophoretic migration of nanoparticles due to the plasmon-enhanced photothermal effect and the associated enhanced local electric field over a plasmonic substrate.
Sep 21st, 2016
 Researchers have demonstrated that nitric-oxide releasing nanoparticles interfere with Staphylococcus aureus (S. aureus) adhesion and prevent biofilm formation on a rat central venous catheters model of infection. Specifically, they demonstrated that a well studied nitric oxide-releasing nanoparticle platform (NO-np) has the potential to reduce the incidence and/or treat central venous catheter infections. The investigators examined the formation of staphylococcal biofilms by confocal and scanning electron microscopy and found that treatment of staphylococcal biofilms with NO-np significantly reduced biofilm thickness and bacterial number compared to control biofilms.
Researchers have demonstrated that nitric-oxide releasing nanoparticles interfere with Staphylococcus aureus (S. aureus) adhesion and prevent biofilm formation on a rat central venous catheters model of infection. Specifically, they demonstrated that a well studied nitric oxide-releasing nanoparticle platform (NO-np) has the potential to reduce the incidence and/or treat central venous catheter infections. The investigators examined the formation of staphylococcal biofilms by confocal and scanning electron microscopy and found that treatment of staphylococcal biofilms with NO-np significantly reduced biofilm thickness and bacterial number compared to control biofilms.

 Subscribe to our Nanotechnology Spotlight feed
Subscribe to our Nanotechnology Spotlight feed





