Showing Spotlights 513 - 520 of 2777 in category All (newest first):
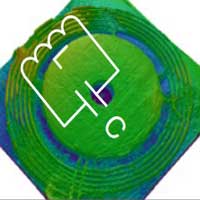 Radio-frequency wireless sensors are essential components of smart objects and internet-of-things components. However, these passive microsensors suffer from poor quality of data and sensitivity due to the environments they operate in and the need for sensors with extremely small footprints. Researchers have recently shown that a wireless system locked to an exceptional point (EP) can enhance the sensitivity of passive wireless sensors in practical applications. New work has theoretically introduced and experimentally demonstrated a new class of parity-time-symmetric RF electronic and telemetric systems, which combine EPs with divergent points.
Radio-frequency wireless sensors are essential components of smart objects and internet-of-things components. However, these passive microsensors suffer from poor quality of data and sensitivity due to the environments they operate in and the need for sensors with extremely small footprints. Researchers have recently shown that a wireless system locked to an exceptional point (EP) can enhance the sensitivity of passive wireless sensors in practical applications. New work has theoretically introduced and experimentally demonstrated a new class of parity-time-symmetric RF electronic and telemetric systems, which combine EPs with divergent points.
Nov 12th, 2019
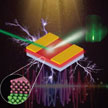
 The goal of the electronics industry has always been to build durable devices with stable performance that last a very long time. 'Transient electronics', however, are designed with the exact opposite goal: to dissolve harmlessly into their surroundings after functioning for a certain amount of time. The fabrication process and the in vivo powering of medical implants that are only made from biodegradable materials are two of the challenges associated with transient electronics. Researchers demonstrate wirelessly powered, frequency-selective magnesium microstructures as promising candidates to be used as power receiver, microheaters and triggering elements for biodegradable implantable medical devices.
The goal of the electronics industry has always been to build durable devices with stable performance that last a very long time. 'Transient electronics', however, are designed with the exact opposite goal: to dissolve harmlessly into their surroundings after functioning for a certain amount of time. The fabrication process and the in vivo powering of medical implants that are only made from biodegradable materials are two of the challenges associated with transient electronics. Researchers demonstrate wirelessly powered, frequency-selective magnesium microstructures as promising candidates to be used as power receiver, microheaters and triggering elements for biodegradable implantable medical devices.
Nov 11th, 2019
 New work provides insight into the control over phase and ordering during halide perovskite epitaxial growth and expands the selection of photoactive materials for growing epitaxial halide perovskites that can be exploited in high-performance electronic applications. Hybrid organic-inorganic halide perovskite has attracted tremendous attention as an exceptional new class of semiconductors for solar harvesting, light emission, lasing and thin-film electronics. However, the toxicity of lead devices and lead manufacturing combined with the instability of organic components have been two key barriers to widespread application. Tin-based inorganic halide perovskites have been considered promising substitutes for their lead analogues.
New work provides insight into the control over phase and ordering during halide perovskite epitaxial growth and expands the selection of photoactive materials for growing epitaxial halide perovskites that can be exploited in high-performance electronic applications. Hybrid organic-inorganic halide perovskite has attracted tremendous attention as an exceptional new class of semiconductors for solar harvesting, light emission, lasing and thin-film electronics. However, the toxicity of lead devices and lead manufacturing combined with the instability of organic components have been two key barriers to widespread application. Tin-based inorganic halide perovskites have been considered promising substitutes for their lead analogues.
Nov 7th, 2019
 As an advanced fabrication technique, 3D printing has been increasingly utilized to fabricate complex 3D objects via digitally controlled deposition of phase change and reactive materials and solvent-based inks. When it comes to batteries, 3D printing has several significant advantages compared with conventional battery fabrication technologies and it opens new avenues for the rapid fabrication of 3D-structured batteries with complex architectures and high performance. In next generation futuristic 3D printed energy architectures batteries and supercapacitors could be printed in virtually any shape.
As an advanced fabrication technique, 3D printing has been increasingly utilized to fabricate complex 3D objects via digitally controlled deposition of phase change and reactive materials and solvent-based inks. When it comes to batteries, 3D printing has several significant advantages compared with conventional battery fabrication technologies and it opens new avenues for the rapid fabrication of 3D-structured batteries with complex architectures and high performance. In next generation futuristic 3D printed energy architectures batteries and supercapacitors could be printed in virtually any shape.
