Peeling off the silicene layers for new electronics
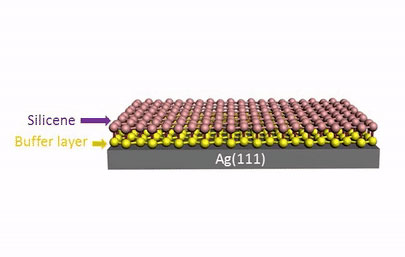 Scientists use oxygen 'scissors' to make freestanding single-atom silicon layer.
Scientists use oxygen 'scissors' to make freestanding single-atom silicon layer.
Aug 1st, 2016
Read more
 Scientists use oxygen 'scissors' to make freestanding single-atom silicon layer.
Scientists use oxygen 'scissors' to make freestanding single-atom silicon layer.
Aug 1st, 2016
Read moreToday, Federal agencies participating in the National Nanotechnology Initiative (NNI) released a white paper describing the collective Federal vision for the emerging and innovative solutions needed to realize the Nanotechnology-Inspired Grand Challenge for Future Computing.
Jul 29th, 2016
Read more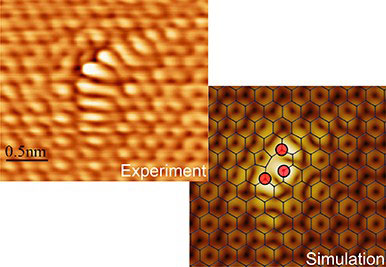 International team shows that modified graphene is 105 times more sensitive at detecting ammonia.
International team shows that modified graphene is 105 times more sensitive at detecting ammonia.
Jul 29th, 2016
Read more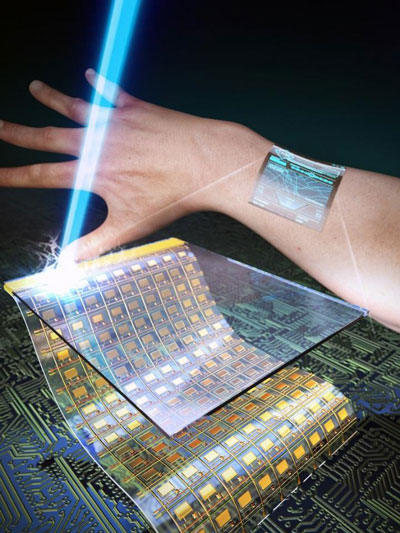 Researchers have developed ultrathin and transparent oxide thin-film transistors for an active-matrix backplane of a flexible display by using the inorganic-based laser lift-off method.
Researchers have developed ultrathin and transparent oxide thin-film transistors for an active-matrix backplane of a flexible display by using the inorganic-based laser lift-off method.
Jul 29th, 2016
Read more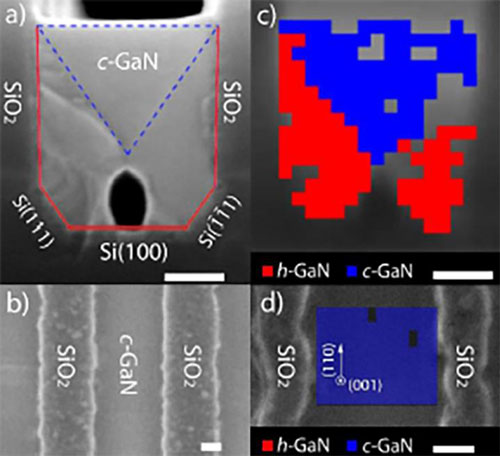 Using an industry-standard semiconductor growth technique, researchers have created gallium nitride (GaN) cubic crystals grown on a silicon substrate that are capable of producing powerful green light for advanced solid-state lighting.
Using an industry-standard semiconductor growth technique, researchers have created gallium nitride (GaN) cubic crystals grown on a silicon substrate that are capable of producing powerful green light for advanced solid-state lighting.
Jul 29th, 2016
Read more Extremely thin stacks of two-dimensional materials, which could deliver applications fine-tuned to the demands of industry, are set to revolutionise the world in the same way that graphene will.
Extremely thin stacks of two-dimensional materials, which could deliver applications fine-tuned to the demands of industry, are set to revolutionise the world in the same way that graphene will.
Jul 29th, 2016
Read moreInvestigators have developed a hydrogel patch that can adhere to tumors in a preclinical model of colon cancer, delivering a local, combination treatment as the elastic gel breaks down over time.
