| Jan 25, 2023 |
Online tool can help researchers synthesize millions of molecules
|
|
(Nanowerk News) Enzymes are substances that cause chemical reactions. Certain types of enzymes, such as polyketide synthases and nonribosomal peptide synthetases, have the ability to shuffle their parts, allowing them to produce new chemicals. If scientists can understand how these enzymes shuffle their parts, they can understand how to use them to synthesize millions of molecules, such as pharmaceuticals and biofuels. However, engineering these enzymes is difficult because scientists don’t fully understand how they work.
|
|
In this study (Nucleic Acids Research, "ClusterCAD 2.0: an updated computational platform for chimeric type I polyketide synthase and nonribosomal peptide synthetase design"), researchers describe the improvements they made to an online tool, ClusterCAD, that helps scientists design and test engineered variants of enzymes.
|
|
Engineering these key enzymes to produce chemicals has become a major focus in synthetic biology. ClusterCAD is the only available tool that helps researchers design these enzymes for synthetic biology applications. Researchers made new improvements to the tool, including an expanded database, powerful search tools, and helpful new features within the interface. These updates will expand the types of chemicals that scientists can access with enzymes engineered by ClusterCAD.
|
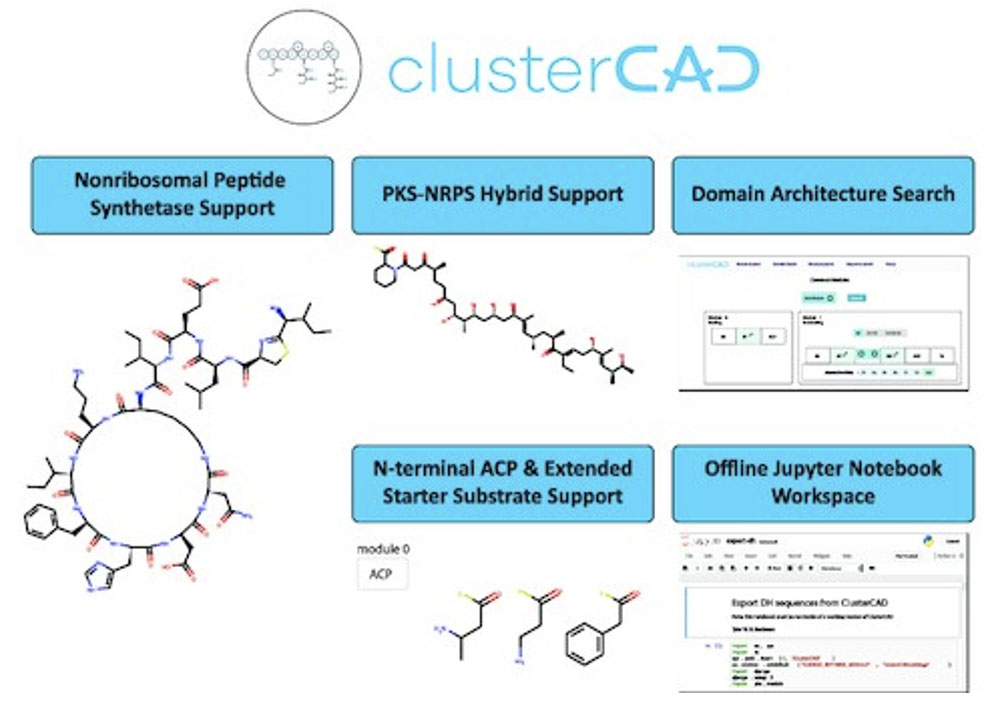 |
| New features in ClusterCAD 2.0 include support for Non-Ribosomal Peptide Synthetases (NRPSs), PKS-NRPS hybrids, a new Domain Architecture search tool, expanded PKS starters, and a Jupyter notebook system for programmatic access. (Image: Xavier Tao, University of California, Berkeley) (click on image to enlarge)
|
|
Researchers made several improvements to the existing ClusterCAD tool. ClusterCAD is a free online platform that simplifies the process of designing and testing engineered enzyme variants for synthetic biology applications. The tool allows users to browse polyketide synthase (PKS) and nonribosomal peptide synthetase (NRPS) gene clusters, which are groups of genes that encode pathways that can produce chemicals.
|
|
With this update, users can now design NRPS clusters within the platform. The researchers also expanded the platform’s database of clusters to be more comprehensive and informative. Other updates provide users with more high-quality clusters available for study, expanded starting points for PKS and NRPS engineering, and improved database versatility and search tools. These updates allow users to explore more chemicals that can be produced through PKS and NRPS engineering.
|

