Shoving protons around
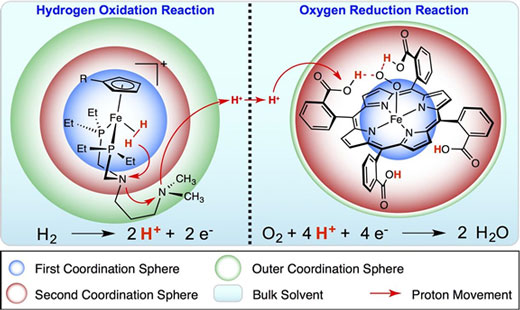 Review highlights molecular-level work involved in creating a design guide for catalysts for use of sustainable energy.
Review highlights molecular-level work involved in creating a design guide for catalysts for use of sustainable energy.
Sep 16th, 2015
Read more
 Review highlights molecular-level work involved in creating a design guide for catalysts for use of sustainable energy.
Review highlights molecular-level work involved in creating a design guide for catalysts for use of sustainable energy.
Sep 16th, 2015
Read more16 sites to give academic, small business and industry researchers access to nanotechnology research.
Sep 16th, 2015
Read more The partnership, called the Research Triangle Nanotechnology Network (RTNN), is led by NC State and is supported by a five-year, $5.5 million grant from the National Science Foundation.
The partnership, called the Research Triangle Nanotechnology Network (RTNN), is led by NC State and is supported by a five-year, $5.5 million grant from the National Science Foundation.
Sep 16th, 2015
Read more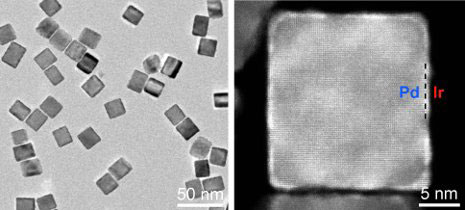 Scientists have developed a new catalyst that could make lab tests like the PSA much more sensitive. And it may even speed up reactions that neutralize toxic industrial chemicals before they enter lakes and streams.
Scientists have developed a new catalyst that could make lab tests like the PSA much more sensitive. And it may even speed up reactions that neutralize toxic industrial chemicals before they enter lakes and streams.
Sep 16th, 2015
Read moreA group of scientists called into question the results of a study where British scientists claimed that they managed to find the missing link in the electromagnetic theory.
Sep 16th, 2015
Read moreResearchers have shown how the development of coated silica nanoparticles could be used in restorative treatment of sensitive teeth and preventing the onset of tooth decay.
Sep 16th, 2015
Read more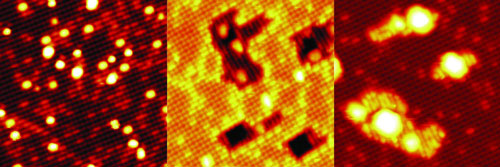 Scientists have figured out how a platinum catalyst works - its remarkable properties are not just due to the platinum, the iron-oxide substrate beneath also plays a role.
Scientists have figured out how a platinum catalyst works - its remarkable properties are not just due to the platinum, the iron-oxide substrate beneath also plays a role.
Sep 16th, 2015
Read more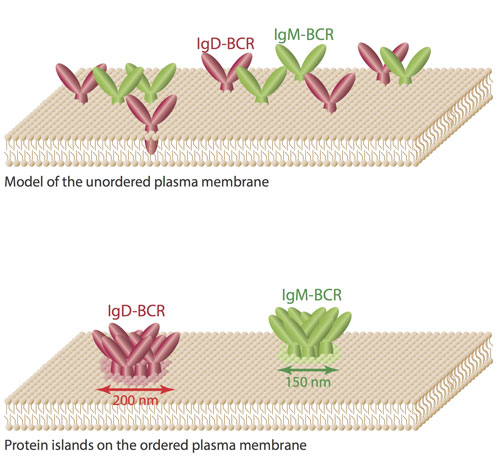 Researchers have applied super-resolution methods to study the organization of receptors on B lymphocytesAntigen receptors on B lymphocytes sense foreign molecules, such as pathogens or vaccines, and activate the B cells to produce antibodies that protect humans against many diseases.
Researchers have applied super-resolution methods to study the organization of receptors on B lymphocytesAntigen receptors on B lymphocytes sense foreign molecules, such as pathogens or vaccines, and activate the B cells to produce antibodies that protect humans against many diseases.
Sep 16th, 2015
Read more Researchers developed a nanostructured system capable of protecting the active compounds of juices and nutritional supplements from high temperatures during the pasteurization process, in order to retain their nutritional properties.
Researchers developed a nanostructured system capable of protecting the active compounds of juices and nutritional supplements from high temperatures during the pasteurization process, in order to retain their nutritional properties.
