| Posted: Sep 21, 2016 |
New work explores thermoelectric screen printing
(Nanowerk News) Thermoelectric conversion is a solid-state and environmentally friendly energy conversion technology with broad applications that include solid-state cooling, energy harvesting and waste heat recovery.
|
|
Flexible thermoelectric devices are especially attractive for waste heat recovery along contoured surfaces and for energy harvesting applications to power sensors, biomedical devices and wearable electronics – an area experiencing exponential growth. However, obtaining low-cost, flexible and efficient thermoelectric materials is extremely difficult due to many materials and manufacturing challenges.
|
|
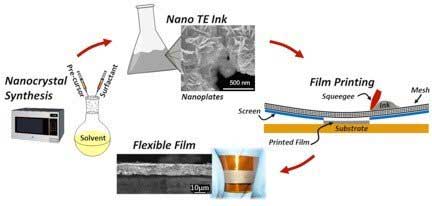
In work led by professor Yanliang Zhang at Boise State University, high-performance and low-cost flexible thermoelectric films and devices were fabricated by an innovative screen-printing process that allows for direct conversion of nanocrystals into flexible thermoelectric devices.
|
 |
|
The precise control of the starting nanocrystals’ shape and surface chemistry and the optimization of the nano-ink and screen-printing process are the key factors giving rise to unprecedented performances in the printed thermoelectric materials.
|
|
The paper on this work is published on the Scientific Reports website ("High-performance and flexible thermoelectric films by screen printing solution-processed nanoplate crystals"). The collaboration with high-tech startup company ThermoAura, focusing on nanocrystal synthesis, also contributed to the success of this work.
|
|
Based on initial cost analysis, the screen-printed films can realize thermoelectric devices at 2-3 cents per watt, an order of magnitude lower than current state-of-the-art commercial devices. Such a cost reduction would make thermoelectrics a very competitive energy conversion technology that could tremendously open up the largely underexplored markets on waste heat recovery.
|
|
This additive printing method not only will benefit thermoelectrics, but also result in a disruptive manufacturing approach for other electronic devices and energy conversion or storage technologies of ultralow cost and flexibility.
|
|
Zhang’s vision on marrying additive manufacturing and advanced energy technology to enable major technology breakthroughs also has been recognized by a major federal funding agency. He recently received an infrastructure award from U.S. Department of Energy to invest an advanced additive printing equipment and establish state-of-the-art additive manufacturing capabilities at Boise State.
|
|
This new capability will enable students to perform cutting edge research on additive manufacturing and their applications on printing sensors, flexible electronics and energy conversion and storage systems.
|

