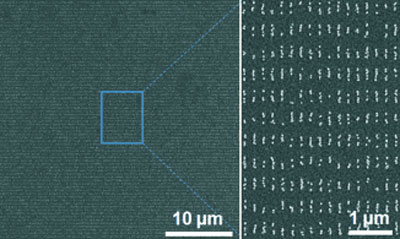
 When Gutenberg developed the principles of modern book printing, books became available to the masses. Hoping to bring technology capable of mass production to the nanometer scale, Udo Bach and this team of scientists at Monash University (Australia) and the Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory (USA) have developed a nanoprinting process modeled on Gutenberg's printing method. Their goal is the simple, inexpensive production of nanotechnological components for solar cells, biosensors, and other electronic systems.
When Gutenberg developed the principles of modern book printing, books became available to the masses. Hoping to bring technology capable of mass production to the nanometer scale, Udo Bach and this team of scientists at Monash University (Australia) and the Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory (USA) have developed a nanoprinting process modeled on Gutenberg's printing method. Their goal is the simple, inexpensive production of nanotechnological components for solar cells, biosensors, and other electronic systems.
Apr 15th, 2011
Read more
 In the BASF Dialogueforum Nano representatives of environmental and consumer organisations, trade unions, scientific institutes and churches (Civil Society Organisations / Non Governmental Organisations) work together with employees of the chemical company BASF SE on various issues related to the subject of nanotechnologies. The 2009 / 2010 dialogueforum, led by the Risk Dialogue Foundation, St. Gallen, resulted in recommendations on how transparency and information can be guaranteed along the product life cycle.
In the BASF Dialogueforum Nano representatives of environmental and consumer organisations, trade unions, scientific institutes and churches (Civil Society Organisations / Non Governmental Organisations) work together with employees of the chemical company BASF SE on various issues related to the subject of nanotechnologies. The 2009 / 2010 dialogueforum, led by the Risk Dialogue Foundation, St. Gallen, resulted in recommendations on how transparency and information can be guaranteed along the product life cycle.
Apr 15th, 2011
Read more
LOPE-C, the premier conference and exhibition of the worldwide organic and printed electronics community, is steering towards a new record in 2011. More than 95 companies are expected to exhibit on the greatly expanded floorspace of 1,300 square meters at the Messe Frankfurt Forum, Germany.
Apr 15th, 2011
Read more
If a new development from labs at MIT pans out as expected, someday the entire surface area of a building's windows could be used to generate electricity - without interfering with the ability to see through them.
Apr 15th, 2011
Read more
A dramatic and surprising magnetic effect of light discovered by University of Michigan researchers could lead to solar power without traditional semiconductor-based solar cells. The researchers found a way to make an "optical battery". In the process, they overturned a century-old tenet of physics.
Apr 14th, 2011
Read more
 One-atom thick chlorine reduces OLED device complexity while enabling record efficiencies.
One-atom thick chlorine reduces OLED device complexity while enabling record efficiencies.
Apr 14th, 2011
Read more
The Semiconductor Industry Association (SIA), representing U.S. leadership in semiconductor manufacturing and design, today announced that Dr. Jeff Welser testified at a hearing on the future of nanotechnology research and the National Nanotechnology Initiative (NNI) on behalf of the SIA, the Semiconductor Research Corporation (SRC) and the Nanoelectronics Research Initiative (NRI) today in the House Committee on Science, Space and Technology's Subcommittee on Research and Science Education.
Apr 14th, 2011
Read more
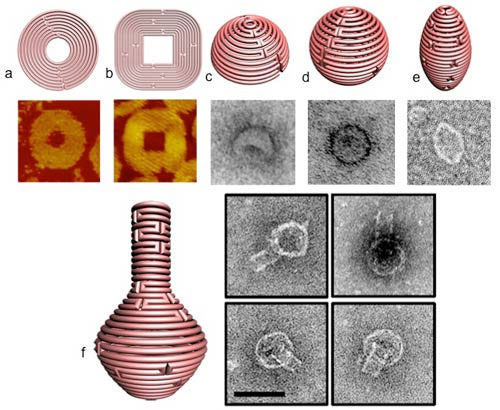 Miniature architectural forms - some no larger than viruses - have been constructed through a revolutionary technique known as DNA origami. Now, Hao Yan, Yan Liu and their colleagues at Arizona State University's Biodesign Institute have expanded the capability of this method to construct arbitrary, two and three-dimensional shapes, mimicking those commonly found in nature.
Miniature architectural forms - some no larger than viruses - have been constructed through a revolutionary technique known as DNA origami. Now, Hao Yan, Yan Liu and their colleagues at Arizona State University's Biodesign Institute have expanded the capability of this method to construct arbitrary, two and three-dimensional shapes, mimicking those commonly found in nature.
