| Posted: Jun 01, 2015 |
Light-powered healing of a wearable electrical conductor
|
|
(Nanowerk News) Mechanical failure along a conductive pathway can cause the unexpected shutdown of electronic devices, ultimately limiting device lifetimes. In particular, wearable electronic devices, which inevitably undergo dynamic and vigorous motions (e.g., bending, folding, or twisting), are much more liable to suffer from such conductive failures compared with conventional flat electronic devices. To address this problem, various systems to realize healable electrical conductors have been proposed; however, rapid, noninvasive, and on-demand healing, factors that are all synergistically required, especially for wearable device applications, still remains challenging to realize.
|
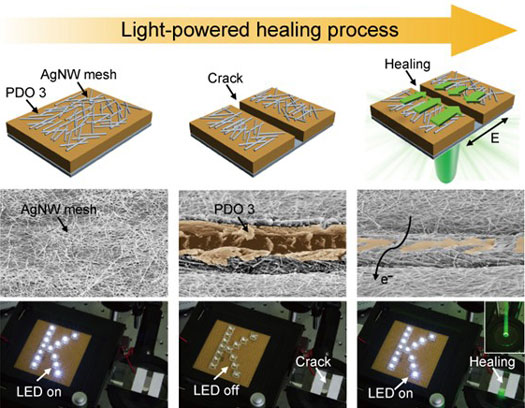 |
| Light-powered healing of electrical conductor: (left to right) pristine, cracked, and optically-healed electrical conductor. (Image: KAIST)
|
|
Professor Jung-Ki Park and Hee-Tak Kim in the Department of Chemical & Biomolecular Engineering at the Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST) have come up with the idea of a light-powered healable electrical conductor. Light-powered healing is implemented via the use of a photochromic soft material (i.e., an azobenzene material), which can be directionally moved along the light polarization. This unique directionality of the material’s movement with respect to light polarization enables an efficient healing process, regardless of crack propagation directions, light incident angles, and the number of cracks.
|
|
By depositing silver nanowires (AgNWs), which are the conducting material used in this study, onto the top layer of the flexible photochromic soft material, this optically healable material has fully functional electrical conductivity. Notably, AgNWs are found to maintain conformable contact with the photochromic soft material, even during the optical healing process. Thus, AgNWs and the photochromic soft material act as conductive pathways and a light-powered cargo carrier, respectively; the synergetic effect detailed from combining these various advantages provides rapid, noninvasive, and on-demand healing for a flexible electronic conductor, making light-powered healing more amenable to dynamically deformable wearable devices beyond existing systems.
|
|
This research was done in collaboration with Professor Seungwoo Lee at Sungkyunkwan University (SKKU). The given work was published in Advanced Functional Materials ("Light-Powered Healing of a Wearable Electrical Conductor") and was highlighted in Nanowerk (Healing electronics with light).
|

