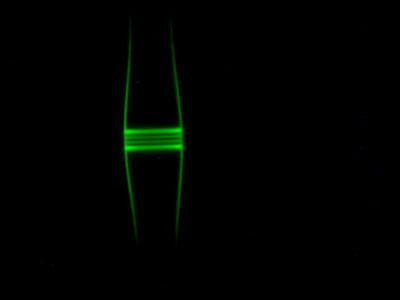
 With just a single atom, light can be switched between two fibre optic cables at the Vienna University of Technology. Such a switch enables quantum phenomena to be used for information and communication technology.
With just a single atom, light can be switched between two fibre optic cables at the Vienna University of Technology. Such a switch enables quantum phenomena to be used for information and communication technology.
Nov 5th, 2013
Read more
 Rice University announced it has established a new academic department to capitalize on the university's research in materials science and nanotechnology.
Rice University announced it has established a new academic department to capitalize on the university's research in materials science and nanotechnology.
Nov 5th, 2013
Read more
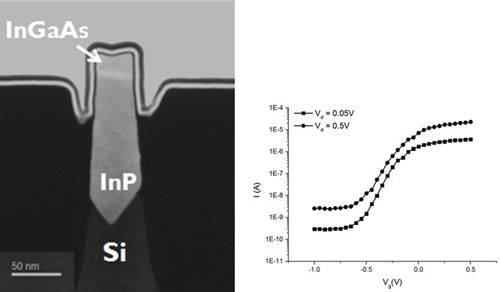 Technology achievement marks significant step towards monolithic heterogeneous integration and non-silicon devices.
Technology achievement marks significant step towards monolithic heterogeneous integration and non-silicon devices.
Nov 5th, 2013
Read more
Researchers at NJIT have developed a flexible battery made with carbon nanotubes that could potentially power electronic devices with flexible displays.
Nov 4th, 2013
Read more
Advances in flexible and stretchable electronics have prompted nanotechnology researchers to explore ways to create stretchable supercapacitors - robust energy storage devices - to power these and other devices.
Nov 4th, 2013
Read more
The winners of the first ever Nanomedicine Award were officially announced during the Nanomedicine Panel at BIO-Europe conference in Vienna, November 4th 2013.
Nov 4th, 2013
Read more
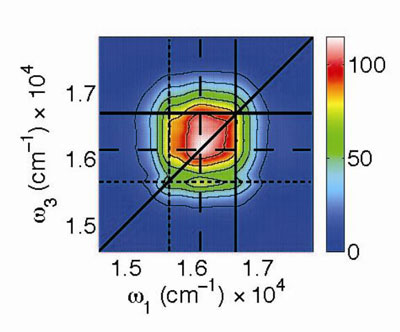 From supersensitive detections of magnetic fields to quantum information processing, the key to a number of highly promising advanced technologies may lie in one of the most common defects in diamonds. Researchers at the Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory (Berkeley Lab) and the University of California (UC) Berkeley have taken an important step towards unlocking this key with the first ever detailed look at critical ultrafast processes in these diamond defects.
From supersensitive detections of magnetic fields to quantum information processing, the key to a number of highly promising advanced technologies may lie in one of the most common defects in diamonds. Researchers at the Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory (Berkeley Lab) and the University of California (UC) Berkeley have taken an important step towards unlocking this key with the first ever detailed look at critical ultrafast processes in these diamond defects.
Nov 4th, 2013
Read more
A new way to build membrane-crossing pores, using Lego-like DNA building blocks, has been developed by scientists at UCL, in collaboration with colleagues at the University of Cambridge and the University of Southampton.
Nov 4th, 2013
Read more
 Toronto-based luxury bespoke tailoring house Garrison Bespoke will launch the first fashion-forward bulletproof suit tomorrow with a live ammo field-testing event.
Toronto-based luxury bespoke tailoring house Garrison Bespoke will launch the first fashion-forward bulletproof suit tomorrow with a live ammo field-testing event.
Nov 4th, 2013
Read more
A new international research collaboration announced today will deliver highly accurate measurements of strain in materials at the nano-scale to drive innovation in next generation electronic devices. The European Metrology Research Programme's Nanostrain project brings together public institutions from across Europe supported by global industry leaders including IBM.
