Showing Spotlights 673 - 680 of 2780 in category All (newest first):
 The growing threat of antibiotic-resistant bacterial strains may pose grave risks for society: A post-antibiotic era means, in effect, an end to modern medicine as we know it. New research findings could point the way to new treatments for now-invincible bacterial foes, not by developing a new antibiotic that would kill these bacteria, but by making them weaker so that they get more easily attacked by our immune system. Understanding the physical mechanisms that underlie this persistent stickiness at the molecular level is instrumental to combat these invaders.
The growing threat of antibiotic-resistant bacterial strains may pose grave risks for society: A post-antibiotic era means, in effect, an end to modern medicine as we know it. New research findings could point the way to new treatments for now-invincible bacterial foes, not by developing a new antibiotic that would kill these bacteria, but by making them weaker so that they get more easily attacked by our immune system. Understanding the physical mechanisms that underlie this persistent stickiness at the molecular level is instrumental to combat these invaders.
Apr 20th, 2018
 The advent of graphene resulted in a massive, world-wide, effort directed at investigation of other two-dimensional (2D) layered materials. One-dimensional (1D) bundled materials have received considerably less attention. Similar to the 2D layered materials with covalently bonded layers separated by the van der Waals gaps, the 1D materials consist of covalently bonded one-dimensional wires with van der Waals gaps between the wires. Researchers now have discovered that quasi-1D nanoribbons reveal an exceptionally high current density at the peak of the stressing DC current. This level of the current density exceeds that in any conventional metals like copper by almost two orders of magnitude.
The advent of graphene resulted in a massive, world-wide, effort directed at investigation of other two-dimensional (2D) layered materials. One-dimensional (1D) bundled materials have received considerably less attention. Similar to the 2D layered materials with covalently bonded layers separated by the van der Waals gaps, the 1D materials consist of covalently bonded one-dimensional wires with van der Waals gaps between the wires. Researchers now have discovered that quasi-1D nanoribbons reveal an exceptionally high current density at the peak of the stressing DC current. This level of the current density exceeds that in any conventional metals like copper by almost two orders of magnitude.
Apr 19th, 2018
 Sensory substitution with flexible electronics is one of the intriguing fields of research that takes place in nanotechnology labs around the world. In line with this focus on human senses, in the future artificial retinas integrated with the human body may not only repair damaged vision but also expand it to see a wider range wavelengths (e.g. ultraviolet light). Researchers now have demonstrated a new self-powered brain-linked vision electronic skin (e-skin) for mimicking the human retina. The general idea of our device design of brain-linked vision electronic skin is constructing an integrated flexible system including photodetector array, information analyzer, signal transmitter, and electricity power unit.
Sensory substitution with flexible electronics is one of the intriguing fields of research that takes place in nanotechnology labs around the world. In line with this focus on human senses, in the future artificial retinas integrated with the human body may not only repair damaged vision but also expand it to see a wider range wavelengths (e.g. ultraviolet light). Researchers now have demonstrated a new self-powered brain-linked vision electronic skin (e-skin) for mimicking the human retina. The general idea of our device design of brain-linked vision electronic skin is constructing an integrated flexible system including photodetector array, information analyzer, signal transmitter, and electricity power unit.
Apr 18th, 2018
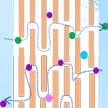 As a promising large-scale energy storage technology, redox flow batteries (RFBs) are attracting increasingly more research attention. For RFB separators, the essential requirement is achieving high ionic conductivity with minimal cross-over at low cost. Researchers now have demonstrated a proof-of-concept graphene oxide (GO) membrane as separator for large-scale energy RFBs. Their work shows that the two-dimensional nanochannel structure and low frictional water flow inside micrometer-thick GO laminates make this material an attractive candidate membrane for large-scale energy storage systems.
As a promising large-scale energy storage technology, redox flow batteries (RFBs) are attracting increasingly more research attention. For RFB separators, the essential requirement is achieving high ionic conductivity with minimal cross-over at low cost. Researchers now have demonstrated a proof-of-concept graphene oxide (GO) membrane as separator for large-scale energy RFBs. Their work shows that the two-dimensional nanochannel structure and low frictional water flow inside micrometer-thick GO laminates make this material an attractive candidate membrane for large-scale energy storage systems.
Apr 17th, 2018
 Researchers demonstrate that helical shaped magnetic nanomotors can be maneuvered inside a living cell. This new and versatile technique has the potential ability to position any payload at any desired location inside a living cell itself, which is of great importance in the field of biology and biophysics. The helical shaped nanomotors are made of mainly silica and a thin layer of magnetic material, while their size is at least ten times smaller than the cell which they enter in. A rotating magnetic field is used to drive the motors inside the cytoplasm with precise control.
