Showing Spotlights 369 - 376 of 2780 in category All (newest first):
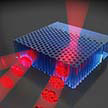 The propagation of light can be radically controlled with tailor-made nanostructures, called photonic crystals. The main feature of such crystals is a forbidden gap: waves with colors within a forbidden range travel only a limited distance - called Bragg length - before being reflected due to Bragg interference. Scientists have discovered a method to tunably steer light deep into photonic crystals, to depths well beyond the Bragg length. By spatially shaping the incident waves, the energy density of the light is enhanced at tunable distances deep inside the crystals.
The propagation of light can be radically controlled with tailor-made nanostructures, called photonic crystals. The main feature of such crystals is a forbidden gap: waves with colors within a forbidden range travel only a limited distance - called Bragg length - before being reflected due to Bragg interference. Scientists have discovered a method to tunably steer light deep into photonic crystals, to depths well beyond the Bragg length. By spatially shaping the incident waves, the energy density of the light is enhanced at tunable distances deep inside the crystals.
Apr 22nd, 2021
 Researchers have significantly enhanced the performance of a surface plasmon resonance (SPR) biosensing platform by adding an atomically thin phase change material to the sensor. This plasmonic sensing device exhibits a detection limit of 1 femtomol for tumor necrosis factor (TNF alpha) biomarkers , which is more than three orders of magnitude compared to current state-of-art nanomaterial-enhanced plasmonic sensors. It also detects small biotin molecules with a sensitivity of 10 femtomols. This sub-attomole detection level is a significant improvement compared to other SPR designs.
Researchers have significantly enhanced the performance of a surface plasmon resonance (SPR) biosensing platform by adding an atomically thin phase change material to the sensor. This plasmonic sensing device exhibits a detection limit of 1 femtomol for tumor necrosis factor (TNF alpha) biomarkers , which is more than three orders of magnitude compared to current state-of-art nanomaterial-enhanced plasmonic sensors. It also detects small biotin molecules with a sensitivity of 10 femtomols. This sub-attomole detection level is a significant improvement compared to other SPR designs.
Apr 19th, 2021
 Although solar-driven water evaporation using sunlight is a promising sustainable strategy, the water production rate via solar technologies remains insufficient to meet practical demands. Addressing this issue, researchers have developed a solar absorber gel to purify water from contaminated sources using only natural sunlight. The hydrogel can force liquid water out of the gel via phase transition when the sun warms the material, so the water purification mechanism does not require water evaporation.
Although solar-driven water evaporation using sunlight is a promising sustainable strategy, the water production rate via solar technologies remains insufficient to meet practical demands. Addressing this issue, researchers have developed a solar absorber gel to purify water from contaminated sources using only natural sunlight. The hydrogel can force liquid water out of the gel via phase transition when the sun warms the material, so the water purification mechanism does not require water evaporation.
Apr 13th, 2021
 A new generation of lenses - metalenses - is starting to replace bulky curved lenses with simple, flat surfaces that use nanostructures to focus light. These flat surfaces - meatsurfaces - have enabled the design of diffraction-based flat devices to replicate the functionalities of conventional lenses with sub-wavelength or few-wavelength thicknesses. Researchers have now successfully designed and experimentally demonstrated an inverse-designed metalens to operate at a near-infrared wavelength.
A new generation of lenses - metalenses - is starting to replace bulky curved lenses with simple, flat surfaces that use nanostructures to focus light. These flat surfaces - meatsurfaces - have enabled the design of diffraction-based flat devices to replicate the functionalities of conventional lenses with sub-wavelength or few-wavelength thicknesses. Researchers have now successfully designed and experimentally demonstrated an inverse-designed metalens to operate at a near-infrared wavelength.
Apr 8th, 2021
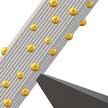 Individual single-walled carbon nanotubes (SWCNTs) have thermal conductivity that is several times higher than copper. However, once researchers start to assemble SWCNTs into macroscale composites, fibers or films, they notice that thermal conduction drops significantly. Employing in situ transmission electron microscopy, researchers visualized a colossal anisotropy of thermal conductivity of nanoscale materials. The team says that their methodology to visualize nanoscale thermal transport is not limited to carbon nanotubes.
