A customizable, fabric-like power source for wearable electronics
 Researchers have created a customizable, fabric-like power source that can be cut, folded or stretched without losing its function.
Researchers have created a customizable, fabric-like power source that can be cut, folded or stretched without losing its function.
Jan 30th, 2018
Read more
 Researchers have created a customizable, fabric-like power source that can be cut, folded or stretched without losing its function.
Researchers have created a customizable, fabric-like power source that can be cut, folded or stretched without losing its function.
Jan 30th, 2018
Read more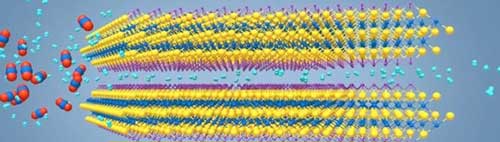 MXene material could help produce clean-burning hydrogen fuel.
MXene material could help produce clean-burning hydrogen fuel.
Jan 29th, 2018
Read more Picture a tiny, makeshift muscle that can curl a 20 milligram suspended weight when exposed to light. Under the right conditions, another mix packs enough power to bench-press a dime.
Picture a tiny, makeshift muscle that can curl a 20 milligram suspended weight when exposed to light. Under the right conditions, another mix packs enough power to bench-press a dime.
Jan 29th, 2018
Read more Scientists have measured how strongly a charge carrier's spin interacts with a magnetic field in diamond. This crucial property shows diamond as a promising material for spintronic devices.
Scientists have measured how strongly a charge carrier's spin interacts with a magnetic field in diamond. This crucial property shows diamond as a promising material for spintronic devices.
Jan 29th, 2018
Read more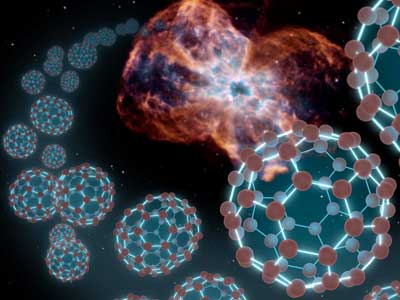 Fullerenes were first discovered by Harry Kroto in the 1970s, a feat for which he and his colleagues received a Nobel Prize in Chemistry. Recently, they have been found in winds emitted by red giants and in interstellar medium.
Fullerenes were first discovered by Harry Kroto in the 1970s, a feat for which he and his colleagues received a Nobel Prize in Chemistry. Recently, they have been found in winds emitted by red giants and in interstellar medium.
Jan 29th, 2018
Read more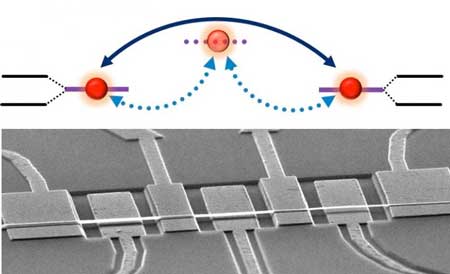 A research team has realized strong coupling between distant phonon modes, by introducing a third resonator as a phonon cavity mode. Varying the resonant frequency of the phonon cavity mode, the coupling strength between distant phonon modes can be continuous tuned.
A research team has realized strong coupling between distant phonon modes, by introducing a third resonator as a phonon cavity mode. Varying the resonant frequency of the phonon cavity mode, the coupling strength between distant phonon modes can be continuous tuned.
Jan 29th, 2018
Read more Researchers have developed flexible vertical micro LEDs (f-VLEDs) using anisotropic conductive film (ACF)-based transfer and interconnection technology.
Researchers have developed flexible vertical micro LEDs (f-VLEDs) using anisotropic conductive film (ACF)-based transfer and interconnection technology.
Jan 29th, 2018
Read more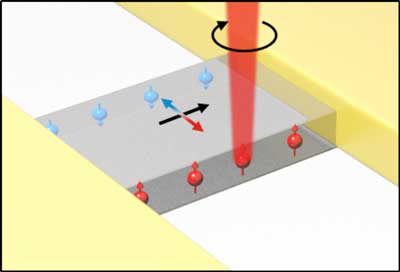 Topological insulators are a fascinating group of materials. A spin-polarization occurs, as soon as an electric current flows in the material. Scientists have measured this now for the first time optically at room temperature.
