| Aug 30, 2017 |
Making 3-D printing safer
|
|
(Nanowerk News) Within the past decade, 3-D printers have gone from bulky, expensive curiosities to compact, more affordable consumer products. At the same time, concerns have emerged that nanoparticles released from the machines during use could affect consumers' health.
|
|
Now researchers report in ACS' Environmental Science & Technology ("Characterization and Control of Nanoparticle Emission during 3D Printing") a way to eliminate almost all nanoparticle emissions from some of these printers.
|
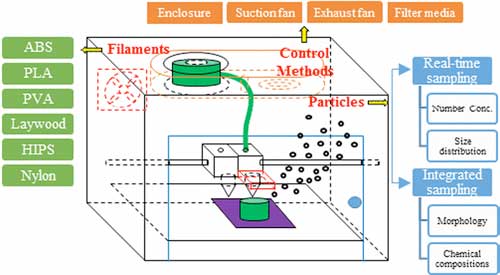 |
| This study aimed to evaluate particle emission characteristics and to evaluate several control methods used to reduce particle emissions during three-dimensional (3D) printing. Experiments for particle characterization were conducted to measure particle number concentrations, emission rates, morphology, and chemical compositions under manufacturer-recommended and consistent-temperature conditions with seven different thermoplastic materials in an exposure chamber. (© ACS)
|
|
Recent studies on 3-D printers have found that when operating, the devices can release volatile organic compounds, aldehydes and nanoparticles into the air. All of these substances have the potential to harm human health. But no research had been reported on strategies for preventing or reducing pollution from the machines.
|
|
So Chungsik Yoon and colleagues decided to focus on testing various approaches for controlling the devices' nanoparticle emissions.
|
|
For their study, the researchers worked with a 3-D printer based on fused-deposition modeling technology, the most commonly used process among commercially available models. They tested seven "inks" made out of thermoplastic materials under different temperatures.
|
|
Of these, high-impact polystyrene and nylon had the highest nanoparticle emission rates; polylactic acid had the lowest. Printing at the manufacturer-recommended temperatures resulted in fewer emissions than doing so at higher temperatures.
|
|
The researchers also analyzed eight methods for controlling pollution from the printers using varying combinations of fans, filters and enclosures. All of the designs removed at least 70 percent of nanoparticle emissions. The most efficient approach eliminated 99.95 percent of such pollution, and involved enclosing the printer and installing a high-efficiency particulate air (HEPA) filter.
|
|
Based on their results, the researchers recommend using low temperatures, low-emitting materials and enclosing 3-D printers with a HEPA or similar filter to reduce the release of nanoparticles.
|

