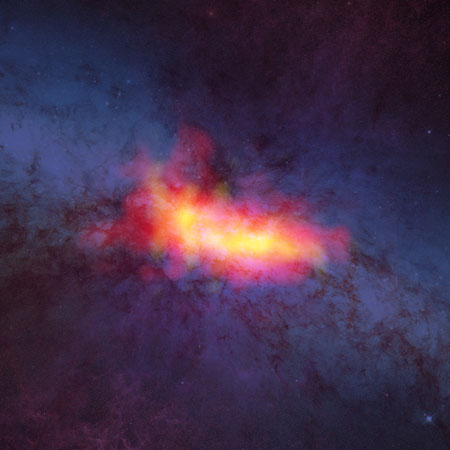
 Using the new, high-frequency capabilities of the National Science Foundation's Robert C. Byrd Green Bank Telescope, astronomers have captured never-before-seen details of the nearby starburst galaxy M82. These new data highlight streamers of material fleeing the disk of the galaxy as well as concentrations of dense molecular gas surrounding pockets of intense star formation.
Using the new, high-frequency capabilities of the National Science Foundation's Robert C. Byrd Green Bank Telescope, astronomers have captured never-before-seen details of the nearby starburst galaxy M82. These new data highlight streamers of material fleeing the disk of the galaxy as well as concentrations of dense molecular gas surrounding pockets of intense star formation.
Dec 9th, 2013
Read more
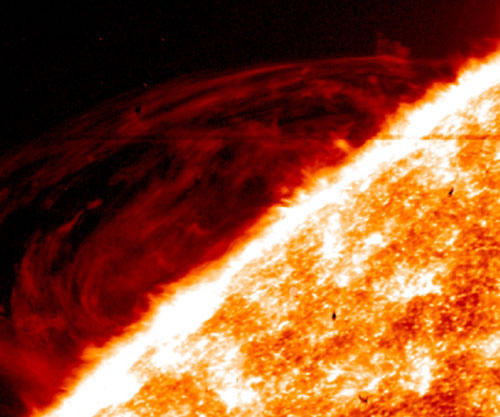 The region located between the surface of the sun and its atmosphere has been revealed as a more violent place than previously understood, according to images and data from NASA's newest solar observatory, the Interface Region Imaging Spectrograph, or IRIS.
The region located between the surface of the sun and its atmosphere has been revealed as a more violent place than previously understood, according to images and data from NASA's newest solar observatory, the Interface Region Imaging Spectrograph, or IRIS.
Dec 9th, 2013
Read more
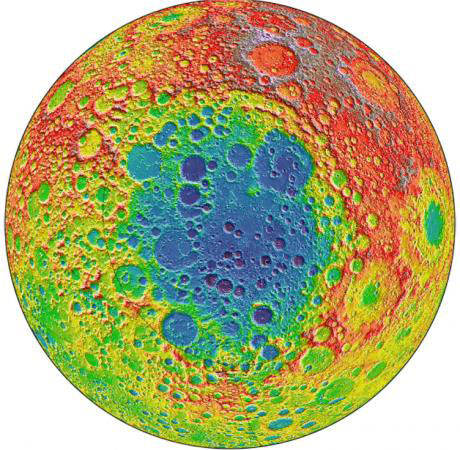 A massive impact on the Moon about 4 billion years ago left a 2,500-mile crater, among the largest known craters in the solar system. Smaller subsequent impacts left craters within that crater. Comparing the spectra of light reflected from the peaks of those craters may yield clues to the composition of the Moon's lower crust and mantle - and would have implications for models of how the Moon formed.
A massive impact on the Moon about 4 billion years ago left a 2,500-mile crater, among the largest known craters in the solar system. Smaller subsequent impacts left craters within that crater. Comparing the spectra of light reflected from the peaks of those craters may yield clues to the composition of the Moon's lower crust and mantle - and would have implications for models of how the Moon formed.
Dec 9th, 2013
Read more
A spacecraft at near-Earth orbit is continuously bombarded by charged particles. Finnish Meteorological Institute has developed a unique model that simulates electron environment in the near-Earth space.
Dec 9th, 2013
Read more
 Planetary instruments from NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Md., hit the trifecta on Dec. 4, running three experiments of the same kind at different places in space.
Planetary instruments from NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Md., hit the trifecta on Dec. 4, running three experiments of the same kind at different places in space.
Dec 6th, 2013
Read more
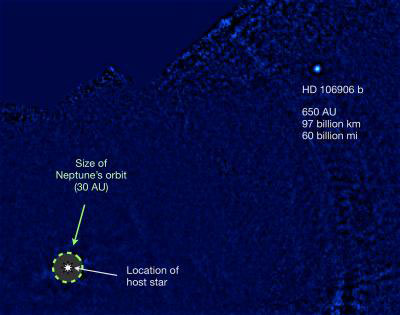 An international team of astronomers, led by a University of Arizona graduate student, has discovered the most distantly orbiting planet found to date around a single, sun-like star. Weighing in at 11 times Jupiter's mass and orbiting its star at 650 times the average Earth-Sun distance, planet HD 106906 b is unlike anything in our own Solar System and defies current planet formation theories.
