| Posted: June 13, 2008 |
Chinese researchers discover low-cost photocatalyst for hydrogen production |
|
(Nanowerk News) Recently, a research group headed by Prof. LI Can with the Dalian Institute of Chemical Physics, Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS) made a remarkable progress in the study of photocatalytic hydrogen production.
|
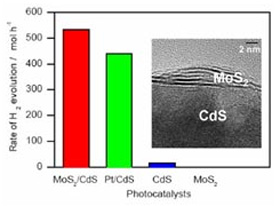 |
| comparison of two photocatalysts
|
|
The synthesis of photocatalysts remains a key problem for solar photocatalytic hydrogen production, and to find low-cost photocatalysts especially poses a challenge for the mass-production of this environmentally friendly energy. In the research, Prof. Li's group has loaded a small amount of MoS2 as a cocatalyst on CdS and then the activity of photocatalytic hydrogen production is found significantly enhanced.
|
|
The rate of hydrogen evolution on CdS is increased by more than 30 times when loaded with only 0.2 wt % of MoS2. The activity of MoS2/CdS is even higher than that of the CdS photocatalysts loaded with different noble metals, such as Pt, Ru, Rh, Pd, and Au. The junction formed between MoS2 and CdS and the excellent H2 activation property of MoS2 are supposed to be responsible for the enhanced photocatalytic activity of MoS2/CdS. This substitute photocatalyst is expected to speed up the development of solar photocatalytic hydrogen production.
|
|
Their research was was published in a recent issue of Journal of American Chemical Society ("Enhancement of Photocatalytic H2 Evolution on CdS by Loading MoS2 as Cocatalyst under Visible Light Irradiation").
|

