What would it take to make a manned mission to Mars a reality? A team of aeronautical and textile engineering students from North Carolina State University believe part of the solution may lie in advanced textile materials. The students joined forces to tackle life-support challenges that the aerospace industry has been grappling with for decades.
May 31st, 2011
Read more
A new lightweight web service interface for accessing massive amounts of life science research data across multiple public and private domains has been developed by researchers at RIKEN, Japan's flagship research institute. Through the powerful RIKEN Scientists' Networking System (SciNetS), the service provides a secure, flexible and light weight interface to millions of data records and their network of semantic relationships, ushering in a new era of collaboration, analysis and information-sharing for life science research and applied innovation.
May 31st, 2011
Read more
David Kaplan and his team at Tufts University haveused genetic engineering techniques to produce a new material that combines the biocompatibility and toughness of silk with the anti-bacterial properties of silver.
May 31st, 2011
Read more
 Phoenicians will return from the Memorial Day weekend to witness installation of the first "Cool Pavement" parking lot in central downtown Phoenix. This 90,000-square-foot temporary parking lot located between First, Second, Taylor and Polk Streets will now help cool the city this summer.
Phoenicians will return from the Memorial Day weekend to witness installation of the first "Cool Pavement" parking lot in central downtown Phoenix. This 90,000-square-foot temporary parking lot located between First, Second, Taylor and Polk Streets will now help cool the city this summer.
May 31st, 2011
Read more
 Independent developer Peter Burke today is pleased to announce iNanotube 1.1 for iOS, his new Education app that graphically instructs users about the detailed atomic structure of carbon nanotubes, a revolutionary class of wires only a few atoms across. Advanced 3D rendering algorithms provide detailed, animated renderings of the design and construction of carbon nanotubes, demonstrating and teaching the fundamentals of the atomic properties of these tiny wires.
Independent developer Peter Burke today is pleased to announce iNanotube 1.1 for iOS, his new Education app that graphically instructs users about the detailed atomic structure of carbon nanotubes, a revolutionary class of wires only a few atoms across. Advanced 3D rendering algorithms provide detailed, animated renderings of the design and construction of carbon nanotubes, demonstrating and teaching the fundamentals of the atomic properties of these tiny wires.
May 31st, 2011
Read more
 The National Nanotechnology Center (NANOTEC) today announced it has entered into an Affiliation Agreement with the School of Pharmacy at West Virginia University, USA to explore collaborative research opportunities in areas related to pharmaceutical and health-related research initiatives.
The National Nanotechnology Center (NANOTEC) today announced it has entered into an Affiliation Agreement with the School of Pharmacy at West Virginia University, USA to explore collaborative research opportunities in areas related to pharmaceutical and health-related research initiatives.
May 31st, 2011
Read more
 Engineering structures on the smallest possible scales - using molecules and individual atoms as building blocks - is both physically and conceptually challenging. An interdisciplinary team of researchers at the University of Pennsylvania has now developed a method of computationally selecting the best of these blocks, drawing inspiration from the similar behavior of proteins in making biological structures.
Engineering structures on the smallest possible scales - using molecules and individual atoms as building blocks - is both physically and conceptually challenging. An interdisciplinary team of researchers at the University of Pennsylvania has now developed a method of computationally selecting the best of these blocks, drawing inspiration from the similar behavior of proteins in making biological structures.
May 30th, 2011
Read more
 A solar-powered sensor station to monitor in real time the concentration of gases that are key culprits in climate change and air pollution has been installed on a Queensland University of Technology Gardens Point roof as part of an international study on solar-powered environmental nano sensors.
A solar-powered sensor station to monitor in real time the concentration of gases that are key culprits in climate change and air pollution has been installed on a Queensland University of Technology Gardens Point roof as part of an international study on solar-powered environmental nano sensors.
May 30th, 2011
Read more
Scientists were able to demonstrate how two remote atomic quantum systems can be prepared in a shared 'entangled' state. This means that one system is a single atom trapped in an optical resonator, and the other one is a Bose-Einstein condensate consisting of hundreds of thousands of ultracold atoms.