Researchers demonstrate that helical shaped magnetic nanomotors can be maneuvered inside a living cell. This new and versatile technique has the potential ability to position any payload at any desired location inside a living cell itself, which is of great importance in the field of biology and biophysics. The helical shaped nanomotors are made of mainly silica and a thin layer of magnetic material, while their size is at least ten times smaller than the cell which they enter in. A rotating magnetic field is used to drive the motors inside the cytoplasm with precise control.
Apr 16th, 2018
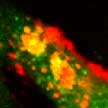 Researchers have demonstrated that a specific type of two-dimensional (2D) nanoparticles, nanosilicates, can grow bone and cartilage tissue from stem cells in the absence of growth factors. These nanoparticles are similar in shape to a coin, but 10 billion times smaller in size. Nanosilicates consist of minerals such as sodium, silicate, magnesium and lithium, which are already present in the body. This avoids the use of growth factors in the human body, which can generate harmful effects including unwanted tissue growth, such as a tumor.
Researchers have demonstrated that a specific type of two-dimensional (2D) nanoparticles, nanosilicates, can grow bone and cartilage tissue from stem cells in the absence of growth factors. These nanoparticles are similar in shape to a coin, but 10 billion times smaller in size. Nanosilicates consist of minerals such as sodium, silicate, magnesium and lithium, which are already present in the body. This avoids the use of growth factors in the human body, which can generate harmful effects including unwanted tissue growth, such as a tumor.
Apr 13th, 2018
 Sepsis is the body's extreme response to an infection. It is life-threatening condition in which bacteria or fungi multiply in a patient's blood - often too fast for antibiotics to help. Without timely treatment, sepsis can rapidly cause tissue damage, organ failure, and death. A critical unmet need in combating sepsis is the lack of accurate early biomarkers that can alert clinicians to a potential life-threatening situation and allow them to take preventative action. In a new study, researchers report the development of a point-of-care platform for rapid sepsis detection, called IBS (integrated biosensor for sepsis).
Sepsis is the body's extreme response to an infection. It is life-threatening condition in which bacteria or fungi multiply in a patient's blood - often too fast for antibiotics to help. Without timely treatment, sepsis can rapidly cause tissue damage, organ failure, and death. A critical unmet need in combating sepsis is the lack of accurate early biomarkers that can alert clinicians to a potential life-threatening situation and allow them to take preventative action. In a new study, researchers report the development of a point-of-care platform for rapid sepsis detection, called IBS (integrated biosensor for sepsis).
Apr 12th, 2018
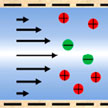 The ability of nanochannels to regulate transported substances in confined spaces is of great research interest in innovative applications, such as high-resolution sensing, filtering, and high-efficiency energy utilization. In the last area, research on nanochannels in energy-related areas continues to face challenges such as low efficiencies, complex preparation processes, and high fabrication costs. Overcoming these challenges is an important and difficult task in the field of energy conversion, energy conservation, and energy recovery.
The ability of nanochannels to regulate transported substances in confined spaces is of great research interest in innovative applications, such as high-resolution sensing, filtering, and high-efficiency energy utilization. In the last area, research on nanochannels in energy-related areas continues to face challenges such as low efficiencies, complex preparation processes, and high fabrication costs. Overcoming these challenges is an important and difficult task in the field of energy conversion, energy conservation, and energy recovery.
Apr 10th, 2018
 The growing threat of antibiotic-resistant bacterial strains may pose grave risks for society: A post-antibiotic era means, in effect, an end to modern medicine as we know it. New research findings could point the way to new treatments for now-invincible bacterial foes, not by developing a new antibiotic that would kill these bacteria, but by making them weaker so that they get more easily attacked by our immune system. Understanding the physical mechanisms that underlie this persistent stickiness at the molecular level is instrumental to combat these invaders.
The growing threat of antibiotic-resistant bacterial strains may pose grave risks for society: A post-antibiotic era means, in effect, an end to modern medicine as we know it. New research findings could point the way to new treatments for now-invincible bacterial foes, not by developing a new antibiotic that would kill these bacteria, but by making them weaker so that they get more easily attacked by our immune system. Understanding the physical mechanisms that underlie this persistent stickiness at the molecular level is instrumental to combat these invaders.
 Subscribe to our Nanotechnology Spotlight feed
Subscribe to our Nanotechnology Spotlight feed





