Nanocubes simplify printing and imaging in color and infrared
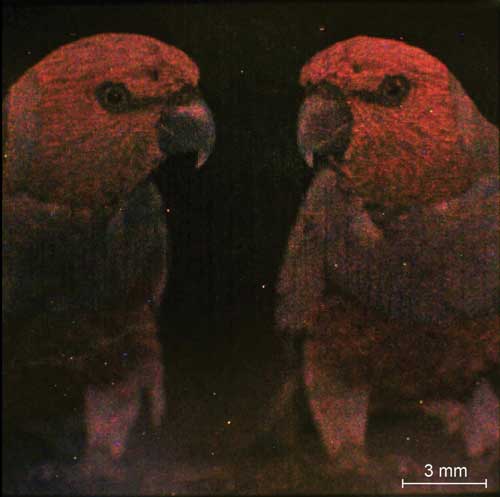 New technology allows multispectral reactions on a single chip.
New technology allows multispectral reactions on a single chip.
Dec 14th, 2016
Read more
 New technology allows multispectral reactions on a single chip.
New technology allows multispectral reactions on a single chip.
Dec 14th, 2016
Read more Researchers have been able to generate multifunctional RNA nanoparticles that could overcome treatment resistance in breast cancer, potentially making existing treatments more effective in these patients.
Researchers have been able to generate multifunctional RNA nanoparticles that could overcome treatment resistance in breast cancer, potentially making existing treatments more effective in these patients.
Dec 14th, 2016
Read more When most living creatures get hurt, they can self-heal and recover from the injury. But, when damage occurs to inanimate objects, they don't have that same ability and typically either lose functionality or have their useful lifecycle reduced. Researchers are working to change that.
When most living creatures get hurt, they can self-heal and recover from the injury. But, when damage occurs to inanimate objects, they don't have that same ability and typically either lose functionality or have their useful lifecycle reduced. Researchers are working to change that.
Dec 14th, 2016
Read more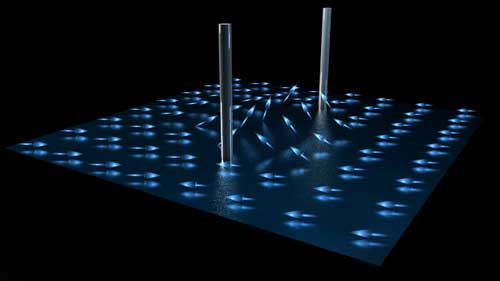 Scientists have discovered half-quantum vortices in superfluid helium. This vortex is a topological defect, exhibited in superfluids and superconductors, which carries a fixed amount of circulating current.
Scientists have discovered half-quantum vortices in superfluid helium. This vortex is a topological defect, exhibited in superfluids and superconductors, which carries a fixed amount of circulating current.
Dec 14th, 2016
Read more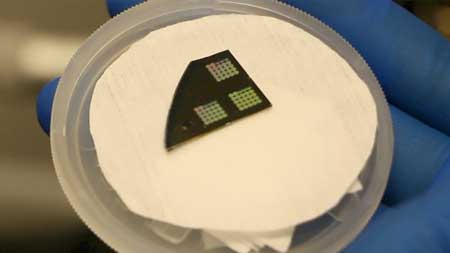 During the international IEDM 2016 conference, researchers showcased a range of concepts and technologies that foreshadow the future of the semiconductor industry.
During the international IEDM 2016 conference, researchers showcased a range of concepts and technologies that foreshadow the future of the semiconductor industry.
Dec 14th, 2016
Read more Our bodies contain Natural Killer (cells - an army that stops cancers and viruses before they can make us sick. A researcher has created a nanoparticle that increases the number of these killers 10,000-fold in the lab and her new technology has generated a licensing agreement that is expected to accelerate the therapy's path to clinical trials.
Our bodies contain Natural Killer (cells - an army that stops cancers and viruses before they can make us sick. A researcher has created a nanoparticle that increases the number of these killers 10,000-fold in the lab and her new technology has generated a licensing agreement that is expected to accelerate the therapy's path to clinical trials.
Dec 14th, 2016
Read more The method, which is at the proof of concept stage, consists of a simple imaging technique and an innovative material to coat the prostheses.
The method, which is at the proof of concept stage, consists of a simple imaging technique and an innovative material to coat the prostheses.