May 30th, 2011
Read more
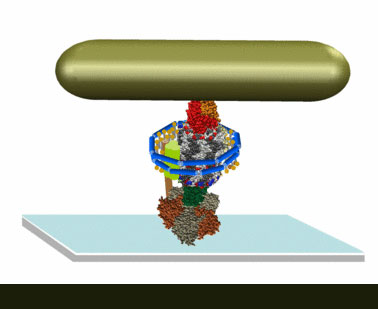 Empowered by a $1.2 million grant from the National Institutes of Health, Arizona State University scientist Wayne Frasch is deciphering how one of the world's smallest molecular motors works in living cells. In the process, he is also casting light on a physics puzzle that has perplexed scientists for more than 40 years.
Empowered by a $1.2 million grant from the National Institutes of Health, Arizona State University scientist Wayne Frasch is deciphering how one of the world's smallest molecular motors works in living cells. In the process, he is also casting light on a physics puzzle that has perplexed scientists for more than 40 years.
May 30th, 2011
Read more
Researchers demonstrate the world's thinnest polarizer, which relies on the coupling, guiding and polarizing of electromagnetic waves by graphene. They claim that this breakthrough will someday allow the integration on all-photonic circuits for high-speed optical communications.
May 30th, 2011
Read more
 Die bisherigen Standardtestverfahren fuer die Risikobewertung von Nanomaterialien sind ungenuegend. Zu diesem Ergebnis kommt eine Studie unter der Federfuehrung des Instituts fuer Umweltwissenschaften der Universitaet Koblenz-Landau.
Die bisherigen Standardtestverfahren fuer die Risikobewertung von Nanomaterialien sind ungenuegend. Zu diesem Ergebnis kommt eine Studie unter der Federfuehrung des Instituts fuer Umweltwissenschaften der Universitaet Koblenz-Landau.
May 30th, 2011
Read more
A simple printing-press technique can produce efficient, flexible full-color displays.
May 30th, 2011
Read more
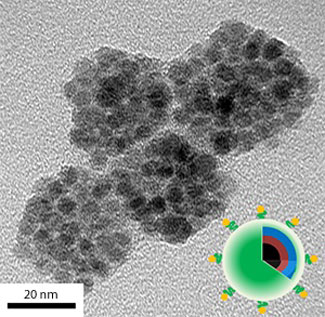 Acid-sensitive nanocarriers simultaneously diagnose tumors and release chemotherapy drugs to target cancer cells.
Acid-sensitive nanocarriers simultaneously diagnose tumors and release chemotherapy drugs to target cancer cells.
May 30th, 2011
Read more
 Using a mechanical grinding technique that allowed them to control the structure of a metal's surface on the nanoscale, Ke Lu and colleagues from the Chinese Academy of Science's Institute for Metal Research in Shenyang have overcome the frustrating tradeoff between strength and brittleness to produce a protective copper surface that is both strong and ductile.
Using a mechanical grinding technique that allowed them to control the structure of a metal's surface on the nanoscale, Ke Lu and colleagues from the Chinese Academy of Science's Institute for Metal Research in Shenyang have overcome the frustrating tradeoff between strength and brittleness to produce a protective copper surface that is both strong and ductile.
May 30th, 2011
Read more
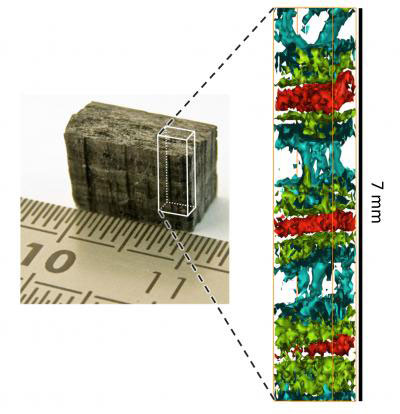 Scientists from Finland and France have developed a new synchrotron X-ray technique that may revolutionize the chemical analysis of rare materials like meteoric rock samples or fossils.
Scientists from Finland and France have developed a new synchrotron X-ray technique that may revolutionize the chemical analysis of rare materials like meteoric rock samples or fossils.
May 29th, 2011
Read more











 Subscribe to our Nanotechnology News feed
Subscribe to our Nanotechnology News feed