Showing Spotlights 841 - 848 of 2784 in category All (newest first):
 Recently, great progress has been made in the development of bio-hybrid devices with enhanced biological, mechanical and electrical designs. Several muscular tissue based actuators have been described and devices with cultured heart cells have also been reported to produce electrical outputs.
Now, researchers have demonstrated a novel bio-hybrid system, the 'Cell Generator'. The researchers integrated piezoelectric material with 3D-engineered living constructs for energy harvesting and electricity generation.
Recently, great progress has been made in the development of bio-hybrid devices with enhanced biological, mechanical and electrical designs. Several muscular tissue based actuators have been described and devices with cultured heart cells have also been reported to produce electrical outputs.
Now, researchers have demonstrated a novel bio-hybrid system, the 'Cell Generator'. The researchers integrated piezoelectric material with 3D-engineered living constructs for energy harvesting and electricity generation.
Mar 31st, 2017
 You surely remember one of the hallmarks of the Mission: Impossible series that shows a secret agent receiving his instructions on a tape or other device that then self-destructs and goes up in a cloud of smoke. Getting pretty close to this Hollywood scenario, minus the smoke, scientists now have demonstrated remote destruction capability of high performance silicon electronics. They also show that in case of tempering, dislocation, or light exposure, electronics on for instance stolen or lost hard drives can self-destruct.
You surely remember one of the hallmarks of the Mission: Impossible series that shows a secret agent receiving his instructions on a tape or other device that then self-destructs and goes up in a cloud of smoke. Getting pretty close to this Hollywood scenario, minus the smoke, scientists now have demonstrated remote destruction capability of high performance silicon electronics. They also show that in case of tempering, dislocation, or light exposure, electronics on for instance stolen or lost hard drives can self-destruct.
Mar 29th, 2017
 The electrode in lithium-ion (Li-ion) batteries is an integrated system in which both active materials and binder systems play critical roles in determining its final properties. In order to improve battery performance, a lot of research is focussing on the development of high-capacity active materials. However, without an efficient binder system, these novel materials can't fulfill their potentials. Researchers have now developed a new binder system with a nano-architecture promotes both electron and ion transport, which enhances the energy per unit mass and volume of the electrode.
The electrode in lithium-ion (Li-ion) batteries is an integrated system in which both active materials and binder systems play critical roles in determining its final properties. In order to improve battery performance, a lot of research is focussing on the development of high-capacity active materials. However, without an efficient binder system, these novel materials can't fulfill their potentials. Researchers have now developed a new binder system with a nano-architecture promotes both electron and ion transport, which enhances the energy per unit mass and volume of the electrode.
Mar 28th, 2017
 In two new studies, researchers show that cement plants can have their carbon dioxide exhaust eliminated while co-producing carbon nanotubes. They demonstrate that with their C2CNT (carbon dioxide into carbon nanotubes) process, a wide portfolio of tailored carbon nanotubes, such as those with special shapes or conductivity can be made. C2CNT is a straightforward process that transforms CO2 to carbon nanotubes by molten electrolysis with inexpensive (nickel and steel) electrodes and low voltage. This synthesis consumes only CO2 and electricity, and is constrained only by the cost of electricity.
In two new studies, researchers show that cement plants can have their carbon dioxide exhaust eliminated while co-producing carbon nanotubes. They demonstrate that with their C2CNT (carbon dioxide into carbon nanotubes) process, a wide portfolio of tailored carbon nanotubes, such as those with special shapes or conductivity can be made. C2CNT is a straightforward process that transforms CO2 to carbon nanotubes by molten electrolysis with inexpensive (nickel and steel) electrodes and low voltage. This synthesis consumes only CO2 and electricity, and is constrained only by the cost of electricity.
Mar 21st, 2017
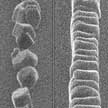 In recent years, researchers working on de-icing and anti-icing strategies have been inspired by biology and nanotechnology to develop nanocoatings and other nanostructured surfaces. Researchers now have demonstrated the ability to spatially control frost nucleation (ice formation from water vapor) and to manipulate ice crystal growth kinetics. This ice nucleation control and the confinement of ice crystal growth direction through manipulating roughness scale have not been reported before.
