| Apr 25, 2024 |
Pacemaker capacitor breakthrough promises 300+ years of life-saving power
(Nanowerk News) Pacemakers are medical devices that make sure that someone's heart beats the way it should. If the heart rhythm is off, the pacemaker delivers a surge of electricity to bring the heart back into rhythm. The pacemaker takes effort into account and delivers faster pulses when needed. For example, when you’re exercising. For these electric pulses, the pacemaker needs a capacitor to rapidly charge and discharge. This provides a high enough electric charge to reset the heart.
|
Billions of charges
|
|
Researcher Minh Duc Nguyen and his colleagues worked on a new design strategy for these capacitors to improve their energy storage, decrease the amount of energy lost every time it is charged or discharged, and increase the number of times they can reliably charge and discharge.
|
|
“It needs to keep up with your heartbeat, so it should be able to charge and discharge up to billions of times. Otherwise, you’ll have to replace the pacemaker every few months”, explains Nguyen.
|
Efficient capacitor
|
|
Nguyen and his team work on a type of capacitor that uses multiple thin layers of different materials. By adding layers they were able to increase the efficiency to over 90%. This means it loses less than 10% of the electric charge used for charging. That is two times less energy loss compared to the usual designs. It functions in a wide temperature range of 25–200 °C and can charge and discharge up to 10 billion times. Enough to do it once every second for over 300 years.
|
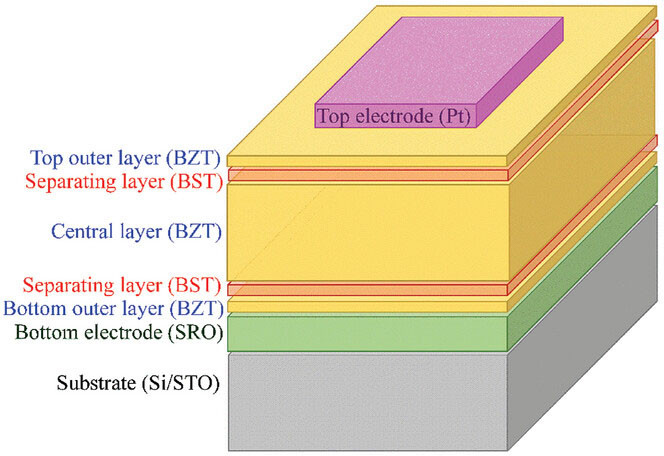 |
| Design of multilayer capacitor according to design rules for optimizing the breakdown field and energy storage capacity in the BZT/BST multilayer system. (Image: Reprinted from DOI:10.1002/adma.202402070, CC BY)
|
Design optimisation rules
|
|
The researchers deduced design optimisation rules for the combination of materials they used. “These rules are expected also to be useful for optimizing other multilayer systems and are therefore very relevant for further increasing the energy storage density of capacitors”, they write in their publication. Paving the way for even better capacitors.
|
|
The research published in Advanced Materials ("Towards Design Rules for Multilayer Ferroelectric Energy Storage Capacitors – A Study Based on Lead-Free and Relaxor-Ferroelectric/Paraelectric Multilayer Devices").
|

