The Institute of Microelectronics (IME), a research institute of the Agency for Science, Technology and Research (A*STAR), has announced the launch of the Copper Wire (Cu-Wire) Bonding Consortium.
Nov 8th, 2010
Read more
Montroseite, a vanadium oxide mineral first discovered 60 years ago, could be used as an anode for greener batteries, say Chinese researchers.
Nov 8th, 2010
Read more
 The American molecular biologist Susan Lindquist from the Whitehead Institute for Biomedical Research in Cambridge, Massachusetts, USA, is the 2010 recipient of the Max Delbruck Medal awarded in Berlin, Germany. Lindquist, who is also a biology professor at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT), was honored for her work on protein folding.
The American molecular biologist Susan Lindquist from the Whitehead Institute for Biomedical Research in Cambridge, Massachusetts, USA, is the 2010 recipient of the Max Delbruck Medal awarded in Berlin, Germany. Lindquist, who is also a biology professor at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT), was honored for her work on protein folding.
Nov 7th, 2010
Read more
 The side effects of chemotherapy could be largely wiped out by a so-called 'magic bullet' nanotechnology system being researched in Dubai, according to an associate professor at Dubai Pharmacy College.
The side effects of chemotherapy could be largely wiped out by a so-called 'magic bullet' nanotechnology system being researched in Dubai, according to an associate professor at Dubai Pharmacy College.
Nov 7th, 2010
Read more
Iran Nanotechnology Initiative Council (INIC) and the Venezuelan Science Ministry's Center for Science and Technology Researches signed a Memorandum of Understanding (MoU) on interacademic cooperation in the field of nanotechnology.
Nov 7th, 2010
Read more
More than 1,000 people, including children, adults and families from throughout upstate New York, converged today on the College of Nanoscale Science and Engineering (CNSE) of the University at Albany to participate in CNSE Community Day, a highlight of CNSE's unprecedented community and educational outreach initiative known as NANOvember.
Nov 5th, 2010
Read more
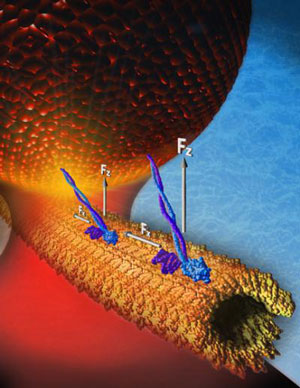 Rice University bioengineers measure pulling power of hitched pairs of protein motors.
Rice University bioengineers measure pulling power of hitched pairs of protein motors.
Nov 5th, 2010
Read more
MIT analysis shows how synthetic systems for capturing the sun's energy could be made more efficient.
Nov 5th, 2010
Read more
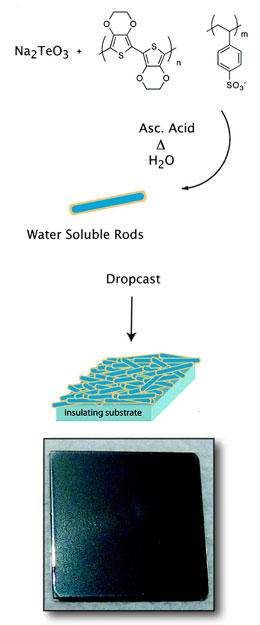 Scientists at the Berkeley Lab constructed a nanoscale composite thermoelectric material by wrapping a polymer that conducts electricity around a nanorod of tellurium - a metal coupled with cadmium in today's most cost-effective solar cells. This composite material is easily spin cast or printed into a film from a water-based solution.
Scientists at the Berkeley Lab constructed a nanoscale composite thermoelectric material by wrapping a polymer that conducts electricity around a nanorod of tellurium - a metal coupled with cadmium in today's most cost-effective solar cells. This composite material is easily spin cast or printed into a film from a water-based solution.
Nov 5th, 2010
Read more
New jobs will be created as the growing EYP-CNSE partnership pursues expanding opportunities for design and engineering of 'green' high-tech facilities.
Nov 5th, 2010
Read more
 Der erste Spatenstich fuer das NanoEnergieTechnikZentrum, kurz NETZ, ist noch ganz frisch: er wurde gestern im Beisein der NRW-Innovationsministerin Svenja Schulze an der Universitaet Duisburg-Essen gesetzt.
Der erste Spatenstich fuer das NanoEnergieTechnikZentrum, kurz NETZ, ist noch ganz frisch: er wurde gestern im Beisein der NRW-Innovationsministerin Svenja Schulze an der Universitaet Duisburg-Essen gesetzt.
Nov 5th, 2010
Read more
Employing new drug-engineering technology, a research team has created a 'nanobioconjugate' drug that may be given by intravenous injection and carried in the blood to target a brain tumor. It is engineered to specifically permeate the tumor cell wall, entering endosomes, mobile compartments within cells.
Nov 5th, 2010
Read more
A research team at the University of Glasgow twisted the light like a corkscrew by using a polarising filter, before shining it onto a specially shaped piece of gold to create the world's first 'super twisting'.
Nov 5th, 2010
Read more
Professor Henny Zandbergen has been awarded an ERC Advanced Grant of 2.5 million euros for his research into improved microscopic technologies. The technologies enable Professor Zandbergen to visualise extremely small structures, such as semiconductor nanowires, all the way down to atomic level.
Nov 5th, 2010
Read more
On December 3, 2010, the Federal Reserve Bank of Dallas, in cooperation with the Semiconductor Industry Association, is hosting a 1-day event 'Sizing Up Nanotechnology: The Economic Impact of Nanoelectronics'.
Nov 5th, 2010
Read more
A cross-disciplinary Small Medicine and Advanced Research Translation (SMART) team led by Prof. Dar-Bin Shieh of Institute of Oral Medicine in Medical College at National Cheng Kung University (NCKU), Tainan, Taiwan, has announced a breakthrough in the precision in-cell gene scission at pre-designed sequence sites using Artificial Targeting Light Activated Nano Scissors (ATLANS) and a custom build photonic device.
Nov 5th, 2010
Read more






 Subscribe to our Nanotechnology News feed
Subscribe to our Nanotechnology News feed