| Posted: Feb 04, 2016 |
Metal oxide sandwiches: New option to manipulate properties of interfaces
(Nanowerk News) Sandwich systems of thin film transition metal oxides display surprising properties at their interfaces. In case of the paradigmatic example of Lanthan-Aluminate ( LaAlO3) and Strontium-Titanate (SrTiO3) both materials are insulators and non-magnetic, while their interface has been observed to display ferromagnetism, high electrical conductivity and even superconductivity.
|
|
Now the team of Manuel Bibes, CNRS Thales at Palaiseau, France, in collaboration with scientists at HZB around Sergio Valencia and several European groups, devised a new approach to tailor interface properties. Together they designed a series of experiments at the synchrotron source BESSY II to shed more light on the emergence of such property changes, identifying a new "knob" for their control (Nature Physics, "Hybridization-controlled charge transfer and induced magnetism at correlated oxide interfaces").
|
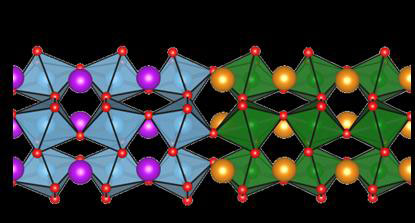 |
| This is a sketch of the structure of both metal oxide layers. Interesting new properties can arise at the interface. (Image: M. Bibes)
|
|
Rare-Earth Elements influence charge transfer
|
|
The samples, which the team of Manuel Bibes did produce, consisted of a sandwich of 2 nm Gadolinium-Titanate (GdTiO3) and "R"-Nickelate (RNiO3) films, where R is a rare-earth element. "We have been able to combine two very different transition metal oxides: whereas in the titanate electrons in the chemical bonds are strongly localized around the ions, in the nickelate side these electrons are shared between Nickel- and Oxygen-ions, and thus highly covalent", Manuel Bibes explains. |
|
When putting both materials together some charge is transferred from the titanate layer to the nickelate one. They investigated this charge transfer process for samples containing different rare-earth elements in the nickelate layer such as Lanthanum, Neodymium and Samarium at BESSY II.
|
|
Their results show that the charge transfer at the interface between the materials strongly depends on the rare earth element in the nickelate layer. Different rare-earth elements have different atomic radii (size).This modifies the interaction between the Ni and O atoms and the degree of "covalency" between Ni and O changes. This was already known, but now the scientists have observed that this also affects the charge transferred from the GdTiO3 to the Nickelate film. "This is the key result", Sergio Valencia from HZB explains. "We have found a new "knob". Covalency (which is controlled by changing R) controls the charge transfer between the titanate and the nickelate."
|
|
Ferromagnetism observed, superconductivity still searched
|
|
Tuning the charge transfer in this way might allow to control the formation of new interfacial phases too. For example, the scientists observed a new ferromagnetic phase at the interface. "Our work may help in the ongoing quest for cuprate-like superconductivity in nickelate heterostructures", Valencia says. "We hope that this study will help to design better interfaces for exploring new exciting new phases of matter at interfaces between covalent materials", Bibes adds.
|