Nov 4th, 2019
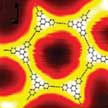 Graphyne is a little known sibling of graphene. Simulations have shown that graphyne's conduction electrons travel extremely fast - as they do in graphene - but in only one direction. That property could help researchers design faster transistors and other electronic components that process one-way current. Graphyne is distinct in being composed of sp and sp2 carbon atoms, which contrasts with graphene containing only sp2 carbon. The coexistence of sp and sp2 carbons in graphyne gives rise to unique physical properties, such as high conductivity and large carrier mobility.
Graphyne is a little known sibling of graphene. Simulations have shown that graphyne's conduction electrons travel extremely fast - as they do in graphene - but in only one direction. That property could help researchers design faster transistors and other electronic components that process one-way current. Graphyne is distinct in being composed of sp and sp2 carbon atoms, which contrasts with graphene containing only sp2 carbon. The coexistence of sp and sp2 carbons in graphyne gives rise to unique physical properties, such as high conductivity and large carrier mobility.
Oct 31st, 2019
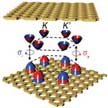 The basic idea of valleytronics is to pass information through two-dimensional (2D) and other very thin conducting materials using the energy valleys - or energy extrema - in their conduction and valence bands. Information can be transmitted by controlling an electron's association with a valley - a manipulation that can be achieved using electric fields, magnetic fields and circularly polarized light. Researchers now have demonstrated a room-temperature approach to manipulating quantum-information carriers, which is usually volatile at room temperature, in a monolayer WSe2 semiconductor.
The basic idea of valleytronics is to pass information through two-dimensional (2D) and other very thin conducting materials using the energy valleys - or energy extrema - in their conduction and valence bands. Information can be transmitted by controlling an electron's association with a valley - a manipulation that can be achieved using electric fields, magnetic fields and circularly polarized light. Researchers now have demonstrated a room-temperature approach to manipulating quantum-information carriers, which is usually volatile at room temperature, in a monolayer WSe2 semiconductor.
Oct 24th, 2019
 Hierarchical structures, spanning multiple length scales from nano- to macroscales, are very common in nature; but only in recent years have they been systematically studied in materials science, in order to understand the specific effects they can have on the mechanical properties of various systems. Researchers have developed a straightforward, cost-efficient, and fast route to fabricate hierarchical porous structures in a 3D printer. With this technique they can process nanoporous materials and fabricate structures from nanometer to centimeter scale.
Hierarchical structures, spanning multiple length scales from nano- to macroscales, are very common in nature; but only in recent years have they been systematically studied in materials science, in order to understand the specific effects they can have on the mechanical properties of various systems. Researchers have developed a straightforward, cost-efficient, and fast route to fabricate hierarchical porous structures in a 3D printer. With this technique they can process nanoporous materials and fabricate structures from nanometer to centimeter scale.
Oct 22nd, 2019
 The increase in production and applications of metal-oxide nanoparticles (MO-NPs) raises concerns for the environment as well as for human health. The terrestrial environment, especially soil, is expected to be the largest repository for environmentally released MO-NPs. Therefore, the accurate determination of environmentally released MO-NPs is imperative to assess the real-time scenario of toxicity to soil biota and the threat to human beings via the food chain.
The increase in production and applications of metal-oxide nanoparticles (MO-NPs) raises concerns for the environment as well as for human health. The terrestrial environment, especially soil, is expected to be the largest repository for environmentally released MO-NPs. Therefore, the accurate determination of environmentally released MO-NPs is imperative to assess the real-time scenario of toxicity to soil biota and the threat to human beings via the food chain.
Oct 21st, 2019
 Radio-frequency wireless sensors are essential components of smart objects and internet-of-things components. However, these passive microsensors suffer from poor quality of data and sensitivity due to the environments they operate in and the need for sensors with extremely small footprints. Researchers have recently shown that a wireless system locked to an exceptional point (EP) can enhance the sensitivity of passive wireless sensors in practical applications. New work has theoretically introduced and experimentally demonstrated a new class of parity-time-symmetric RF electronic and telemetric systems, which combine EPs with divergent points.
Radio-frequency wireless sensors are essential components of smart objects and internet-of-things components. However, these passive microsensors suffer from poor quality of data and sensitivity due to the environments they operate in and the need for sensors with extremely small footprints. Researchers have recently shown that a wireless system locked to an exceptional point (EP) can enhance the sensitivity of passive wireless sensors in practical applications. New work has theoretically introduced and experimentally demonstrated a new class of parity-time-symmetric RF electronic and telemetric systems, which combine EPs with divergent points.
 Subscribe to our Nanotechnology Spotlight feed
Subscribe to our Nanotechnology Spotlight feed





