Showing Spotlights 585 - 592 of 2782 in category All (newest first):
 Alpha-synuclein is a protein whose function in the healthy brain is currently unknown. It is of great interest to Parkinson's researchers because it is a major constituent of Lewy bodies, protein clumps that are the pathological hallmark of Parkinson's disease (PD). Scientists believe that the self-assembly of alpha-synuclein into oligomers and fibrils is linked to progress and pathogenesis of the disease. A new study suggest that important characteristics of the fibrillation process, such as surface charge and surface functional group, should be considered in the development of nanotechnology-based therapeutic approaches.
Alpha-synuclein is a protein whose function in the healthy brain is currently unknown. It is of great interest to Parkinson's researchers because it is a major constituent of Lewy bodies, protein clumps that are the pathological hallmark of Parkinson's disease (PD). Scientists believe that the self-assembly of alpha-synuclein into oligomers and fibrils is linked to progress and pathogenesis of the disease. A new study suggest that important characteristics of the fibrillation process, such as surface charge and surface functional group, should be considered in the development of nanotechnology-based therapeutic approaches.
Mar 19th, 2019
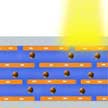 Recent research in nanofluidics has adopted reconstructed layered two-dimensional (2D) sheets as a promising material platform for nanofluidics. These membranes contain a high volume fraction of interconnected 2D nanochannels. In new work, researchers demonstrate a coupled photon-electron-ion transport phenomenon through graphene oxide membranes. It shows a straightforward way on how to power the transport in 2D layered materials using the energy of light.
Recent research in nanofluidics has adopted reconstructed layered two-dimensional (2D) sheets as a promising material platform for nanofluidics. These membranes contain a high volume fraction of interconnected 2D nanochannels. In new work, researchers demonstrate a coupled photon-electron-ion transport phenomenon through graphene oxide membranes. It shows a straightforward way on how to power the transport in 2D layered materials using the energy of light.
Mar 18th, 2019
 In recent years, all-optical modulators (AOMs) have attracted significant interests due to their low power consumption, broad bandwidth, and potential in all-optical fields. Among these, AOMs based on the high photothermal efficiency of antimonene, exhibit remarkable advantages for their large modulation depth, wide operating wavelength range, and easy implementation.
Researchers demonstrated that an antimonene-based AOM was successfully utilized to actively Q-switch a fiber laser in a fully photonics domain and this actively modulated laser represented all-optically tunable output parameters, and easy time synchronization.
In recent years, all-optical modulators (AOMs) have attracted significant interests due to their low power consumption, broad bandwidth, and potential in all-optical fields. Among these, AOMs based on the high photothermal efficiency of antimonene, exhibit remarkable advantages for their large modulation depth, wide operating wavelength range, and easy implementation.
Researchers demonstrated that an antimonene-based AOM was successfully utilized to actively Q-switch a fiber laser in a fully photonics domain and this actively modulated laser represented all-optically tunable output parameters, and easy time synchronization.
Mar 15th, 2019
 Inspired by chiral molecular structures, scientists are developing strategies to build artificial chiral materials by mimicking natural molecular structures using functional materials. Specifically, metal nanomaterials exhibit tailorable optical properties upon excitation of surface plasmons and become one of the most promising components to realize chiral optical metamaterials. New work provides a macroscopic model to understand the origin of chirality because the structures of the chiral meta-molecules are observable under a microscope and also the optical chirality is several orders of magnitude stronger than the intrinsic chirality of organic molecules.
Inspired by chiral molecular structures, scientists are developing strategies to build artificial chiral materials by mimicking natural molecular structures using functional materials. Specifically, metal nanomaterials exhibit tailorable optical properties upon excitation of surface plasmons and become one of the most promising components to realize chiral optical metamaterials. New work provides a macroscopic model to understand the origin of chirality because the structures of the chiral meta-molecules are observable under a microscope and also the optical chirality is several orders of magnitude stronger than the intrinsic chirality of organic molecules.
Mar 14th, 2019
 Electronic tattoos (e-tattoos) are an extremely thin form of wearable electronics. They are lightweight and soft, which allows them to be intimately mounted on human skin for noninvasive, high-fidelity sensing. During the operation of e-tattoos, they are constantly exposed to external mechanical inputs such as bending, twisting, pressing, and cutting, which may cause mechanical damage and lead to malfunction. Now, researchers have demonstrated a self-healing silk e-tattoo that shows high sensitivity to multiple stimuli, including strain, humidity, and temperature based on a unique graphene, silk fibroin, Ca2+ combination.