Individual single-walled carbon nanotubes (SWCNTs) have thermal conductivity that is several times higher than copper. However, once researchers start to assemble SWCNTs into macroscale composites, fibers or films, they notice that thermal conduction drops significantly. Employing in situ transmission electron microscopy, researchers visualized a colossal anisotropy of thermal conductivity of nanoscale materials. The team says that their methodology to visualize nanoscale thermal transport is not limited to carbon nanotubes.
Apr 6th, 2021
 Wearable flexible sensors have recently emerged as promising alternatives for human healthcare monitoring due to their lightweight and thin-film-based nature. However, few of these flexible sensor systems are applicable to neonatal monitoring, especially sleeping posture detection. Researchers now report a versatile laser-induced-graphene-based integrated sensor system, which can wirelessly monitor sleeping postures, respiration rate, and diaper wetness with feedback alarm functions.
Wearable flexible sensors have recently emerged as promising alternatives for human healthcare monitoring due to their lightweight and thin-film-based nature. However, few of these flexible sensor systems are applicable to neonatal monitoring, especially sleeping posture detection. Researchers now report a versatile laser-induced-graphene-based integrated sensor system, which can wirelessly monitor sleeping postures, respiration rate, and diaper wetness with feedback alarm functions.
Mar 31st, 2021
 Researchers demonstrate label-free chiral detection of metabolic molecules at picomolar level through microbubble-induced rapid accumulation of biomolecules on plasmonic chiral sensors, which shows a 10-million times enhancement in sensitivity comparing to state-of-the-art plasmonic chiral sensors. The researchers achieved their ultrahigh sensitivity in chiral sensing of biomolecules by utilizing two enhancement mechanisms: the microbubble-induced accumulation of biomolecules onto the chiral plasmonic substrates; and the subsequent plasmon-enhanced chiral sensing.
Researchers demonstrate label-free chiral detection of metabolic molecules at picomolar level through microbubble-induced rapid accumulation of biomolecules on plasmonic chiral sensors, which shows a 10-million times enhancement in sensitivity comparing to state-of-the-art plasmonic chiral sensors. The researchers achieved their ultrahigh sensitivity in chiral sensing of biomolecules by utilizing two enhancement mechanisms: the microbubble-induced accumulation of biomolecules onto the chiral plasmonic substrates; and the subsequent plasmon-enhanced chiral sensing.
Mar 30th, 2021
 Researchers have demonstrated the large-scale fabrication of skin-interfaced printed microfluidic patches, capable of multiplexed electrochemical detection of biomarkers from human sweat. This sensor continuously and simultaneously measures the level of biomarkers such as lactate, Na+, K+, and pH during sweating. The skin-worn sensor can selectively measure analytes even in the presence of other interfering species present in sweat. The patch is integrated with a custom-made miniature printed circuit board that enables multiplexed decoding of sweat and wireless signal transduction to the host devices and is completely free from any sensor-to-sensor transfer of signals.
Researchers have demonstrated the large-scale fabrication of skin-interfaced printed microfluidic patches, capable of multiplexed electrochemical detection of biomarkers from human sweat. This sensor continuously and simultaneously measures the level of biomarkers such as lactate, Na+, K+, and pH during sweating. The skin-worn sensor can selectively measure analytes even in the presence of other interfering species present in sweat. The patch is integrated with a custom-made miniature printed circuit board that enables multiplexed decoding of sweat and wireless signal transduction to the host devices and is completely free from any sensor-to-sensor transfer of signals.
Mar 29th, 2021
 The propagation of light can be radically controlled with tailor-made nanostructures, called photonic crystals. The main feature of such crystals is a forbidden gap: waves with colors within a forbidden range travel only a limited distance - called Bragg length - before being reflected due to Bragg interference. Scientists have discovered a method to tunably steer light deep into photonic crystals, to depths well beyond the Bragg length. By spatially shaping the incident waves, the energy density of the light is enhanced at tunable distances deep inside the crystals.
The propagation of light can be radically controlled with tailor-made nanostructures, called photonic crystals. The main feature of such crystals is a forbidden gap: waves with colors within a forbidden range travel only a limited distance - called Bragg length - before being reflected due to Bragg interference. Scientists have discovered a method to tunably steer light deep into photonic crystals, to depths well beyond the Bragg length. By spatially shaping the incident waves, the energy density of the light is enhanced at tunable distances deep inside the crystals.
 Subscribe to our Nanotechnology Spotlight feed
Subscribe to our Nanotechnology Spotlight feed