Apr 14th, 2011
Read more
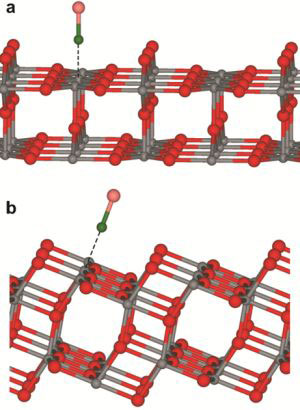 The exploitation and utilization of new energy sources are considered to be among today's major challenges. Solar energy plays a central role, and its direct conversion into chemical energy, for example hydrogen generation by water splitting, is one of its interesting variants. Titanium oxide-based photocatalysis is the presently most efficient, yet little understood conversion process. Scientists have studied the basic mechanisms of photochemistry by the example of titania and have presented new detailed findings.
The exploitation and utilization of new energy sources are considered to be among today's major challenges. Solar energy plays a central role, and its direct conversion into chemical energy, for example hydrogen generation by water splitting, is one of its interesting variants. Titanium oxide-based photocatalysis is the presently most efficient, yet little understood conversion process. Scientists have studied the basic mechanisms of photochemistry by the example of titania and have presented new detailed findings.
Apr 14th, 2011
Read more
The direct conversion of sunlight into electricity using photovoltaics is becoming an increasingly important technology for renewable energy generation as a replacement for fossil fuels, with applications from large-scale generation to roof-top solar panels and even mobile phones. But photovoltaics still accounts for only a marginal fraction of global energy supply. One of the main reasons for this is the relatively high cost of the base material - silicon - used in the most common type of solar cell.
Apr 14th, 2011
Read more
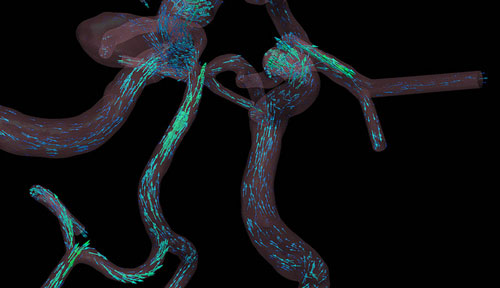 Newer, faster supercomputers have allowed scientists to create detailed models of blood flow that help doctors understand what happens at the molecular level and, consequently, how heart and blood diseases can be treated.
Newer, faster supercomputers have allowed scientists to create detailed models of blood flow that help doctors understand what happens at the molecular level and, consequently, how heart and blood diseases can be treated.
Apr 14th, 2011
Read more
The supercomputer is an important milestone of Europe's contribution to the Broader Approach (BA), an Agreement signed between Europe and Japan to complement the ITER project through various R+D activities which are developed in the field of nuclear fusion.
Apr 14th, 2011
Read more
 Engineers at UC San Diego are using nanotechnology to increase the efficiency and enhance the performance of fuel cells, which could boost renewable energy options and reduce toxic emissions.
Engineers at UC San Diego are using nanotechnology to increase the efficiency and enhance the performance of fuel cells, which could boost renewable energy options and reduce toxic emissions.
Apr 14th, 2011
Read more
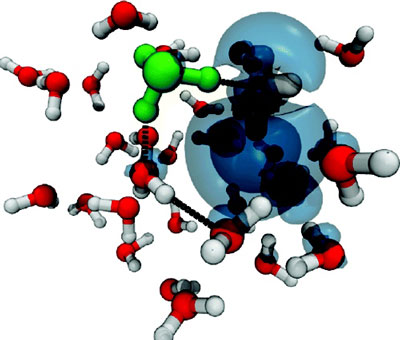 How do you simulate the behaviour of protons and amino acids on the computer? How do you depict experiments to study their behaviour as more or less water is introduced? These questions may seem trivial in this age of powerful computers. Yet, it turns out this task will remain almost impossible to solve until new mathematical algorithms are found.
How do you simulate the behaviour of protons and amino acids on the computer? How do you depict experiments to study their behaviour as more or less water is introduced? These questions may seem trivial in this age of powerful computers. Yet, it turns out this task will remain almost impossible to solve until new mathematical algorithms are found.
Apr 14th, 2011
Read more
CEA-Leti, a leading global research center committed to creating and commercializing innovation in micro- and nanotechnologies, is hosting its third workshop on innovative memory technologies at MINATEC on Wednesday, June 29, 2011.
Apr 14th, 2011
Read more
BfR Workshop confirms incomplete data situation concerning the health risks of nanoscale silver.
Apr 14th, 2011
Read more
 When Gutenberg developed the principles of modern book printing, books became available to the masses. Hoping to bring technology capable of mass production to the nanometer scale, Udo Bach and this team of scientists at Monash University (Australia) and the Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory (USA) have developed a nanoprinting process modeled on Gutenberg's printing method. Their goal is the simple, inexpensive production of nanotechnological components for solar cells, biosensors, and other electronic systems.
When Gutenberg developed the principles of modern book printing, books became available to the masses. Hoping to bring technology capable of mass production to the nanometer scale, Udo Bach and this team of scientists at Monash University (Australia) and the Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory (USA) have developed a nanoprinting process modeled on Gutenberg's printing method. Their goal is the simple, inexpensive production of nanotechnological components for solar cells, biosensors, and other electronic systems.







 Subscribe to our Nanotechnology News feed
Subscribe to our Nanotechnology News feed