| May 08, 2019 | |
Move over, silicon switches: There's a new way to compute(Nanowerk News) Logic and memory devices, such as the hard drives in computers, now use nanomagnetic mechanisms to store and manipulate information. Unlike silicon transistors, which have fundamental efficiency limitations, they require no energy to maintain their magnetic state: Energy is needed only for reading and writing information. |
|
| One method of controlling magnetism uses electrical current that transports spin to write information, but this usually involves flowing charge. Because this generates heat and energy loss, the costs can be enormous, particularly in the case of large server farms or in applications like artificial intelligence, which require massive amounts of memory. Spin, however, can be transported without a charge with the use of a topological insulator - a material whose interior is insulating but that can support the flow of electrons on its surface. | |
| In a newly published Physical Review Applied paper ("Voltage-Controlled Topological Spin Switch for Ultralow-Energy Computing: Performance Modeling and Benchmarking"), researchers from New York University introduce a voltage-controlled topological spin switch (vTOPSS) that requires only electric fields, rather than currents, to switch between two Boolean logic states, greatly reducing the heat generated and energy used. | |
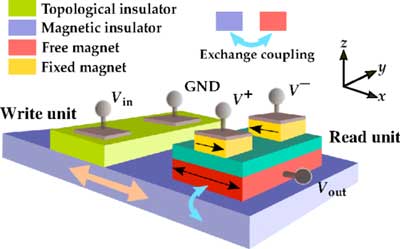 |
|
| Copy and invert functions implemented with the VTOPSS. In the write unit, an input voltage signal applied across the TI layer causes spin accumulation at the interface of the TI and MI layers, which exerts a spin torque on the magnetization of the MI layer to reverse it. The read unit has a MTJ exchange-coupled to the MI layer that allows reading of the information in the MI layer. The polarity of the output voltage can be changed on the fly by change of the polarity of the voltages on the MTJ stack, allowing both inverting and noninverting logic to be realized with the same primitive/layout. (© Physical Review Applied) | |
| The team is comprised of Shaloo Rakheja, an assistant professor of electrical and computer engineering at the NYU Tandon School of Engineering, and Andrew D. Kent, an NYU professor of physics and director of the University's Center for Quantum Phenomena, along Michael E. Flatté, a professor at the University of Iowa. | |
| Rakheja employs a simple analogy to explain the impact of switching between two states more effectively. "Imagine if you were preparing a recipe and had to go into a different room anytime you needed an ingredient before returning to the kitchen to add it," she says. "It's just as inefficient when the portions of computing hardware needed to do a calculation and the portions needed to store it are not well integrated." | |
| While heterostructure devices like theirs, composed of a magnetic insulator and topological insulator, are still slightly slower than silicon transistors, vTOPSS increases functionality and circuit design possibilities, as it has integrated logic and non-volatile memory. "This is ultimately a matter of user experience and added features," Rakheja says. | |
| Because vTOPPS will reduce reliance on cloud memory, it also holds the potential for making computing safer, as hackers will have greater difficulty gaining access to a system's hardware. Next steps will include further optimization at the materials and design level to improve the switching speed, as well as developing prototypes. |
| Source: NYU Tandon School of Engineering | |
|
Subscribe to a free copy of one of our daily Nanowerk Newsletter Email Digests with a compilation of all of the day's news. |
