Nanofoam catalysts efficiently generates hydrogen from water
 Researchers have found a way to more efficiently generate hydrogen from water - an important key to making clean energy more viable.
Researchers have found a way to more efficiently generate hydrogen from water - an important key to making clean energy more viable.
Feb 1st, 2018
Read more
 Researchers have found a way to more efficiently generate hydrogen from water - an important key to making clean energy more viable.
Researchers have found a way to more efficiently generate hydrogen from water - an important key to making clean energy more viable.
Feb 1st, 2018
Read more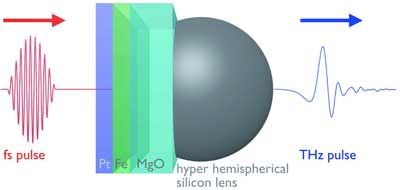 Physicists use a quantum magnetic current flow, so-called spin current, in magnetic metal nanostructures. The cost-effective and material-saving technology has the potential for industry applications.
Physicists use a quantum magnetic current flow, so-called spin current, in magnetic metal nanostructures. The cost-effective and material-saving technology has the potential for industry applications.
Feb 1st, 2018
Read more Shaped like a spine, new design enables remarkable flexibility, high energy density, and stable voltage, no matter how it is flexed or twisted.
Shaped like a spine, new design enables remarkable flexibility, high energy density, and stable voltage, no matter how it is flexed or twisted.
Feb 1st, 2018
Read more A team of researchers has developed a non-invasive method of delivering drugs directly to cancerous tissue using magnetic forces, a form of treatment that could significantly reduce the toxic side effects of chemotherapy.
A team of researchers has developed a non-invasive method of delivering drugs directly to cancerous tissue using magnetic forces, a form of treatment that could significantly reduce the toxic side effects of chemotherapy.
Feb 1st, 2018
Read more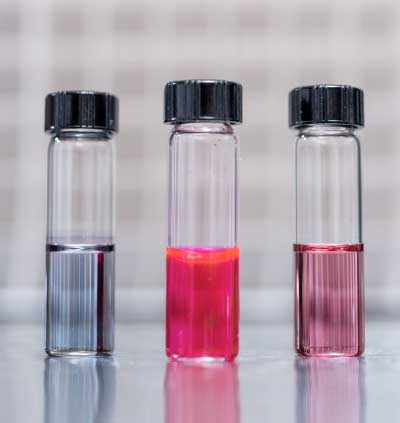 'Hairy nanoparticles made with light-sensitive materials that assemble themselves could one day become nano-carriers providing doctors a new way to simultaneously introduce both therapeutic drugs and cancer-fighting heat into tumors.
'Hairy nanoparticles made with light-sensitive materials that assemble themselves could one day become nano-carriers providing doctors a new way to simultaneously introduce both therapeutic drugs and cancer-fighting heat into tumors.
Feb 1st, 2018
Read more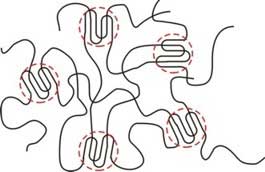 Researchers have found out how the regularity of polypropylene molecules and thermal treatment affect the mechanical properties of the end product. Their new insights make it possible to synthesize a material with predetermined properties, such as elasticity or hardness.
Researchers have found out how the regularity of polypropylene molecules and thermal treatment affect the mechanical properties of the end product. Their new insights make it possible to synthesize a material with predetermined properties, such as elasticity or hardness.
Feb 1st, 2018
Read more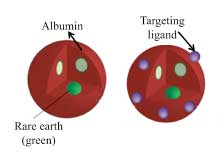 Tests in mice show the particles are better than MRI and CT at tracking cancer's progress.
Tests in mice show the particles are better than MRI and CT at tracking cancer's progress.
Jan 31st, 2018
Read more New research ha revealed that nanocrystals made of cesium lead halide perovskites is the first discovered material which the ground exciton state is 'bright', making it an attractive candidate for more efficient solid-state lasers and light emitting diodes (LEDs).
New research ha revealed that nanocrystals made of cesium lead halide perovskites is the first discovered material which the ground exciton state is 'bright', making it an attractive candidate for more efficient solid-state lasers and light emitting diodes (LEDs).
Jan 31st, 2018
Read more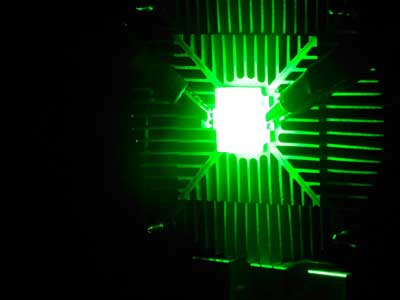 Scientists have been working to develop a new process, which could lead to a new generation of high-definition (HD), paving the way for brighter, lighter and more energy efficient TVs and smart devices.