An international team of astronomers, led by a University of Arizona graduate student, has discovered the most distantly orbiting planet found to date around a single, sun-like star. Weighing in at 11 times Jupiter's mass and orbiting its star at 650 times the average Earth-Sun distance, planet HD 106906 b is unlike anything in our own Solar System and defies current planet formation theories.
Dec 5th, 2013
Read more
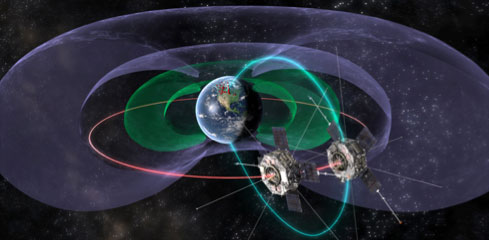 By analyzing data from NASA's Van Allen probes, U of A physicist Ian Mann and colleagues at NASA and other institutes, have been able to measure and identify the 'smoking gun' of a planetary scale process that accelerates particles to speeds close to the speed of light within the Van Allen radiation belt.
By analyzing data from NASA's Van Allen probes, U of A physicist Ian Mann and colleagues at NASA and other institutes, have been able to measure and identify the 'smoking gun' of a planetary scale process that accelerates particles to speeds close to the speed of light within the Van Allen radiation belt.
Dec 5th, 2013
Read more
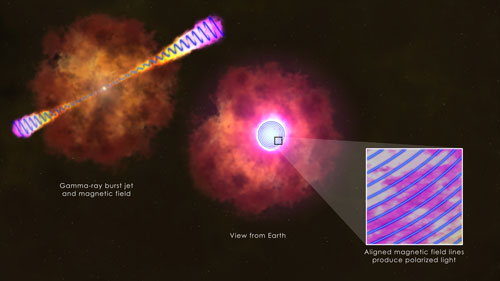 A new study using observations from a novel instrument provides the best look to date at magnetic fields at the heart of gamma-ray bursts, the most energetic explosions in the universe. An international team of astronomers from Britain, Slovenia and Italy has glimpsed the infrastructure of a burst's high-speed jet.
A new study using observations from a novel instrument provides the best look to date at magnetic fields at the heart of gamma-ray bursts, the most energetic explosions in the universe. An international team of astronomers from Britain, Slovenia and Italy has glimpsed the infrastructure of a burst's high-speed jet.
Dec 4th, 2013
Read more
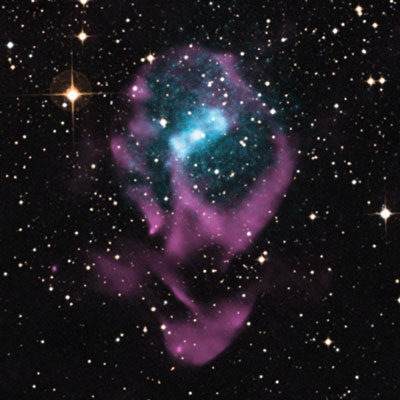 X-rays streaming toward Earth from the region near a neutron star that is cannibalizing its companion star have revealed the pair to be the youngest "X-ray binary" yet known. The discovery, by a team that includes a Penn State astronomer, also solves a long-unsolved mystery about this record-breaking object, named Circinus X-1.
X-rays streaming toward Earth from the region near a neutron star that is cannibalizing its companion star have revealed the pair to be the youngest "X-ray binary" yet known. The discovery, by a team that includes a Penn State astronomer, also solves a long-unsolved mystery about this record-breaking object, named Circinus X-1.
Dec 4th, 2013
Read more
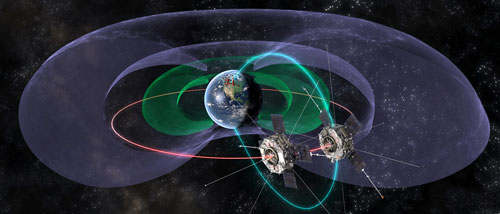 Just over a year since launch, NASA's Van Allen Probes mission continues to unravel longstanding mysteries of Earth's high-energy radiation belts that encircle our planet and pose hazards to orbiting satellites and astronauts.
Just over a year since launch, NASA's Van Allen Probes mission continues to unravel longstanding mysteries of Earth's high-energy radiation belts that encircle our planet and pose hazards to orbiting satellites and astronauts.