Topological insulators are a fascinating group of materials. A spin-polarization occurs, as soon as an electric current flows in the material. Scientists have measured this now for the first time optically at room temperature.
Jan 29th, 2018
Read more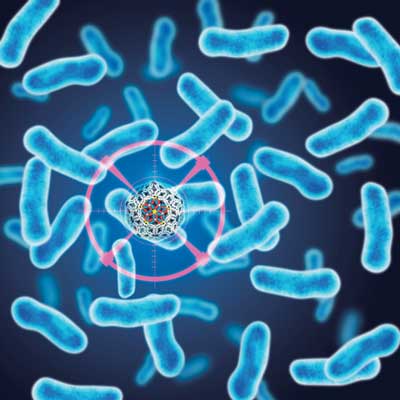 Scientists have developed a synthetic 'virus' that kills bacteria on first contact.
Scientists have developed a synthetic 'virus' that kills bacteria on first contact.
Jan 29th, 2018
Read more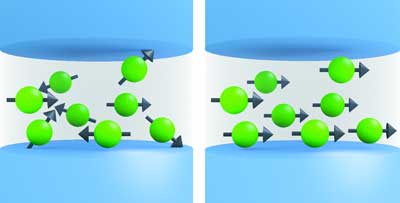 Researchers have built a superconducting switch that 'learns' like a biological system and could connect processors and store memories in future computers operating like the human brain.
Researchers have built a superconducting switch that 'learns' like a biological system and could connect processors and store memories in future computers operating like the human brain.
Jan 29th, 2018
Read more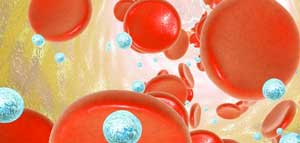 Nanoparticles that transport medicines to a specific part of the human body are usually broken down in the liver prematurely. Researchers have discovered a new method to prevent this from happening.
Nanoparticles that transport medicines to a specific part of the human body are usually broken down in the liver prematurely. Researchers have discovered a new method to prevent this from happening.
Jan 29th, 2018
Read more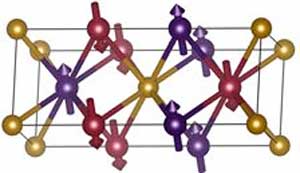 Physicists demonstrate technologically feasible read-out and writing of digital information in antiferromagnets / Basic principle for ultrafast and stable magnetic memory.
Physicists demonstrate technologically feasible read-out and writing of digital information in antiferromagnets / Basic principle for ultrafast and stable magnetic memory.
Jan 29th, 2018
Read more Ultrathin, rigid silicon segments that are wired through interdigitated metal contacts produce ultraflexible high-performance solar cells.
Ultrathin, rigid silicon segments that are wired through interdigitated metal contacts produce ultraflexible high-performance solar cells.
Jan 29th, 2018
Read more Gold nanospheres can be manipulated on surfaces with nanometer precision using the effects of solvent evaporation.
Gold nanospheres can be manipulated on surfaces with nanometer precision using the effects of solvent evaporation.
Jan 29th, 2018
Read more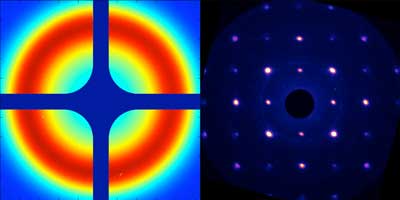 Combining X-ray and electron data, researchers observe the rapid atomic response of iron-platinum nanoparticles to light, which could help control future magnetic data storage devices.
Combining X-ray and electron data, researchers observe the rapid atomic response of iron-platinum nanoparticles to light, which could help control future magnetic data storage devices.
Jan 26th, 2018
Read more Recent improvements could allow rectennas - which convert electromagnetic fields at optical frequencies directly to electrical current - to operate low-power devices such as temperature sensors.
Recent improvements could allow rectennas - which convert electromagnetic fields at optical frequencies directly to electrical current - to operate low-power devices such as temperature sensors.
Jan 26th, 2018
Read more