Scientists have been working to develop a new process, which could lead to a new generation of high-definition (HD), paving the way for brighter, lighter and more energy efficient TVs and smart devices.
Jan 31st, 2018
Read more New research has demonstrated how the nano-architecture of a silkworm?s fiber causes 'Anderson localization of light', a discovery that could lead to various innovations and a better understanding of light transport and heat transfer.
New research has demonstrated how the nano-architecture of a silkworm?s fiber causes 'Anderson localization of light', a discovery that could lead to various innovations and a better understanding of light transport and heat transfer.
Jan 31st, 2018
Read more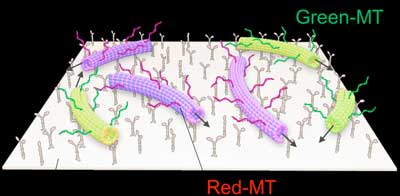 Researchers have developed DNA-assisted molecular robots that autonomously swarm in response to chemical and physical signals, paving the way for developing future nano-machines.
Researchers have developed DNA-assisted molecular robots that autonomously swarm in response to chemical and physical signals, paving the way for developing future nano-machines.
Jan 31st, 2018
Read more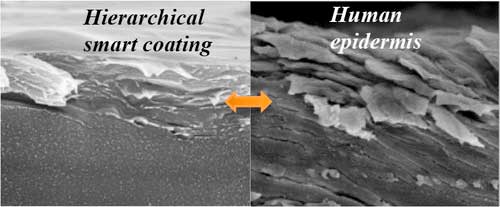 Researchers have reported the development of a smart coating that is as hard as tooth enamel on the outside but can heal itself like skin can.
Researchers have reported the development of a smart coating that is as hard as tooth enamel on the outside but can heal itself like skin can.
Jan 31st, 2018
Read more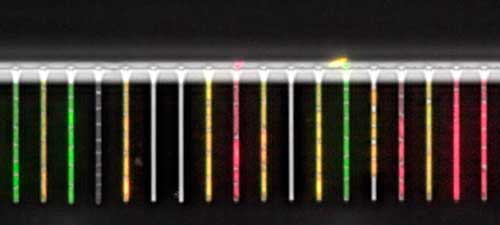 This integrated setup can be used to study gene regulation in single bacterial cells in response to dynamically controlled environmental changes.
This integrated setup can be used to study gene regulation in single bacterial cells in response to dynamically controlled environmental changes.
Jan 31st, 2018
Read more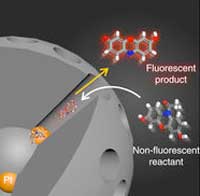 Chemists have measured the effects of nanoconfinement in catalysis by tracking single molecules as they dive down 'nanowells' and react with catalysts at the bottom.
Chemists have measured the effects of nanoconfinement in catalysis by tracking single molecules as they dive down 'nanowells' and react with catalysts at the bottom.
Jan 31st, 2018
Read more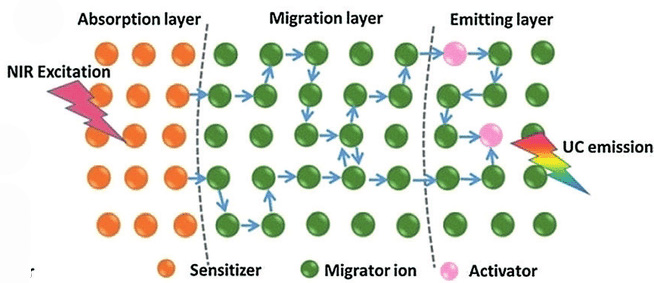 Through a collaborative approach of advanced spectroscopy and theoretical modelling, researchers were able to establish that the migration of excitation energy greatly affects the upconversion dynamics.
Through a collaborative approach of advanced spectroscopy and theoretical modelling, researchers were able to establish that the migration of excitation energy greatly affects the upconversion dynamics.
Jan 31st, 2018
Read more Dentistry researchers have developed a filling material with tiny particles made by self-assembly of antimicrobial drugs, designed to stop bacteria in its tracks.
Dentistry researchers have developed a filling material with tiny particles made by self-assembly of antimicrobial drugs, designed to stop bacteria in its tracks.
Jan 30th, 2018
Read more