| Jun 30, 2011 |
Dust-size dragonflies and microvalves make mark at annual MEMS student design contest
|
|
(Nanowerk News) A dragonfly as small as a dust mote, its four tiny wings beating like it had momentarily alit on a lily pad, and a highly sensitive microvalve were the big winners in this year's student design contest for extraordinarily tiny devices at Sandia National Laboratories.
|
|
The winners — Texas Tech University for the novel insect and Carnegie Mellon University for the valve — were announced at a recent Sandia awards ceremony.
|
|
There, student researchers presented their microelectromechanical system (MEMS) designs to the scrutiny of Sandia engineers. Sandia will fabricate all students' design submissions using Sandia's advanced fabrication process (called SUMMiT V™). The procedure makes MEMS devices with five levels of polysilicon (the most of any standard process), and is especially well-suited for making the complex mechanisms dreamed up by student contestants.
|
 |
| Texas Tech students won in the novel design category for their MEMS-based dragonfly design.
|
|
Other institutions competing at the annual event included the universities of Oklahoma and Utah, and the Air Force Institute of Technology.
|
|
The dragonfly opens new possibilities in the design of aerial surveillance devices, which have many uses, from quantifying the radiation leaking from damaged Japanese nuclear reactors to delineating enemy positions. Components in state-of-the-art micro air machines range from 15 cm to slightly less than 1 cm. The insect-inspired device is smaller, with biologically mimetic wings approximately 0.5 millimeters long (about the width of five human hairs) and 0.1 mm wide. It is intended to generate aerodynamic lift and thrust by flapping its wings instead of a motor-driven propeller or jet thrust. Flapping is achieved when small intermittent electric currents cause thermal expansion and contraction in the wings. Clever engineering uses the wing material's response to create strokes that are more aerodynamic and hence more efficient.
|
|
"Among the countless insect species able to fly, we chose the dragonfly because it flaps its wings in the vertical direction, rather than back-and-forth or in a rotary motion," said Texas Tech student Sahil Oak. "The vertical motion of the large wings in our design not only provides greater surface area for lift than most flying insects but the wings cool faster, enabling faster flapping."
|
|
The work was supervised by TTU faculty advisor Tim Dallas.
|
|
CMU Education design
|
|
Carnegie Mellon student design for a MEMS-based electrostatically operated microvalve won in the educational category. (Image courtesy of Carnegie Mellon University) Click on the thumbnail for a high-resolution image.
|
|
Valves are the largely under appreciated method by which advanced technical societies control the flow of fluids. Commonly, their motions are screw-based like a shower, kitchen sink or garden hose bib, or they are switch-based, using a ball and flapper valves like most toilets, heart valve prostheses and ink-jet printers. The winning project from Carnegie Mellon featured a micro-switch-based valve that makes possible very fine control over tiny amounts of liquid flow. This valve requires only picoJoules of energy to switch its state. The test module the students designed will help determine characteristics that would create the most efficient and lowest leakage microvalves on Earth. They ultimately may enable the creation of tiny, flow-through microvalves for experiments in biological research laboratories and in medical facilities seeking to quickly analyze a patient's medical state from tiny fluid samples.
|
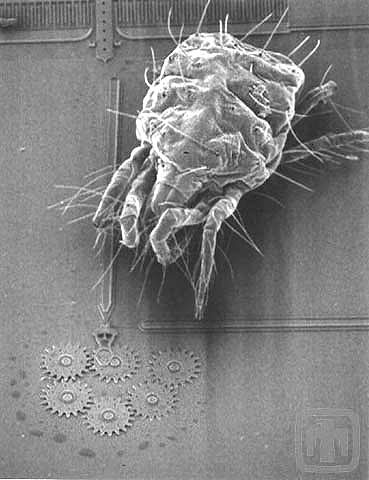 |
| A gear chain with a mite approaching.
|
|
"One of the most common types of microvalves is electrostatically operated, which is the model for our design," says Carnegie Mellon student research lead Vitali Brand. "The best microvalves are useful in certain fuel cell designs and in microengines because they can close or open in less than one-thousandth of a second and function against heavy pressures without leaking."
|
|
CMU professorial oversight was provided by Maarten de Boer.
|
|
The student contest, open to institutional members of the Sandia-led MEMS University Alliance program, provides an arena for the nation's student engineers to hone their skills in designing and using microdevices. Such devices are used to probe biological cells, arrange and operate components of telecommunications and high-tech machinery, operate many home devices and strengthen national security.
|
|
The MEMS University Alliance is part of Sandia's outreach to universities to improve engineering education. It is open to any US institution of higher learning, and most recently has extended an invitation to select Mexican universities to help that country develop its technological base.
|
|
The alliance provides classroom teaching materials and licenses for Sandia's special SUMMiT V™ design tools at a reasonable cost, so universities that lack fabrication facilities can develop a curriculum in MEMS. The design competition is growing within the University Alliance, which now has more than 20 members.
|
|
The entire contest process takes almost nine months. It starts with students developing ideas for a device, followed by creation of an accurate computer model of a design that might work, analysis of the design and, finally, design submission. Sandia's MEMS experts and university professors review the design and determine the winners.
|
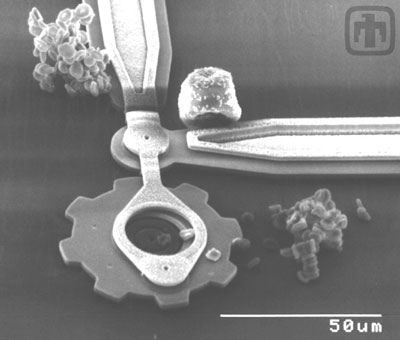 |
| Drive gear chain and linkages, with a grain of pollen (top right) and coagulated red blood cells (lower right, top left) to demonstrate scale.
|
|
Sandia's state-of-the-art MESA fabrication facility then creates parts for each of the entrants. The design competition capitalizes on Sandia's confidence in achieving first-pass fabrication success, which restricts the entire process to a reasonable student timeframe.
|
|
Fabricated parts are shipped back to the university students for lengthy tests to determine whether the final product matches the purpose of the original computer simulation.
|
|
The University Alliance coordinates with the Sandia-led National Institute for Nano Engineering (NINE), providing additional opportunities for students to self-direct their engineering education, and the Sandia/Los Alamos Center for Integrated Nanotechnologies (CINT), a DOE Office of Science center with the most up-to-date nanotechnology tools.
|
|
Travel by 26 students and five professors to the awards ceremony was made possible by grants from SPIE.
|