Dec 14th, 2016
Read more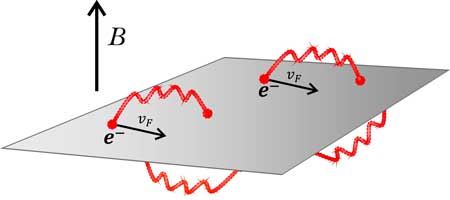 Collective electron interaction, mediated by photons across space-time under a weak magnetic field, explains the special conductivity of the one-atom-thick material.
Collective electron interaction, mediated by photons across space-time under a weak magnetic field, explains the special conductivity of the one-atom-thick material.
Dec 14th, 2016
Read more A newly funded project plans to gain new insights into the catalytic abilities of nanoparticles, particularly how the size, shape and chemical state of the particles change during a catalytic reaction.
A newly funded project plans to gain new insights into the catalytic abilities of nanoparticles, particularly how the size, shape and chemical state of the particles change during a catalytic reaction.
Dec 14th, 2016
Read more A team of engineers has developed a new method for creating entire device arrays directly on the copper substrates used for the commercial manufacture of graphene. Complete and fully-functional devices can then be transferred to a substrate of choice, such as silicon, plastics or even textiles.
A team of engineers has developed a new method for creating entire device arrays directly on the copper substrates used for the commercial manufacture of graphene. Complete and fully-functional devices can then be transferred to a substrate of choice, such as silicon, plastics or even textiles.
Dec 14th, 2016
Read more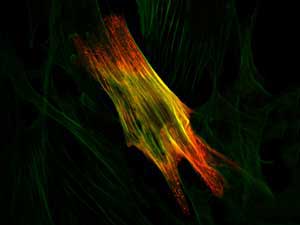 Modeling the fluorescence enhancing capabilities of materials paves the way for more sensitive biological and chemical tracking technologies.
Modeling the fluorescence enhancing capabilities of materials paves the way for more sensitive biological and chemical tracking technologies.
Dec 14th, 2016
Read more A team of researchers has developed a novel method for trapping potentially harmful gases within microscopic organo-metallic structures.
A team of researchers has developed a novel method for trapping potentially harmful gases within microscopic organo-metallic structures.
Dec 14th, 2016
Read more Researchers have developed a new ultrafast X-ray technique which could revolutionise our understanding of structure and function at the atomic and molecular level.
Researchers have developed a new ultrafast X-ray technique which could revolutionise our understanding of structure and function at the atomic and molecular level.
Dec 13th, 2016
Read more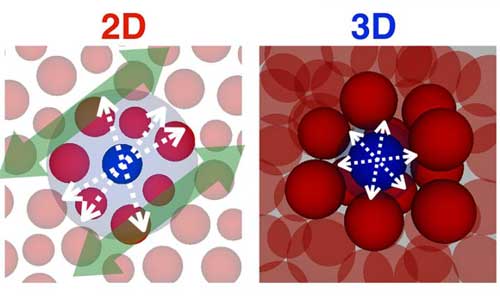 Scientists have found that the thermal motion of 2-D glass grows infinitely, which might possibly alter the mechanism of glass transition in low dimensions.
Scientists have found that the thermal motion of 2-D glass grows infinitely, which might possibly alter the mechanism of glass transition in low dimensions.
Dec 13th, 2016
Read more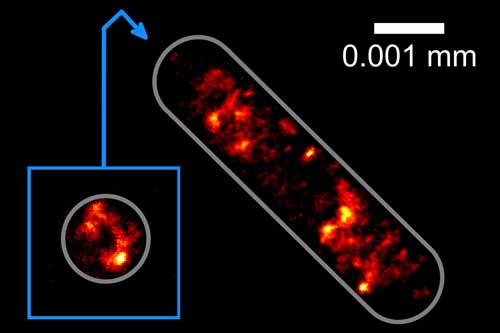 The new method enables researchers to take cells that cannot be anchored on surfaces and then use an optical trap to study them at a very high resolution.
The new method enables researchers to take cells that cannot be anchored on surfaces and then use an optical trap to study them at a very high resolution.
Dec 13th, 2016
Read more Scientists have developed a new type anode material that would be used in place of a conventional graphite anode, which they claim will lead to lighter and longer-lasting batteries for everything from personal devices to electric vehicles.
Scientists have developed a new type anode material that would be used in place of a conventional graphite anode, which they claim will lead to lighter and longer-lasting batteries for everything from personal devices to electric vehicles.
Dec 13th, 2016
Read more