In recent years, researchers working on de-icing and anti-icing strategies have been inspired by biology and nanotechnology to develop nanocoatings and other nanostructured surfaces. Researchers now have demonstrated the ability to spatially control frost nucleation (ice formation from water vapor) and to manipulate ice crystal growth kinetics. This ice nucleation control and the confinement of ice crystal growth direction through manipulating roughness scale have not been reported before.
Mar 17th, 2017
 Researchers demonstrate a novel mechansim for the realization of an optical waveguide. This opens the possibility to realize a waveguide without any modulation of the refractive index. The optical delay necessary for the beam confinement is not achieved by a local modulation of the speed of light, but through an exotic effect called 'geometric phase'. Geometric phase is a temporal delay associated with changes in the propagation of light polarization, the latter corresponding roughly to the oscillation direction of the electromagnetic field.
Researchers demonstrate a novel mechansim for the realization of an optical waveguide. This opens the possibility to realize a waveguide without any modulation of the refractive index. The optical delay necessary for the beam confinement is not achieved by a local modulation of the speed of light, but through an exotic effect called 'geometric phase'. Geometric phase is a temporal delay associated with changes in the propagation of light polarization, the latter corresponding roughly to the oscillation direction of the electromagnetic field.
Mar 14th, 2017
 Photodetectors with a spectral response from the ultraviolet (UV) to visible light have significant importance in modern industrial and scientific applications such as imaging, communication, environmental monitoring and day and nighttime surveillance. Compared to other materials, the photo-current conversions of two-dimensional transition metal dichalcogenides such as MoS2 nanosheets are impressive, making them great candidates for next-generation visible light photodetectors. Researchers have now developed a facile and low-cost solution processing strategy to fabricate mechanically flexible 2D organic-inorganic hybrid thin-film photodetectors on a conventional filter paper.
Photodetectors with a spectral response from the ultraviolet (UV) to visible light have significant importance in modern industrial and scientific applications such as imaging, communication, environmental monitoring and day and nighttime surveillance. Compared to other materials, the photo-current conversions of two-dimensional transition metal dichalcogenides such as MoS2 nanosheets are impressive, making them great candidates for next-generation visible light photodetectors. Researchers have now developed a facile and low-cost solution processing strategy to fabricate mechanically flexible 2D organic-inorganic hybrid thin-film photodetectors on a conventional filter paper.
Mar 9th, 2017
 An recent analysis of the combined effect of nanoparticles and substrates on the concentration of mobile ions in liquid crystals considers both 100% pure and contaminated with ions substrates and nanoparticles. The results could be very useful for engineers trying to apply nanotechnology to liquid crystal devices. Specifically, the control of mobile ions in liquid crystals by means of nanoparticles and substrates of the cell tailored for specific applications - liquid crystal displays, light shutters, switches, modulators, etc.
An recent analysis of the combined effect of nanoparticles and substrates on the concentration of mobile ions in liquid crystals considers both 100% pure and contaminated with ions substrates and nanoparticles. The results could be very useful for engineers trying to apply nanotechnology to liquid crystal devices. Specifically, the control of mobile ions in liquid crystals by means of nanoparticles and substrates of the cell tailored for specific applications - liquid crystal displays, light shutters, switches, modulators, etc.
Mar 8th, 2017
 Recently, great progress has been made in the development of bio-hybrid devices with enhanced biological, mechanical and electrical designs. Several muscular tissue based actuators have been described and devices with cultured heart cells have also been reported to produce electrical outputs.
Now, researchers have demonstrated a novel bio-hybrid system, the 'Cell Generator'. The researchers integrated piezoelectric material with 3D-engineered living constructs for energy harvesting and electricity generation.
Recently, great progress has been made in the development of bio-hybrid devices with enhanced biological, mechanical and electrical designs. Several muscular tissue based actuators have been described and devices with cultured heart cells have also been reported to produce electrical outputs.
Now, researchers have demonstrated a novel bio-hybrid system, the 'Cell Generator'. The researchers integrated piezoelectric material with 3D-engineered living constructs for energy harvesting and electricity generation.
 Subscribe to our Nanotechnology Spotlight feed
Subscribe to our Nanotechnology Spotlight feed