Sep 16th, 2015
Read more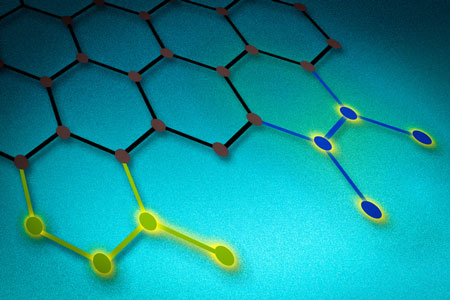 Material could replace precious metals and produce precisely controlled electrochemical reactivity.
Material could replace precious metals and produce precisely controlled electrochemical reactivity.
Sep 16th, 2015
Read more Biomedical engineers report a new way to induce human mesenchymal stem cells to differentiate into neuron-like cells: treating them with exosomes from rat-derived progenitor cells. In combination with synthetic nanoparticles now in development, researchers hope to make synthetic exosomes, inducing neuron growth without neural progenitor cells.
Biomedical engineers report a new way to induce human mesenchymal stem cells to differentiate into neuron-like cells: treating them with exosomes from rat-derived progenitor cells. In combination with synthetic nanoparticles now in development, researchers hope to make synthetic exosomes, inducing neuron growth without neural progenitor cells.
Sep 15th, 2015
Read more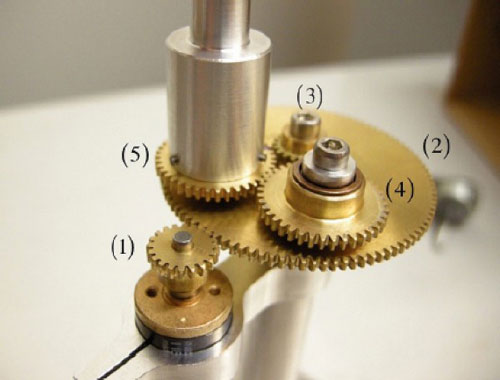 A simple mechanism can control the swimming direction of magnetotactic bacteria - a group of bacteria that orient along the earth's magnetic field and are of interest to scientists studying geology, environmental change and more.
A simple mechanism can control the swimming direction of magnetotactic bacteria - a group of bacteria that orient along the earth's magnetic field and are of interest to scientists studying geology, environmental change and more.
Sep 15th, 2015
Read more Researchers show how natural materials like plant cellulose can self-assemble into surfaces with stunning optical properties - including shiny iridescence and colors that change depending on the humidity.
Researchers show how natural materials like plant cellulose can self-assemble into surfaces with stunning optical properties - including shiny iridescence and colors that change depending on the humidity.
Sep 15th, 2015
Read more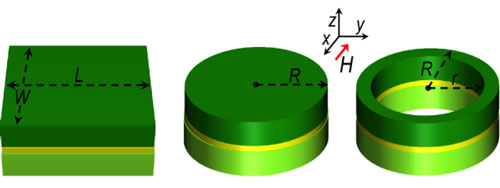 Researchers have calculated that the Nobel Prize-winning device called a Josephson junction could precisely convert a signal from megahertz to gigahertz - with potential uses in metrology and telecommunications.
Researchers have calculated that the Nobel Prize-winning device called a Josephson junction could precisely convert a signal from megahertz to gigahertz - with potential uses in metrology and telecommunications.
Sep 15th, 2015
Read more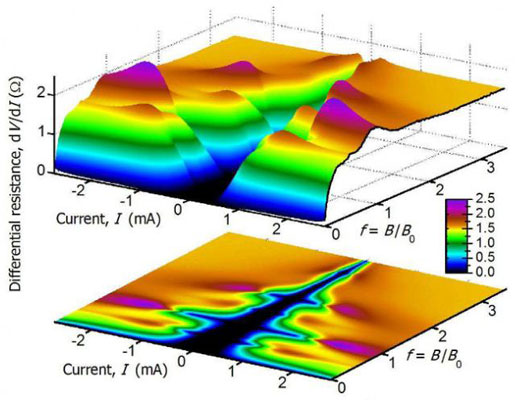 An international group of physicists recently presented results of experiments testing a new phenomenon. The results may assist scientists in the creation of an essentially new kind of electronics - Mott transition, or the transition of an insulator to a conductor.
An international group of physicists recently presented results of experiments testing a new phenomenon. The results may assist scientists in the creation of an essentially new kind of electronics - Mott transition, or the transition of an insulator to a conductor.
Sep 15th, 2015
Read moreResearch paves the way for alloys that are 3x stronger than steel yet bend like gum.
Sep 15th, 2015
Read more