Squid skin could be the solution to camouflage material
 Scientists have turned the animal's pigment particles into spools of fiber that can be used for a number of things.
Scientists have turned the animal's pigment particles into spools of fiber that can be used for a number of things.
Feb 27th, 2018
Read more
 Scientists have turned the animal's pigment particles into spools of fiber that can be used for a number of things.
Scientists have turned the animal's pigment particles into spools of fiber that can be used for a number of things.
Feb 27th, 2018
Read more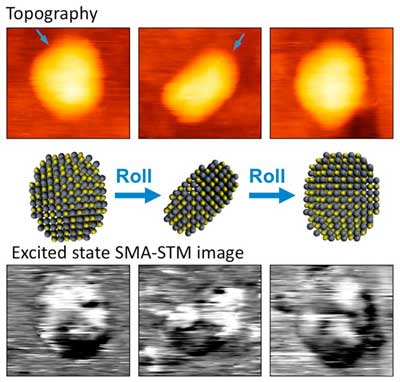 Researchers have developed an imaging technique that uses a tiny, super sharp needle to nudge a single nanoparticle into different orientations and capture 2-D images to help reconstruct a 3-D picture.
Researchers have developed an imaging technique that uses a tiny, super sharp needle to nudge a single nanoparticle into different orientations and capture 2-D images to help reconstruct a 3-D picture.
Feb 27th, 2018
Read more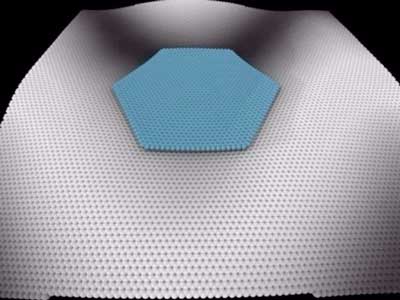 Researchers have explained for the first time the mystery of why adhesive tape is so useful for graphene production.
Researchers have explained for the first time the mystery of why adhesive tape is so useful for graphene production.
Feb 27th, 2018
Read more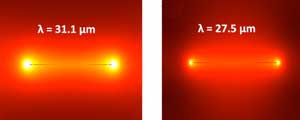 Scientists have studied the optical characteristics of a special type of material made of a single layer of phosphorus atoms for the benefit of detecting and interacting with infrared light.
Scientists have studied the optical characteristics of a special type of material made of a single layer of phosphorus atoms for the benefit of detecting and interacting with infrared light.
Feb 27th, 2018
Read more An international team of scientists has discovered a new type of silicon that could be used to control light beams in a new kind of photonic chip - a chipset where information is carried by light beams rather than electrical currents.
An international team of scientists has discovered a new type of silicon that could be used to control light beams in a new kind of photonic chip - a chipset where information is carried by light beams rather than electrical currents.
Feb 27th, 2018
Read more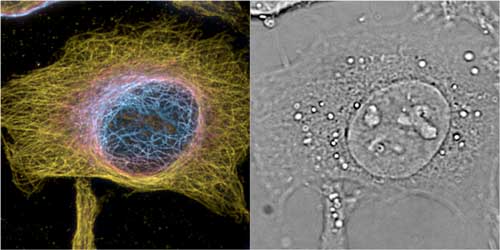 A research team has developed a technique that can perform both 3D super-resolution microscopy and fast 3D phase imaging in a single instrument.
A research team has developed a technique that can perform both 3D super-resolution microscopy and fast 3D phase imaging in a single instrument.
Feb 27th, 2018
Read more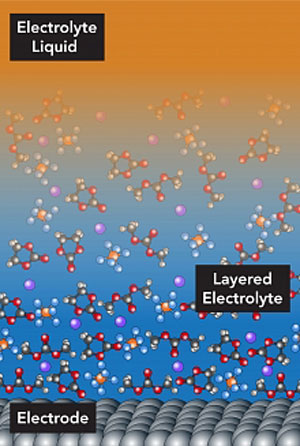 Lithium ions have to travel through layers of molecules in the electrolyte liquid before they can enter or leave a lithium-ion battery electrode. Tweaking this process could help batteries charge faster.
Lithium ions have to travel through layers of molecules in the electrolyte liquid before they can enter or leave a lithium-ion battery electrode. Tweaking this process could help batteries charge faster.
Feb 26th, 2018
Read more Yarn weaved from carbon nanotubes monitors brain control of organ functions in rats, paves way for disease diagnosis and treatment at single nerve level.
Yarn weaved from carbon nanotubes monitors brain control of organ functions in rats, paves way for disease diagnosis and treatment at single nerve level.
Feb 26th, 2018
Read more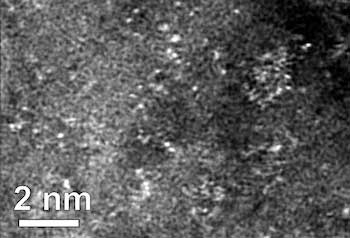 Study of graphene catalysts finds trace of manganese, suggests better ultrathin fuel-cell components.
