Stuart Parkin of IBM Research - Almaden in San Jose has become a fellow of the Gutenberg Research College (GFK) of Johannes Gutenberg University Mainz and will be mentoring Mainz postgraduates.
May 6th, 2011
Read more
If pathogens enter into our water supply network many people may fall ill quickly. To protect us against this biological threat, researchers have developed a detection system partly based on nanotechnology that can warn authorities in time.
May 6th, 2011
Read more
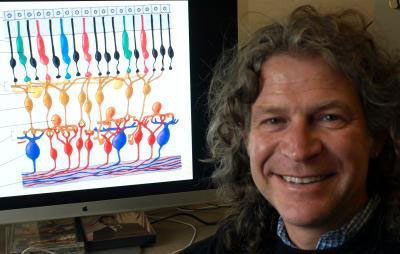 University of Oregon physicist Richard Taylor is leading effort to design fractal devices to put in eyes.
University of Oregon physicist Richard Taylor is leading effort to design fractal devices to put in eyes.
May 5th, 2011
Read more
The Defense Advanced Research Projects Agency (DARPA) has released a request for Information to solicit ideas and information to support its 100 Year Starship Study program.
May 5th, 2011
Read more
Measurement of 'hot' electrons could have solar energy payoff.
May 5th, 2011
Read more
Wissenschaftler der Uni Hamburg konnten erstmals ein funktionierendes Spintronik-Logik-Bauteil verwirklichen, das aus wenigen magnetischen Atomen aufgebaut ist. Beim Schalten des realisierten logischen Oder-Gatters ist im Gegensatz zu herkoemmlichen elektronischen Bauteilen kein Stromfluss noetig, da nur die magnetische Ausrichtung der Atome umgeschaltet wird.
May 5th, 2011
Read more
Flash forward 20 years... What if our best efforts to lower carbon emissions, wean off fossil fuels, and plan for a soaring population weren't enough? Would we ask ourselves why we didn't take action sooner, transforming the ideas from our greatest innovators into the technologies needed to prepare for a more secure and sustainable future?
May 5th, 2011
Read more
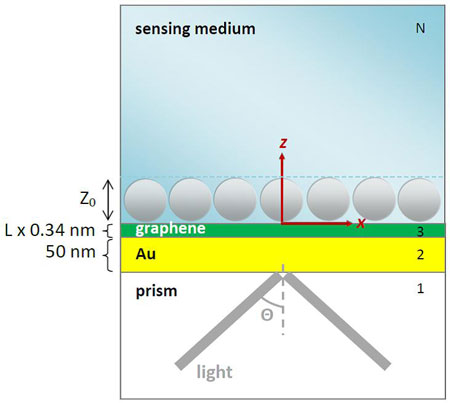 Adding a few graphene layers onto the conventional gold-film surface plasmon resonance (SPR) biosensor will boost up its sensitivity dramatically. The improved sensitivity comes from the graphene layer's increased adsorption of biomolecules and the graphene layer's optical modification to the SPR.
Adding a few graphene layers onto the conventional gold-film surface plasmon resonance (SPR) biosensor will boost up its sensitivity dramatically. The improved sensitivity comes from the graphene layer's increased adsorption of biomolecules and the graphene layer's optical modification to the SPR.
May 5th, 2011
Read more
 Researchers from the Vienna Center for Quantum Science and Technology at the University of Vienna and the Institute of Quantum Optics and Quantum Information at the Austrian Academy of Sciences used a quantum mechanical system in the laboratory to simulate complex many-body systems.
Researchers from the Vienna Center for Quantum Science and Technology at the University of Vienna and the Institute of Quantum Optics and Quantum Information at the Austrian Academy of Sciences used a quantum mechanical system in the laboratory to simulate complex many-body systems.
May 5th, 2011
Read more
The ICPC Nanonet Project invites you to take part in person or online in the 3rd ICPC Nanonet Annual Workshop to be held on may 24-25, 2011 at the St Petersburg Hotel.
May 5th, 2011
Read more
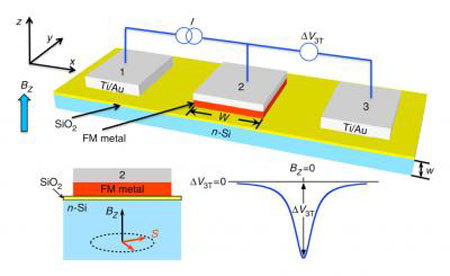 Researchers in the Materials Science and Technology division of the Naval Research Laboratory have recently demonstrated electrical injection, detection and precession of spin accumulation in silicon, the cornerstone material of modern device technology, at temperatures up to 225 degrees Celsius.
Researchers in the Materials Science and Technology division of the Naval Research Laboratory have recently demonstrated electrical injection, detection and precession of spin accumulation in silicon, the cornerstone material of modern device technology, at temperatures up to 225 degrees Celsius.
May 5th, 2011
Read more
A world-first cattle vaccine based on nanotechnology could provide protection from the Bovine Viral Diarrhoea Virus (BVDV), which costs the Australian cattle industry tens of millions of dollars in lost revenue each year.
May 5th, 2011
Read more
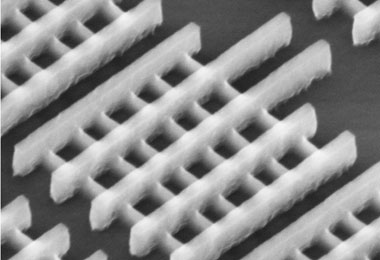 Intel Corporation today announced a significant breakthrough in the evolution of the transistor, the microscopic building block of modern electronics. For the first time since the invention of silicon transistors over 50 years ago, transistors using a three-dimensional structure will be put into high-volume manufacturing.
Intel Corporation today announced a significant breakthrough in the evolution of the transistor, the microscopic building block of modern electronics. For the first time since the invention of silicon transistors over 50 years ago, transistors using a three-dimensional structure will be put into high-volume manufacturing.
May 4th, 2011
Read more
 The Nanoinformatics 2020 Roadmap is the first broad-based nanotech community effort to attempt to comprehensively meet the needs and goals of nanoinformatics, which is the intersection of nanotechnology, computer science and data management.
The Nanoinformatics 2020 Roadmap is the first broad-based nanotech community effort to attempt to comprehensively meet the needs and goals of nanoinformatics, which is the intersection of nanotechnology, computer science and data management.
May 4th, 2011
Read more
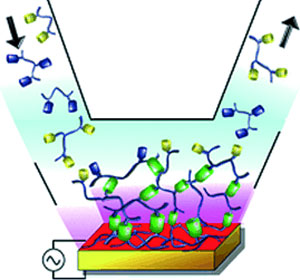 Copper ions as morphogens for the formation of polymer films by click chemistry.
Copper ions as morphogens for the formation of polymer films by click chemistry.
May 4th, 2011
Read more
In a new study, UCLA scientists report that by using engineered mesoporous silica nanoparticles as delivery vehicles, they were able to achieve significant increases in the percentage of drug-carrying nanoparticles that reach and are retained at tumor sites.
May 4th, 2011
Read more








 Subscribe to our Nanotechnology News feed
Subscribe to our Nanotechnology News feed