| Jul 25, 2019 | |
Microwave dynamic therapy as a novel, effective cancer treatment |
|
| (Nanowerk Spotlight) Researchers at the Technical Institute of Physics and Chemistry, Chinese Academy of Sciences, have for the first time proposed a novel tumor treatment strategy for microwave dynamic therapy (MDT) to effectively treat cancers. This technique can promote the efficacy of dynamic treatment of deep tumors in clinical research and could have a broad range of applications. | |
| Photodynamic therapy (PDT), refers to the production of localized reactive oxygen species (ROS), which plays an important role in cancer treatment, to destroy cancer cells and inhibit tumor growth. | |
| PDT has spatiotemporal selectivity and local therapeutic effects, and it is a minimally invasive process with minimal systemic toxicity and relatively few side effects. Despite these advantages, the low penetration of photons limits PDT's effectiveness. | |
| Correspondingly, microwaves (MW) have deep tissue penetrating and fast heating ability, and are a promising energy source to trigger the ROS generation for tumor therapy. However, as far as we know, there have been no reports on the use of MDT in tumor therapy to date, because microwave energy is generally considered insufficient for inducing free radical generation. The reason is that the microwave has energy of only of 10-3 eV, which is too low to cleave chemical bonds. | |
| The Chinese research team found that liquid metal eutectic gallium-indium (EGaIn) supernanoparticles can generate ROS under MW irradiation. That makes them suitable as microwave sensitizers for revolutionizing the ROS generation techniques. | |
| To prepare the IL-LM-ZrO2 supernanoparticles, liquid metals of EGaIn alloy containing 75.5% Ga and 24.5% In by weight and ionic liquid (IL) are uniformly loaded into mesoporous ZrO2 nanoparticles. | |
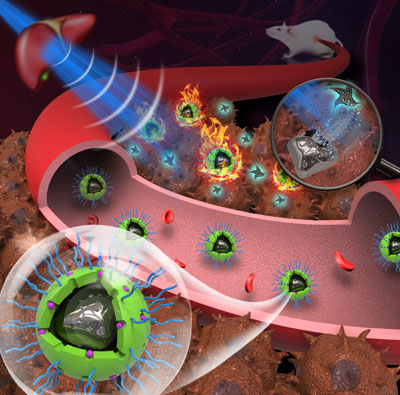 |
|
| Using microwave as sole energy source, combined microwave dynamic therapy (MDT) and microwave thermal therapy (MWTT) have been achieved simultaneously by dual-functional PEG-IL-LM-ZrO2 supernanoparticles for the first time in the subcutaneous tumor model and the orthotopic HCC mouse model. (Image: Technical Institute of Physics and Chemistry, Chinese Academy of Sciences) | |
| These findings are described in the journal Nano Letters ("Dual-Functional Supernanoparticles with Microwave Dynamic Therapy and Microwave Thermal Therapy"). | |
| The dual-functional PEG-IL-LM-ZrO2 supernanoparticles were designed with uniform size and good colloidal stability, realizing highly effective MDT and MWTT simultaneously for the first time by using microwave as sole energy source. Liquid metals play a crucial role in ROS generation and inducing apoptosis of tumor cells under microwave irradiation. | |
| The electron spin resonance spectrum manifested that IL-LM-ZrO2 supernanoparticles mainly produced ·OH and ·O2 under microwave irradiation in solution. | |
| Under the combined treatment of MDT and MWTT, the tumor inhibition rate for mice is as high as 92.2 ± 6.8% in the subcutaneous tumor models. Remarkable, 40% of the tumor-bearing mice were completely cured in the orthotopic HCC mouse models. | |
| The supernanoparticles current strategy can effectively realize the combined treatment of MWTT and MDT without additive of H2O2, which paves a new route for the development of tumor treatment in the future. | |
| Dr. Xianwei Meng who led the research team said: "This work opens the door of MDT and lays a foundation for clinical minimally invasive MDT and MWTT treatment. This microwave dynamic effect could improve the efficacy of dynamic treatment to deep-seated tumor in clinical studies." | |
|
Provided by Technical Institute of Physics and Chemistry, Chinese Academy of Sciences
as a Nanowerk exclusive
|
|
|
Become a Spotlight guest author! Join our large and growing group of guest contributors. Have you just published a scientific paper or have other exciting developments to share with the nanotechnology community? Here is how to publish on nanowerk.com. |
|
