| Feb 12, 2019 |
Moving artificial leaves out of the lab and into the air
|
|
(Nanowerk News) Artificial leaves mimic photosynthesis — the process whereby plants use water and carbon dioxide from the air to produce carbohydrates using energy from the sun. But even state-of-the-art artificial leaves, which hold promise in reducing carbon dioxide from the atmosphere, only work in the laboratory because they use pure, pressurized carbon dioxide from tanks.
|
|
But now, researchers from the University of Illinois at Chicago have proposed a design solution that could bring artificial leaves out of the lab and into the environment. Their improved leaf, which would use carbon dioxide — a potent greenhouse gas — from the air, would be at least 10 times more efficient than natural leaves at converting carbon dioxide to fuel.
|
|
Their findings are reported in the journal ACS Sustainable Chemistry & Engineering("Assessment of Artificial Photosynthetic Systems for Integrated Carbon Capture and Conversion").
|
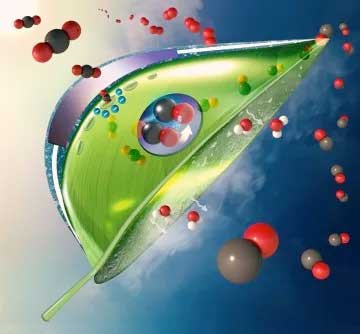 |
| An artificial, bio-inspired leaf. Carbon dioxide (red and black balls) enter the leaf as water (white and red balls) evaporates from the bottom of the leaf. An artificial photosystem (purple circle at the center of the leaf) made of a light absorber coated with catalysts converts carbon dioxide to carbon monoxide and converts water to oxygen (shown as double red balls) using sunlight. (Image: Meenesh Singh)
|
|
“So far, all designs for artificial leaves that have been tested in the lab use carbon dioxide from pressurized tanks. In order to implement successfully in the real world, these devices need to be able to draw carbon dioxide from much more dilute sources, such as air and flue gas, which is the gas given off by coal-burning power plants,” said Meenesh Singh, assistant professor of chemical engineering in the UIC College of Engineering and corresponding author on the paper.
|
|
Unhooking the pressurized carbon dioxide supply from these leaves means that they must have a way to collect and concentrate carbon dioxide from the air to drive their artificial photosynthetic reactions.
|
|
Singh and his colleague Aditya Prajapati, a graduate student in his lab, proposed solving this problem by encapsulating a traditional artificial leaf inside a transparent capsule made of a semi-permeable membrane of quaternary ammonium resin and filled with water. The membrane allows water from inside to evaporate out when warmed by sunlight. As water passes out through the membrane, it selectively pulls in carbon dioxide from the air.
|
|
The artificial photosynthetic unit inside the capsule is made up of a light absorber coated with catalysts that convert the carbon dioxide to carbon monoxide, which can be siphoned off and used as a basis for the creation of various synthetic fuels. Oxygen is also produced and can either be collected or released into the surrounding environment.
|
|
“By enveloping traditional artificial leaf technology inside this specialized membrane, the whole unit is able to function outside, like a natural leaf,” Singh said.
|
|
According to their calculations, 360 leaves, each 1.7 meters long and 0.2 meters wide, would produce close to a half-ton of carbon monoxide per day that could be used as the basis for synthetic fuels. Three hundred and sixty of these artificial leaves covering a 500-meter square area would be able to reduce carbon dioxide levels by 10 percent in the surrounding air within 100 meters of the array in one day.
|
|
“Our conceptual design uses readily available materials and technology, that when combined can produce an artificial leaf that is ready to be deployed outside the lab where it can play a significant role in reducing greenhouse gases in the atmosphere,” Singh said.
|