Dec 4th, 2013
Read more
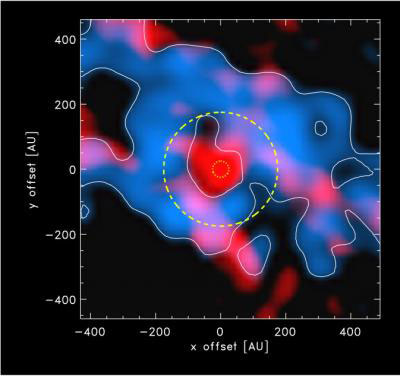 A star is formed when a large cloud of gas and dust condenses and eventually becomes so dense that it collapses into a ball of gas, where the pressure heats the matter, creating a glowing gas ball - a star is born. New research from the Niels Bohr Institute, among others, shows that a young, newly formed star in the Milky Way had such an explosive growth, that it was initially about 100 times brighter than it is now.
A star is formed when a large cloud of gas and dust condenses and eventually becomes so dense that it collapses into a ball of gas, where the pressure heats the matter, creating a glowing gas ball - a star is born. New research from the Niels Bohr Institute, among others, shows that a young, newly formed star in the Milky Way had such an explosive growth, that it was initially about 100 times brighter than it is now.
Dec 4th, 2013
Read more
 In a finding of relevance to the search for life in our solar system, researchers have shown the subsurface ocean on Jupiter's moon Europa may have deep currents and circulation patterns with heat and energy transfers capable of sustaining biological life. The findings, summarized in this week's online edition of Nature Geosciences, are based on numerical models accounting for the formation of the chaos terrains, one of Europa's most prominent surface features.
In a finding of relevance to the search for life in our solar system, researchers have shown the subsurface ocean on Jupiter's moon Europa may have deep currents and circulation patterns with heat and energy transfers capable of sustaining biological life. The findings, summarized in this week's online edition of Nature Geosciences, are based on numerical models accounting for the formation of the chaos terrains, one of Europa's most prominent surface features.
Dec 3rd, 2013
Read more
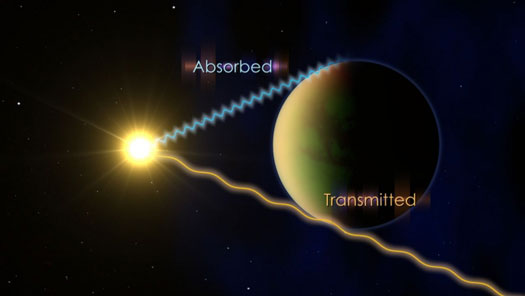 Using the powerful eye of NASA's Hubble Space Telescope, two teams of scientists have found faint signatures of water in the atmospheres of five distant planets. The presence of atmospheric water was reported previously on a few exoplanets orbiting stars beyond our solar system, but this is the first study to conclusively measure and compare the profiles and intensities of these signatures on multiple worlds.
Using the powerful eye of NASA's Hubble Space Telescope, two teams of scientists have found faint signatures of water in the atmospheres of five distant planets. The presence of atmospheric water was reported previously on a few exoplanets orbiting stars beyond our solar system, but this is the first study to conclusively measure and compare the profiles and intensities of these signatures on multiple worlds.
Dec 3rd, 2013
Read more
 The ALHAMBRA project has identified and classified more than half a million galaxies, after seven years of close observation of the universe from the Observatory of Calar Alto and thanks to a technique that breaks the stars energy in their colours through astronomical filters.
The ALHAMBRA project has identified and classified more than half a million galaxies, after seven years of close observation of the universe from the Observatory of Calar Alto and thanks to a technique that breaks the stars energy in their colours through astronomical filters.
Dec 2nd, 2013
Read more
 China launched the Chang'e-3 lunar probe with the country's first moon rover aboard early on Monday, marking a significant step toward deep space exploration.
China launched the Chang'e-3 lunar probe with the country's first moon rover aboard early on Monday, marking a significant step toward deep space exploration.
Dec 2nd, 2013
Read more
Until now, scientists were pretty sure they knew how the surface of a neutron star - a super dense star that forms when a large star explodes and its core collapses into itself - can heat itself up. However, research by a team of scientists led by a Michigan State University physicist has researchers rethinking that.
Dec 1st, 2013
Read more
astroEDU is a platform that allows educators to discover, review, distribute, improve and remix astronomy education activities, and offers a free peer-review service by professionals in education and science.
Nov 29th, 2013
Read more
The Milky Way Galaxy comprises hundreds of billions stars. An ambitious ESA project will map around a billion of these. The European funded GREAT network will train young researchers across Europe to help make sense of this wealth of data.
Nov 29th, 2013
Read more
 Using the new, high-frequency capabilities of the National Science Foundation's Robert C. Byrd Green Bank Telescope, astronomers have captured never-before-seen details of the nearby starburst galaxy M82. These new data highlight streamers of material fleeing the disk of the galaxy as well as concentrations of dense molecular gas surrounding pockets of intense star formation.
Using the new, high-frequency capabilities of the National Science Foundation's Robert C. Byrd Green Bank Telescope, astronomers have captured never-before-seen details of the nearby starburst galaxy M82. These new data highlight streamers of material fleeing the disk of the galaxy as well as concentrations of dense molecular gas surrounding pockets of intense star formation.
 Subscribe to our Space Exploration News feed
Subscribe to our Space Exploration News feed