Jul 29th, 2016
Read more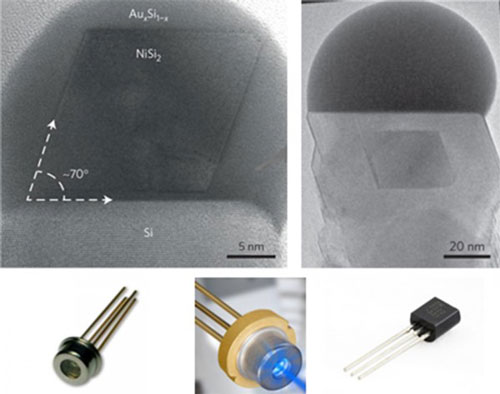 This development could lead to new materials for ultra-small transistors, diodes, and more.
This development could lead to new materials for ultra-small transistors, diodes, and more.
Jul 29th, 2016
Read more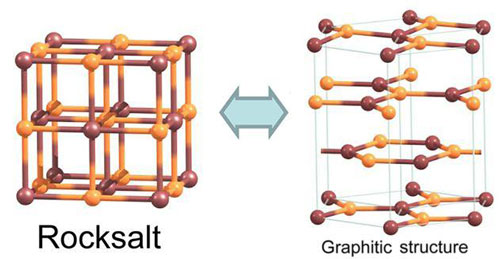 Physicists use supercomputers to find a way of making 'imitation graphene' from salt.
Physicists use supercomputers to find a way of making 'imitation graphene' from salt.
Jul 29th, 2016
Read more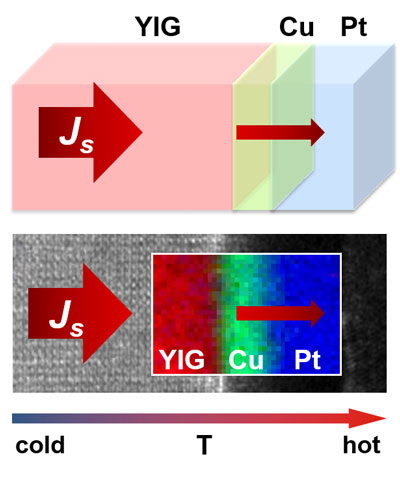 Direct correlation between temperature dependent generation of spin currents and atomic composition of interfaces found.
Direct correlation between temperature dependent generation of spin currents and atomic composition of interfaces found.
Jul 29th, 2016
Read more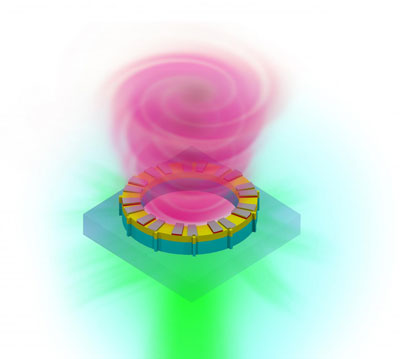 The optics advancement may solve an approaching data bottleneck by helping to boost computing power and information transfer rates tenfold.
The optics advancement may solve an approaching data bottleneck by helping to boost computing power and information transfer rates tenfold.
Jul 29th, 2016
Read more Researchers employ novel approach to assemble peptoids on a solid surface.
Researchers employ novel approach to assemble peptoids on a solid surface.
Jul 29th, 2016
Read moreResearchers are investigating bimetallic nanoparticles to more effectively control their adsorption properties for capturing carbon dioxide from the atmosphere.
Jul 28th, 2016
Read more Enzyme-based sensors detection lactate levels in sweat.
Enzyme-based sensors detection lactate levels in sweat.
Jul 28th, 2016
Read more Researchers received a $1.8 million grant from the National Cancer Institute to apply their nanotechnology expertise to more effectively deliver cancer drugs into tumor cells and combat cancer drug resistance.
Researchers received a $1.8 million grant from the National Cancer Institute to apply their nanotechnology expertise to more effectively deliver cancer drugs into tumor cells and combat cancer drug resistance.
Jul 28th, 2016
Read more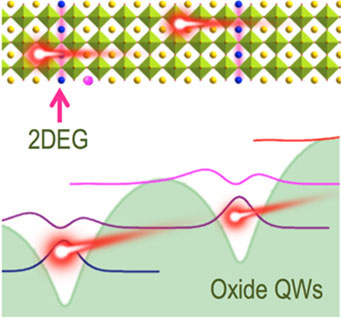 Meticulously designed oxide thin films exhibit well-defined ON/OFF states that could be used in small, energy-efficient electronics.
Meticulously designed oxide thin films exhibit well-defined ON/OFF states that could be used in small, energy-efficient electronics.
Jul 28th, 2016
Read more