| Dec 14, 2018 | |
A summary of electrospun nanofibers as drug delivery system(Nanowerk News) In recent studies, nanotechnology has proven to be an interesting approach towards solving problems in the field of medicine. Dr. Jose Manuel Cornejo Bravo demonstrates the use of electrospun polymeric nanofibers as an interesting method for drug delivery systems application (Current Drug Delivery, "A Summary of Electrospun Nanofibers as Drug Delivery System: Drugs Loaded and Biopolymers Used as Matrices"). |
|
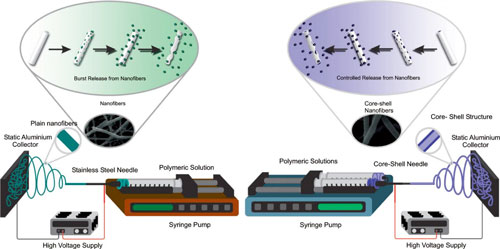 |
|
| Electrospun Nanofibers as Drug Delivery System. (click on image to enlarge) | |
| Electrospun polymeric nanofibers offer a high surface-to-volume ratio which can greatly improve some processes such as cell binding and proliferation, drug loading, and mass transfer processes. | |
| Perhaps the most important application of electrospinning is drug delivery optimization, which can be achieved by using these materials for the controlled release of active substances ranging from antibiotics and anticancer agents to macromolecules such as proteins and DNA. | |
| This method improves the treatment process, as drugs with low solubility can be loaded into fibers, improving their bioavailability while also attaining controlled release. | |
| Dr Bravo's research presents an overview of reported drugs loaded into fibers which can be used as drug delivery systems. Drugs with different biological functions such as anti-inflammatory, anti-microbial, anticancer, cardiovascular, anti-histamine, gastrointestinal, palliative and contraception, were used for this purpose. | |
| Along with the drugs used, the electrospinning techniques used for each system as well as polymers used as matrices for nanofiber preparation were also pertinent to the research. Each drug was tested using different combinations of electrospinning techniques and polymers suited best for the drug delivery system. Used altogether in such synergy, electrospun polymeric nanofibers proved to be much more advantageous over other drug delivery systems. | |
| Dr Bravo notes that improvements to these methods may requires further research on the fabrication, characterization and design of relevant nanomaterials. |
| Source: Bentham Science Publishers | |
|
Subscribe to a free copy of one of our daily Nanowerk Newsletter Email Digests with a compilation of all of the day's news. |