Nov 4th, 2013
Read more
Physicists at the University of Basel have been successful in generating photons with only one color. This is useful for quantum information. The scientists have actively stabilized the wavelength of the photons emitted by a semiconductor thereby neutralizing the charge noise in the semiconductor.
Nov 4th, 2013
Read more
The Nanotechnology Industries Association (NIA) today launched its Regulatory Monitoring Database. This Database is a comprehensive tool that allows its users to monitor nano-specific regulations and standards around the world.
Nov 4th, 2013
Read more
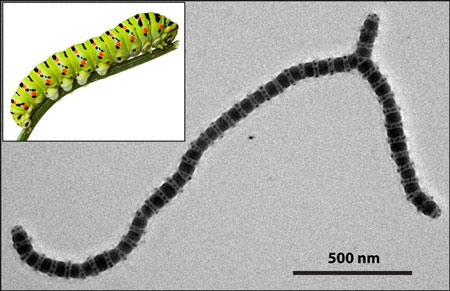 Zellen von Pflanzen und Tieren sind ein prominentes Beispiel daf�r, wie die Natur - ausgehend von molekularen Strukturen des Erbguts - in einer zielgerichteten, vorprogrammierten Weise immer gr��ere Einheiten aufbaut. Die Nanotechnologie versucht dieses Bottom-up-Prinzip zu kopieren, indem sie die F�higkeit von Nanopartikeln zur selbst�ndigen Strukturbildung nutzt.
Zellen von Pflanzen und Tieren sind ein prominentes Beispiel daf�r, wie die Natur - ausgehend von molekularen Strukturen des Erbguts - in einer zielgerichteten, vorprogrammierten Weise immer gr��ere Einheiten aufbaut. Die Nanotechnologie versucht dieses Bottom-up-Prinzip zu kopieren, indem sie die F�higkeit von Nanopartikeln zur selbst�ndigen Strukturbildung nutzt.
Nov 4th, 2013
Read more
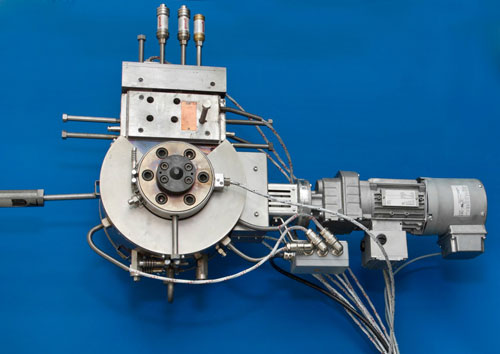 Nanoparticle additives can make plastics scratch and flame proof, or give them antibacterial properties. For this to work, the particle distribution within the plastic compound must be absolutely correct. A new device is now able to test the distribution in real time.
Nanoparticle additives can make plastics scratch and flame proof, or give them antibacterial properties. For this to work, the particle distribution within the plastic compound must be absolutely correct. A new device is now able to test the distribution in real time.
Nov 4th, 2013
Read more
 Flickering fa�ades, curved monitors, flashing clothing, fluorescent wallpaper, flexible solar cells - and all printable. This is no make-believe vision of the future; it will soon be possible using a new printing process for organic light-emitting diodes.
Flickering fa�ades, curved monitors, flashing clothing, fluorescent wallpaper, flexible solar cells - and all printable. This is no make-believe vision of the future; it will soon be possible using a new printing process for organic light-emitting diodes.
Nov 4th, 2013
Read more
The European FP7 Project NanoDiode has officially unveiled its website. Visitors will be able to find the latest information on what activities will be being done by the project around the EU, what publications are considered vital to an understanding, and betterment, of nanotechnology dissemination activities, and see how NanoDiode aims to inspire, educate, co-create and engage with society on nanotechnologies.
Nov 4th, 2013
Read more
 With just a single atom, light can be switched between two fibre optic cables at the Vienna University of Technology. Such a switch enables quantum phenomena to be used for information and communication technology.
With just a single atom, light can be switched between two fibre optic cables at the Vienna University of Technology. Such a switch enables quantum phenomena to be used for information and communication technology.







 Subscribe to our Nanotechnology News feed
Subscribe to our Nanotechnology News feed