| Posted: February 25, 2009 |
'Silver nanoparticle' microscope may shed new light on cancer, bone diseases |
|
(Nanowerk News) In a finding that could help speed the understanding of diseases ranging from cancer to osteoporosis, researchers in Utah are reporting development of a new microscope technique that uses “silver nanoparticle” mirrors to reveal hidden details inside bones, cancer cells, and other biological structures.
|
|
The method also can help identify structural damage in a wide variety of materials, including carbon-fiber plastics used in airplanes, the researchers say. Their study is scheduled for the March issue of ACS’ Nano Letters (Toward Subdiffraction Transmission Microscopy of Diffuse Materials with Silver Nanoparticle White-Light Beacons).
|
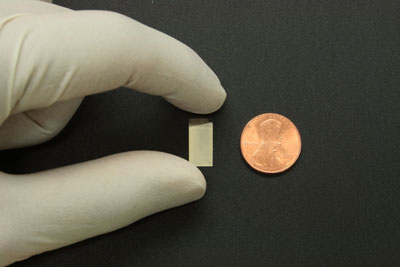 |
| A silver nanoparticle mirror shown next to a penny for scale. The new mirror could be used in microscopes to reveal hidden details inside bones, cancer cells, and other structures. (Image: John Lupton, University of Utah)
|
|
In the new study, John Lupton and colleagues point out that one of the most powerful, widely used tools for imaging hidden biological structures is fluorescence microscopy, which requires the specimen to be treated with fluorescent dyes or stains. But the dyes used to visualize the structures can kill living cells, limiting the effectiveness of the technique, the researchers note.
|
|
The scientists improved on this technique by using an infrared laser to excite clusters of silver nanoparticles, each about 1/5000th the width of a human hair, placed below the material being studied. The particles focus intense beams of light up through the sample to reveal information about the composition and structure of the substance examined, the scientists say. In laboratory studies, they used the new technique to view the iridescent green scales of the so-called “photonic beetle,” whose scales may provide clues to designing new, more powerful solar cells and computer chips, the scientists say."
|