Study of graphene catalysts finds trace of manganese, suggests better ultrathin fuel-cell components.
Feb 26th, 2018
Read more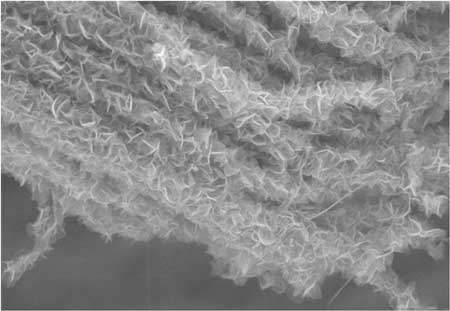 Mechanical engineers have designed a super-efficient and long-lasting electrode for supercapacitors. The device's design was inspired by the structure and function of leaves on tree branches, and it is more than 10 times more efficient than other designs.
Mechanical engineers have designed a super-efficient and long-lasting electrode for supercapacitors. The device's design was inspired by the structure and function of leaves on tree branches, and it is more than 10 times more efficient than other designs.
Feb 26th, 2018
Read more New ultra-thin coating responds to heat and cold.
New ultra-thin coating responds to heat and cold.
Feb 26th, 2018
Read more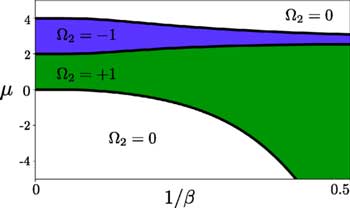 Merging of Majorana particles in a topological superconductor opens new avenues for quantum technologies.
Merging of Majorana particles in a topological superconductor opens new avenues for quantum technologies.
Feb 26th, 2018
Read more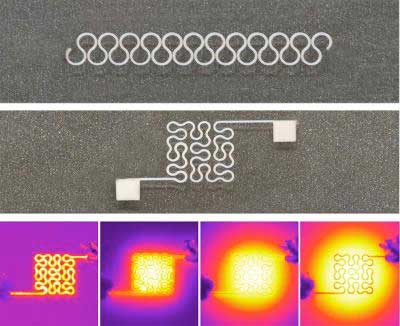 Researchers have developed a new technique that allows them to print circuits on flexible, stretchable substrates using silver nanowires. The advance makes it possible to integrate the material into a wide array of electronic devices.
Researchers have developed a new technique that allows them to print circuits on flexible, stretchable substrates using silver nanowires. The advance makes it possible to integrate the material into a wide array of electronic devices.
Feb 26th, 2018
Read more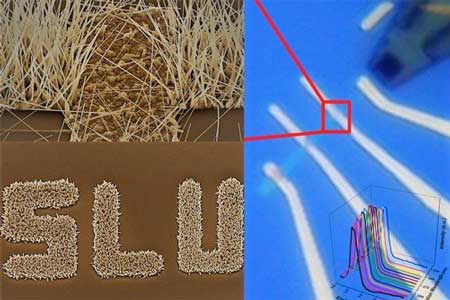 The new mask-free fabrication approach uses a liquid ink precursor to produce nanoscale materials, allowing researchers to predict and optimize the geometric shape of the resulting structure.
The new mask-free fabrication approach uses a liquid ink precursor to produce nanoscale materials, allowing researchers to predict and optimize the geometric shape of the resulting structure.
Feb 26th, 2018
Read more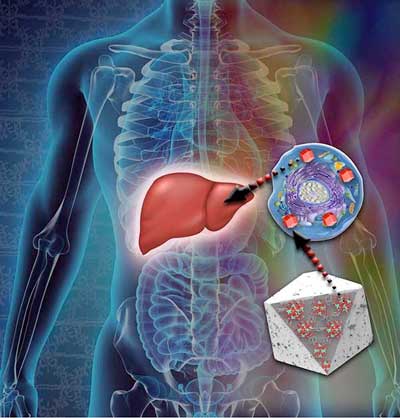 Scientists have designed and synthesized nanoparticles that glow red and are stable, useful properties for tracking cancer growth and spread.
Scientists have designed and synthesized nanoparticles that glow red and are stable, useful properties for tracking cancer growth and spread.
Feb 26th, 2018
Read more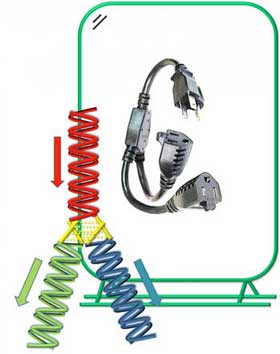 Researchers have recently designed, created and tested a DNA circuit capable of splitting and combining current, much like an adapter that can connect multiple appliances to a wall outlet.
Researchers have recently designed, created and tested a DNA circuit capable of splitting and combining current, much like an adapter that can connect multiple appliances to a wall outlet.
Feb 26th, 2018
Read more