| Jun 03, 2020 | |
Smart gold nanocages break chemoresistance(Nanowerk News) Chemotherapeutic drugs are the cornerstone in the treatment of numerous malignancies. However, the present chemotherapy is still far from being satisfactory mainly owing to the severe side effects of the chemotherapeutic agents and drug resistance of cancer cells. |
|
| Thus, constructing an ideal chemotherapeutic strategy to reverse drug resistance is needed. | |
| Researchers from the Shenzhen Institutes of Advanced Technology (SIAT) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences have developed a smart nanosystem with enhanced curative efficacy and lower side effects. | |
| The study was published in Journal of Controlled Release ("Smart gold nanocages for mild heat-triggered drug release and breaking chemoresistance"). | |
 |
|
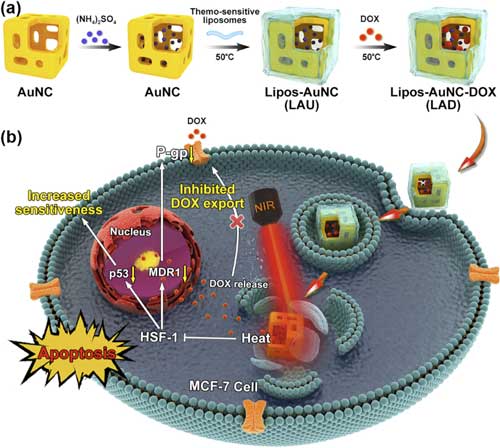
| Illustration shows thermo-sensitive liposome coated gold nanocages with DOX loading (LAD) for photothermally triggered drug release and breaking chemoresistance. (Image: SIAT) | |
| This smart nanosystem consists of thermo-sensitive liposome coated gold nanocages with doxorubicin (DOX) loading (LAD) for near-infrared (NIR)-triggered drug release and chemo-photothermal combination therapy of breast cancer. | |
| The biocompatible liposomes coating facilitated the cellular uptake of LAD and meanwhile avoided drug leakage during the circulation. | |
| More importantly, LAD exhibited controllable photothermal conversion property and produced mild heat under NIR irradiation, which not only triggered DOX release and transferred DOX from lysosome to nucleus, but also elicited the mild heat cell killing effect to improve the curative efficiency. | |
| Further mechanism study revealed that mild heat could reverse drug resistance by down-regulation of the chemoresistance-related markers, and inhibited DOX export and increased drug sensitiveness, thereby prominently increased the anticancer efficiency. | |
| This smart and versatile LAD nanoplatform is promising in the fields of drug controlled release and chemo-photothermal combination therapy. |
| Source: Chinese Academy of Sciences | |
|
Subscribe to a free copy of one of our daily Nanowerk Newsletter Email Digests with a compilation of all of the day's news. |
