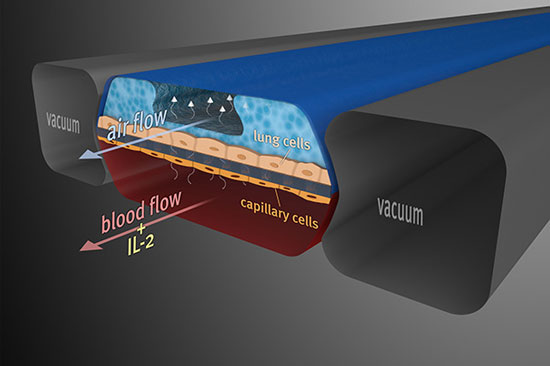
 Researchers at the Wyss Institute for Biologically Inspired Engineering at Harvard University have mimicked pulmonary edema in a microchip lined by living human cells. They used this "lung-on-a-chip" to study drug toxicity and identify potential new therapies to prevent this life-threatening condition.
Researchers at the Wyss Institute for Biologically Inspired Engineering at Harvard University have mimicked pulmonary edema in a microchip lined by living human cells. They used this "lung-on-a-chip" to study drug toxicity and identify potential new therapies to prevent this life-threatening condition.
Nov 15th, 2012
Read more
Insights into the genetic code of pigs that reveal how the species evolved could improve the health of animals in future.
Nov 14th, 2012
Read more
Based on a unique technology developed by A*STAR Singapore, these inventive and easy-to-use kits are versatile, effective and quick in the screening for modulators of protein-DNA interactions, as well as quality control (QC) analysis of transcription factor production.
Nov 14th, 2012
Read more
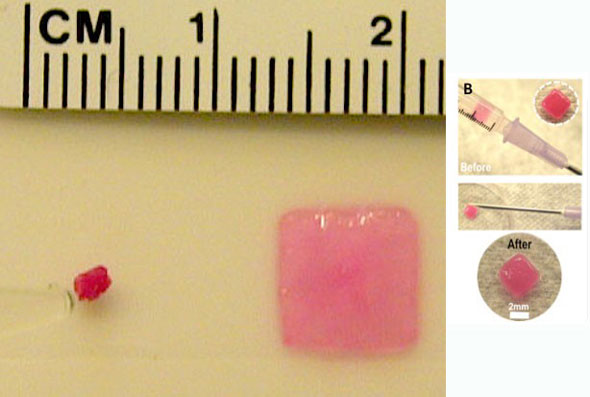 Bioengineers at Harvard have developed a gel-based sponge that can be molded to any shape, loaded with drugs or stem cells, compressed to a fraction of its size, and delivered via injection. Once inside the body, it pops back to its original shape and gradually releases its cargo, before safely degrading.
Bioengineers at Harvard have developed a gel-based sponge that can be molded to any shape, loaded with drugs or stem cells, compressed to a fraction of its size, and delivered via injection. Once inside the body, it pops back to its original shape and gradually releases its cargo, before safely degrading.
Nov 13th, 2012
Read more
International collaboration reveals timing mechanism in formation of vertebrae.
Nov 13th, 2012
Read more
 Researchers uncover how microorganisms on the ocean floor protect the atmosphere against methane.
Researchers uncover how microorganisms on the ocean floor protect the atmosphere against methane.
Nov 12th, 2012
Read more
In a move that could potentially revolutionise major UK industries and help us to meet serious social and environmental challenges, the Biotechnology and Biological Sciences Research Council (BBSRC) has announced an unprecedented GBP 20m worth of synthetic biology projects.
Nov 12th, 2012
Read more
 T�bingen and Berlin scientists investigate pathogens by help of solid-state nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy.
T�bingen and Berlin scientists investigate pathogens by help of solid-state nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy.
Nov 12th, 2012
Read more
Scientists studying the genes and proteins of human cells infected with a common cold virus have identified a new gene identification technique that could increase the genetic information we hold on animals by around 70 to 80 per cent. The findings could revolutionise our understanding of animal genetics and disease, and improve our knowledge of dangerous viruses such as SARS that jump the species barrier from animals to humans.
Nov 12th, 2012
Read more
Scientists at Stanford University have developed an intracellular remote control: a simple way to activate and track proteins, the busiest of cellular machines, using beams of light.
Nov 8th, 2012
Read more
 A phosphate switch to fine-tune the protein production in the cells.
A phosphate switch to fine-tune the protein production in the cells.
Nov 8th, 2012
Read more
 New antibiotic and anti-cancer chemicals may one day be synthesised using biotechnology, following CSIRO?s discovery of the three genes that combine to provide soldier beetles with their potent predator defence system.
New antibiotic and anti-cancer chemicals may one day be synthesised using biotechnology, following CSIRO?s discovery of the three genes that combine to provide soldier beetles with their potent predator defence system.
Nov 8th, 2012
Read more
 With the help of information technology (IT), Penn State professor Mark Guiltinan makes the world a sweeter place.
With the help of information technology (IT), Penn State professor Mark Guiltinan makes the world a sweeter place.
Nov 7th, 2012
Read more
 A new power-free microfluidic chip developed by researchers at the RIKEN Advanced Science Institute (ASI) enables detection of microRNA from extremely small sample volume in only 20 minutes. By drastically reducing the time and quantity of sample required for detection, the chip lays the groundwork for early-stage point-of-care diagnosis of diseases such as cancer and Alzheimer's.
A new power-free microfluidic chip developed by researchers at the RIKEN Advanced Science Institute (ASI) enables detection of microRNA from extremely small sample volume in only 20 minutes. By drastically reducing the time and quantity of sample required for detection, the chip lays the groundwork for early-stage point-of-care diagnosis of diseases such as cancer and Alzheimer's.
Nov 7th, 2012
Read more
 For the first time, researchers power an implantable electronic device using an electrical potential - a natural battery - deep in the inner ear.
For the first time, researchers power an implantable electronic device using an electrical potential - a natural battery - deep in the inner ear.
Nov 7th, 2012
Read more
The doctoral dissertation of Milja Veps�l�inen, M.Sc. (microbiology), prepared at the Finnish Environment Institute, involved developing a test pattern designed to measure soil biological diversity. The aim is to measure the activity potential of enzymes produced by soil microbes.
Nov 7th, 2012
Read more
A team of scientists researching the effect of long-term molecular evolution (the study of DNA, RNA and proteins) have produced findings which suggest most amino-acid substitutions have different fitness effects in different species. This is an important breakthrough as there is now evidence to show that a genetic background determines whether a modification, which is the main factor regulating evolution at the level of proteins, is beneficial, harmful or inconsequential.
Nov 6th, 2012
Read more
Scientists at the Universities of Liverpool and Glasgow have uncovered a possible new method of enhancing nerve repair in the treatment of spinal cord injuries.
Nov 5th, 2012
Read more
 Researchers at the Wyss Institute for Biologically Inspired Engineering at Harvard University have mimicked pulmonary edema in a microchip lined by living human cells. They used this "lung-on-a-chip" to study drug toxicity and identify potential new therapies to prevent this life-threatening condition.
Researchers at the Wyss Institute for Biologically Inspired Engineering at Harvard University have mimicked pulmonary edema in a microchip lined by living human cells. They used this "lung-on-a-chip" to study drug toxicity and identify potential new therapies to prevent this life-threatening condition.
 Subscribe to our Biotechnology News feed
Subscribe to our Biotechnology News feed






