| Sep 26, 2013 |
InfraStructs - embedding information tags inside 3D printed objects (w/video)
|
|
(Nanowerk News) How can the physical objects of tomorrow be embedded with information? As digital fabrication technologies, such as 3D printing, rapidly scale and expand – how do these objects become readable and interactive in the digital world?
|
|
InfraStructs, are material-based passive tags that embed machine-readable information inside digitally fabricated objects for imaging in the Terahertz region. Terahertz imaging can safely penetrate many common materials, opening up new possibilities for encoding hidden information as part of the fabrication process.
|
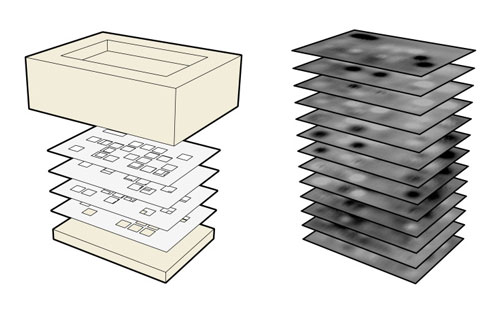 |
| InfraStructs create a layered internal structure (left). The object interior is scanned to create a volumetric image that is decoded inti meaningful information (right).
|
|
Researchers from Carnegie Mellon University and Microsoft Research outline the design, fabrication, imaging, and data processing steps to fabricate information inside physical objects ("InfraStructs: Fabricating Information Inside Physical Objects for Imaging in the Terahertz Region"; pdf).
|
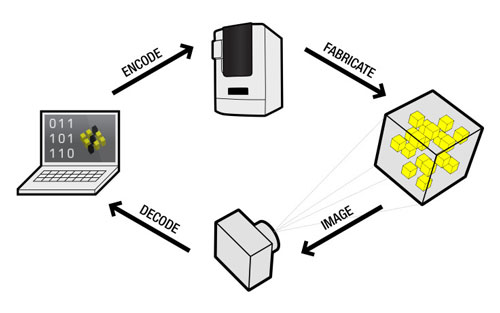 |
| InfraStructs are created by (left) encoding information into a digital model that is then (top) fabricated with material transitions inside a physical object. The object’s internal volume is (right) imaged in the THz region and (bottom) decoded into meaningful information.
|
|
In their paper, they present prototype tag designs for location encoding, pose estimation, object identification, data storage, and authentication.
|
|
They also provide detailed analysis of the constraints and performance considerations for designing InfraStruct tags.
|
|
Future application scenarios range from production line inventory, to customized game accessories, to mobile robotics.
|
|
|


