| Dec 04, 2017 |
Astronomer's map reveals location of mysterious fast-moving gas
|
|
(Nanowerk News) An Australian scientist has created the most detailed map ever of clouds of high-velocity gas in the Universe around us.
|
|
The map covers the entire sky and shows curious clouds of neutral hydrogen gas that are moving at a different speed to the normal rotation of the Milky Way.
|
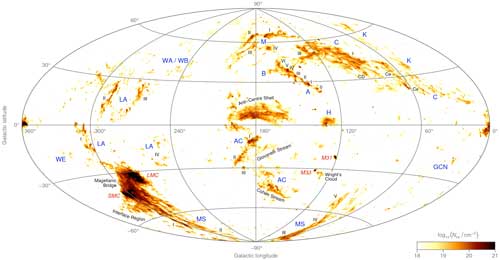 |
| An all-sky map showing the location and column density of neutral hydrogen gas belonging to the high-velocity clouds of the Milky Way and two neighbouring galaxies, the Large and Small Magellanic Clouds. (Image: ICRAR) (click on image to enlarge)
|
|
It was created by astronomer Dr Tobias Westmeier, from The University of Western Australia node of the International Centre for Radio Astronomy Research, and published today in the leading journal Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society.
|
|
Dr Westmeier said the map suggests that at least 13 per cent of the sky is covered by high-velocity clouds.
|
|
“These gas clouds are moving towards or away from us at speeds of up to a few hundred kilometres per second,” he said. “They are clearly separate objects.”
|
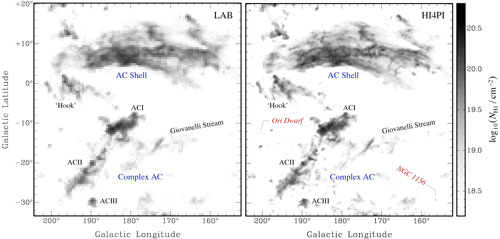 |
| A comparison of the high-velocity neutral hydrogen gas detected by the Leiden/Argentine/Bonn (LAB) survey and the new HI4PI survey for the same region of the sky, showing the great improvement in resolution and spatial sampling of the new map. (Image: ICRAR) (click on image to enlarge)
|
|
The map was compiled by taking a picture of the sky and masking out gas that is moving at the same pace as the Milky Way to show the location of gas travelling at a different speed.
|
|
The result is the most sensitive and highest resolution all-sky map of high-velocity clouds ever created.
|
|
It shows the gas in spectacular detail, revealing never before seen filaments, branches and clumps within the clouds.
|
|
“Starting to see all that structure within these high-velocity clouds is very exciting,” Dr Westmeier said.
|
|
“It’s something that wasn’t really visible in the past, and it could provide new clues about the origin of these clouds and the physical conditions within them.”
|
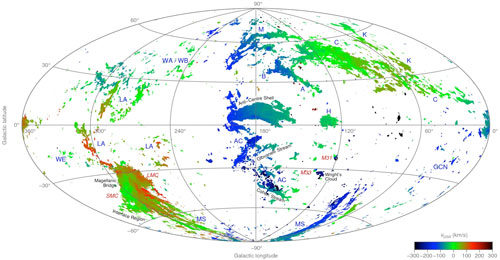 |
| An all-sky map showing the radial velocity of neutral hydrogen gas belonging to the high-velocity clouds of the Milky Way and two neighbouring galaxies, the Large and Small Magellanic Clouds. (Image: ICRAR) (click on image to enlarge)
|
|
The research used data from the HI4PI survey, a study of the entire sky released late last year. The survey combines observations from CSIRO’s Parkes Observatory in Australia and the Effelsberg 100m Radio Telescope operated by the Max-Planck Institute for Radio Astronomy in Germany.
|
|
Dr Westmeier said astronomers had proposed several hypotheses about where high-velocity clouds come from.
|
|
“We know for certain the origin of one of the long trails of gas, known as the Magellanic Stream, because it seems to be connected to the Large and Small Magellanic Clouds,” he said.
|
|
“But all the rest, the origin is unknown.”
|
|
Until about a decade ago, even the distances to high-velocity clouds had been a mystery, Dr Westmeier said.
|
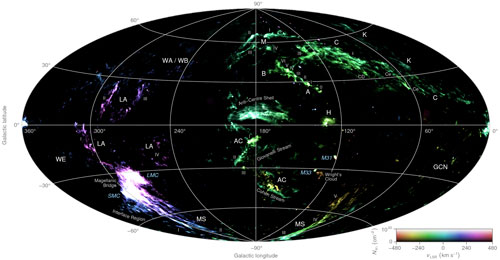 |
| A false-colour all-sky map combining the column density and radial velocity of high-velocity neutral hydrogen gas detected by the HI4PI survey. Brightness corresponds to column density and hue to radial velocity. (Image: ICRAR) (click on image to enlarge)
|
|
“We now know that the clouds are very close to the Milky Way, within about 30,000 light years of the disc,” he said. |
|
“That means it’s likely to either be gas that is falling into the Milky Way or outflows from the Milky Way itself.
|
|
“For example, if there is star formation or a supernova explosion it could push gas high above the disc.”
|
|
The map will be freely available to astronomers around the world, helping us to learn more about high-velocity clouds and the local Universe.
|
Original Publications
|
|
‘A new all-sky map of Galactic high-velocity clouds from the 21-cm HI4PI survey’, published in the Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society on December 4th, 2017. Available via http://www.icrar.org/gasclouds
|
|
HI4PI survey paper: ‘HI4PI: A full-sky HI survey based on EBHIS and GASS’, published in Astronomy & Astrophysics in October, 2016. Available via http://bit.ly/2nr5ybF
|

