| Posted: Feb 24, 2015 |
The European nanotechnology roadmap for graphene
|
|
(Nanowerk News) In October 2013, academia and industry came together to form the Graphene Flagship. Now with 142 partners in 23 countries, and a growing number of associate members, the Graphene Flagship was established following a call from the European Commission to address big science and technology challenges of the day through long-term, multidisciplinary R&D efforts.
|
|
In a 200-page open-access paper published in the Royal Society of Chemistry journal Nanoscale ("Science and technology roadmap for graphene, related two-dimensional crystals, and hybrid systems"), more than 60 academics and industrialists lay out a science and technology roadmap for graphene, related two-dimensional crystals, other 2D materials, and hybrid systems based on a combination of different 2D crystals and other nanomaterials. The roadmap covers the next ten years and beyond, and its objective is to guide the research community and industry toward the development of products based on graphene and related materials.
|
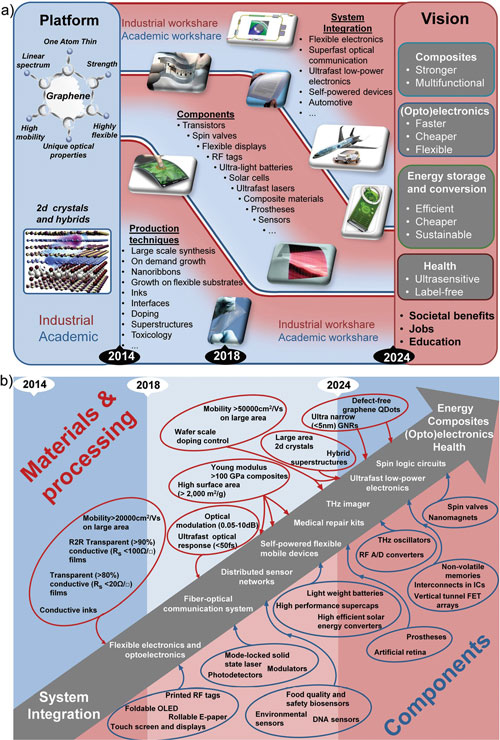 |
| The science and technology roadmaps follow a hierarchical structure where the strategic level in a) is connected to the more detailed roadmap shown in b). These general roadmaps are the condensed form of the topical roadmaps presented in the previous sections, and give technological targets for key applications to become commercially competitive and the forecasts for when the targets are predicted to be met. (click on image to enlarge)
|
|
Graphene - a two-dimensional material made up of sheets of carbon atoms - and related materials are expected to revolutionise the fields in which they are applied, and they have the potential to become the materials of the 21st century. They will supplement and at times replace existing substances in a range of applications. Two-dimensional materials shall in some cases be integrated into existing platforms in order to enhance them. For example, graphene could be integrated into silicon photonics, exploiting established technology for constructing integrated circuits.
|
|
The roadmap highlights three broad areas of activity. The first task is to identify new layered materials, assess their potential, and develop reliable, reproducible and safe means of producing them on an industrial scale. Identification of new device concepts enabled by 2D materials is also called for, along with the development of component technologies. The ultimate goal is to integrate components and structures based on 2D materials into systems capable of providing new functionalities and application areas.
|
|
Eleven science and technology themes are identified in the roadmap. These are: fundamental science, health and environment, production, electronic devices, spintronics, photonics and optoelectronics, sensors, flexible electronics, energy conversion and storage, composite materials, and biomedical devices. The roadmap addresses each of these areas in turn, with timelines.
|
|
Research areas outlined in the roadmap correspond broadly with current flagship work packages, with the addition of a work package devoted to the growing area of biomedical applications, to be included in the next phase of the flagship. A recent independent assessment has confirmed that the Graphene Flagship is firmly on course, with hundreds of research papers, numerous patents and marketable products to its name.
|
|
Roadmap timelines predict that, before the end of the ten-year period of the flagship, products will be close to market in the areas of flexible electronics, composites, and energy, as well as advanced prototypes of silicon-integrated photonic devices, sensors, high-speed electronics, and biomedical devices.
|
|
"This publication concludes a four-year effort to collect and coordinate state-of-the-art science and technology of graphene and related materials," says Andrea Ferrari, director of the Cambridge Graphene Centre, and chairman of the Executive Board of the Graphene Flagship. "We hope that this open-access roadmap will serve as the starting point for academia and industry in their efforts to take layered materials and composites from laboratory to market." Ferrari led the roadmap effort with Italian Institute of Technology physicist Francesco Bonaccorso, who is a Royal Society Newton Fellow of the University of Cambridge, and a Fellow of Hughes Hall.
|
|
"We are very proud of the joint effort of the many authors who have produced this roadmap," says Jari Kinaret, director of the Graphene Flagship. "The roadmap forms a solid foundation for the graphene community in Europe to plan its activities for the coming years. It is not a static document, but will evolve to reflect progress in the field, and new applications identified and pursued by industry."
|

