| Posted: Jun 30, 2014 |
Unzipping nanotubes by smashing them at 15000 miles per hour
|
|
(Nanowerk News) Carbon nanotubes “unzipped” into graphene nanoribbons by a chemical process invented at Rice University are finding use in all kinds of projects, but Rice scientists have now found a chemical-free way to unzip them.
|
|
The Rice lab of materials scientist Pulickel Ajayan discovered that nanotubes that hit a target end first turn into mostly ragged clumps of atoms. But nanotubes that happen to broadside the target unzip into handy ribbons that can be used in composite materials for strength and applications that take advantage of their desirable electrical properties.
|
|
The Rice researchers led by graduate student Sehmus Ozden reported their finding in the American Chemical Society journal Nano Letters ("Unzipping Carbon Nanotubes at High Impact").
|
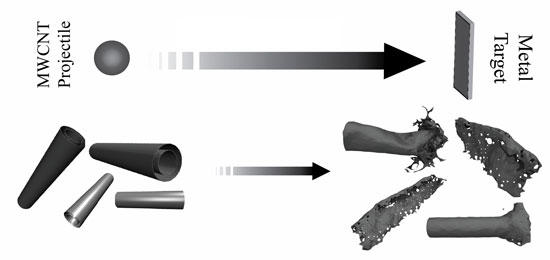 |
| Carbon nanotubes can be unzipped into nanoribbons by firing them at high velocity at a target, but only the ones that land lengthwise will unzip, according to researchers at Rice University. Tests evaluated nanotubes that impacted the target at various angles to see the results. (Credit: Ajayan Group/Rice University)
|
|
The result was a surprise, Ozden said. “Until now, we knew we could use mechanical forces to shorten and cut carbon nanotubes. This is the first time we have showed carbon nanotubes can be unzipped using mechanical forces.”
|
|
The researchers fired pellets of randomly oriented, multiwalled carbon nanotubes from a light gas gun built by the Rice lab of materials scientist Enrique Barrera with funding from NASA. The pellets impacted an aluminum target in a vacuum chamber at about 15,000 miles per hour. When they inspected the resulting carbon rubble, they found nanotubes that smashed into the target end first or at a sharp angle simply deformed into a crumpled nanotube. But tubes that hit lengthwise actually split into ribbons with ragged edges.
|
|
“Hypervelocity impact tests are mostly used to simulate the impact of different projectiles on shields, spacecraft and satellites,” Ozden said. “We were investigating possible applications for carbon nanotubes in space when we got this result.”
|
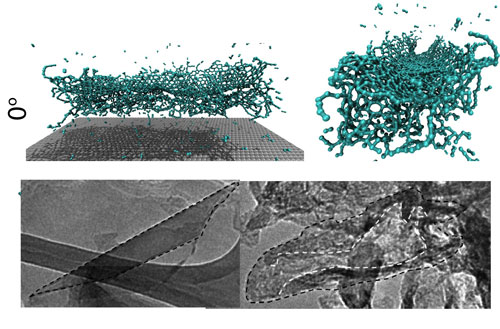 |
| Molecular simulations and electron microscope images show what happens to a carbon nanotube when the end of it strikes a target directly at about 15,000 miles per hour. Rice University researchers found the nanotubes split into useful nanoribbons. (Credit: Ajayan Group/Rice University)
|
|
The effect was confirmed through molecular simulations. They showed that when multiwalled tubes impact the target, the outer tube flattens, hitting the inside tubes and unzipping them in turn. Single-wall nanotubes do just the opposite; when the tube flattens, the bottom wall hits the inside of the top wall, which unzips from the middle out to the edges.
|
|
Ozden explained that the even distribution of stress along the belly-flopping nanotube, which is many times longer than it is wide, breaks carbon bonds in a line nearly simultaneously.
|
|
The researchers said 70 to 80 percent of the nanotubes in a pellet unzip to one degree or another.
|
|
Ozden said the process eliminates the need to clean chemical residues from nanoribbons produced through current techniques. “One-step, chemical-free, clean and high-quality graphene nanoribbons can be produced using our method. They’re potential candidates for next-generation electronic materials,” he said.
|