Electronic tattoos (e-tattoos) are an extremely thin form of wearable electronics. They are lightweight and soft, which allows them to be intimately mounted on human skin for noninvasive, high-fidelity sensing. During the operation of e-tattoos, they are constantly exposed to external mechanical inputs such as bending, twisting, pressing, and cutting, which may cause mechanical damage and lead to malfunction. Now, researchers have demonstrated a self-healing silk e-tattoo that shows high sensitivity to multiple stimuli, including strain, humidity, and temperature based on a unique graphene, silk fibroin, Ca2+ combination.
Mar 8th, 2019
 Scientists have experimentally realized a plasmonic aerosol by efficiently transitioning liquid suspensions of gold nanorods into the gas phase and simultaneously measuring their optical spectra. They demonstrated that these aerosols are optically homogeneous, thermodynamically stable, with wide wavelength tunability (by controlling the aspect ratio of the nanorods) and have extremely large sensitivities to their environment. This novel plasmonic material could potentially open the door to many interesting applications ranging from geoengineering, vacuum microelectronics, molecular diagnostics, nanomedicines, nanojet printing and nonlinear optics.
Scientists have experimentally realized a plasmonic aerosol by efficiently transitioning liquid suspensions of gold nanorods into the gas phase and simultaneously measuring their optical spectra. They demonstrated that these aerosols are optically homogeneous, thermodynamically stable, with wide wavelength tunability (by controlling the aspect ratio of the nanorods) and have extremely large sensitivities to their environment. This novel plasmonic material could potentially open the door to many interesting applications ranging from geoengineering, vacuum microelectronics, molecular diagnostics, nanomedicines, nanojet printing and nonlinear optics.
Mar 6th, 2019
 Ionic conductors are a class of materials with key roles in energy storage, solar energy conversion, sensors, and electronic devices. In their quest towards eco-friendly alternatives for the current type of ionic conductors, researchers have developed an alternative green option based on organic silk and inorganic green laponite for the display and wearables industry via flexible and eco-friendly ionics. This could ultimately enable a wide range of applications within the field of flexible and wearable electronics.
Ionic conductors are a class of materials with key roles in energy storage, solar energy conversion, sensors, and electronic devices. In their quest towards eco-friendly alternatives for the current type of ionic conductors, researchers have developed an alternative green option based on organic silk and inorganic green laponite for the display and wearables industry via flexible and eco-friendly ionics. This could ultimately enable a wide range of applications within the field of flexible and wearable electronics.
Mar 5th, 2019
 Researchers demonstrate a display pixel that can switch on and off at least 1000 times faster than pixels that use conventional liquid crystal materials. They show that plasmonic gold nanorods - which interact very strongly with light - can be aligned using electric fields, and they use this alignment to control the amount of light that can pass through the pixel. By engineering the dimensions and material structure of the nanorods, the scientists design pixels that work with different colors of light, both visible and infrared.
Researchers demonstrate a display pixel that can switch on and off at least 1000 times faster than pixels that use conventional liquid crystal materials. They show that plasmonic gold nanorods - which interact very strongly with light - can be aligned using electric fields, and they use this alignment to control the amount of light that can pass through the pixel. By engineering the dimensions and material structure of the nanorods, the scientists design pixels that work with different colors of light, both visible and infrared.
Mar 4th, 2019
 Alpha-synuclein is a protein whose function in the healthy brain is currently unknown. It is of great interest to Parkinson's researchers because it is a major constituent of Lewy bodies, protein clumps that are the pathological hallmark of Parkinson's disease (PD). Scientists believe that the self-assembly of alpha-synuclein into oligomers and fibrils is linked to progress and pathogenesis of the disease. A new study suggest that important characteristics of the fibrillation process, such as surface charge and surface functional group, should be considered in the development of nanotechnology-based therapeutic approaches.
Alpha-synuclein is a protein whose function in the healthy brain is currently unknown. It is of great interest to Parkinson's researchers because it is a major constituent of Lewy bodies, protein clumps that are the pathological hallmark of Parkinson's disease (PD). Scientists believe that the self-assembly of alpha-synuclein into oligomers and fibrils is linked to progress and pathogenesis of the disease. A new study suggest that important characteristics of the fibrillation process, such as surface charge and surface functional group, should be considered in the development of nanotechnology-based therapeutic approaches.
 Subscribe to our Nanotechnology Spotlight feed
Subscribe to our Nanotechnology Spotlight feed





