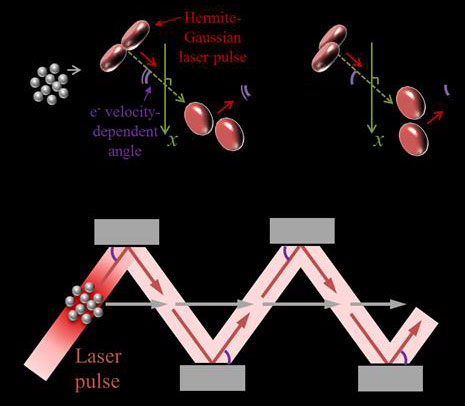
 A new, all-optical method for compressing narrow electron pulses to a billionth of a billionth of a second could improve real-time movies of chemical reactions and other ultrafast processes.
A new, all-optical method for compressing narrow electron pulses to a billionth of a billionth of a second could improve real-time movies of chemical reactions and other ultrafast processes.
Oct 13th, 2015
Read more
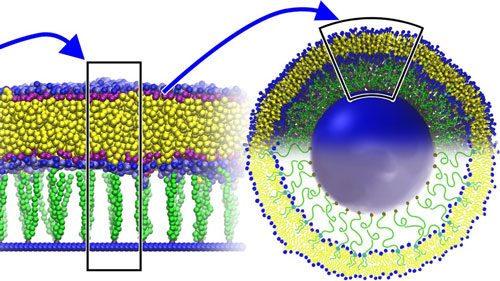 Computational models suggest new design for nanoparticles used in targeted drug delivery.
Computational models suggest new design for nanoparticles used in targeted drug delivery.
Oct 13th, 2015
Read more
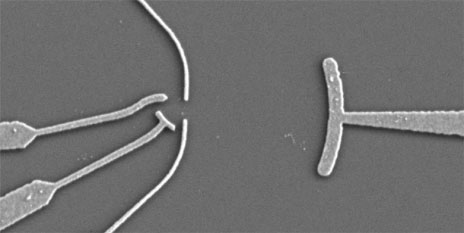 Resonators are an important tool in physics. The curved mirrors inside the resonators usually focus light waves that act, for instance, on atoms. Physicists have now managed to build a resonator for electrons and to direct the standing waves thus created onto an artificial atom.
Resonators are an important tool in physics. The curved mirrors inside the resonators usually focus light waves that act, for instance, on atoms. Physicists have now managed to build a resonator for electrons and to direct the standing waves thus created onto an artificial atom.
Oct 13th, 2015
Read more
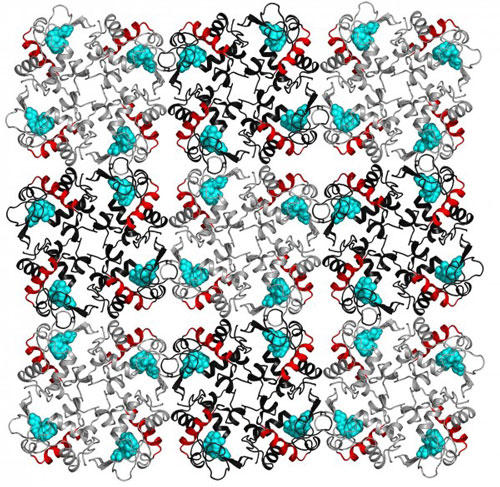 So-called Froehlich condensation, a state in which protein molecules' vibrational modes coalesce at the lowest frequency, was first predicted almost five decades ago, but never experimentally demonstrated until now.
So-called Froehlich condensation, a state in which protein molecules' vibrational modes coalesce at the lowest frequency, was first predicted almost five decades ago, but never experimentally demonstrated until now.
Oct 13th, 2015
Read more
 In addition to utilizing food and beverage waste that would otherwise decompose and be of no use, this development can also reduce potentially harmful waste from LEDs generally made from toxic elements.
In addition to utilizing food and beverage waste that would otherwise decompose and be of no use, this development can also reduce potentially harmful waste from LEDs generally made from toxic elements.
Oct 13th, 2015
Read more
Researchers have found a new way to capture energy from sunlight by using molecules that contain iron. The hope is to develop efficient and environmentally friendly solar energy applications.
Oct 13th, 2015
Read more
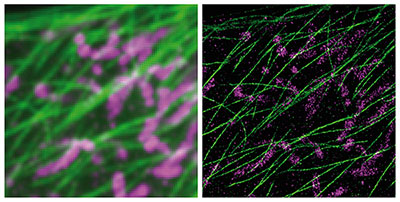 The new startup seeks to bring unprecedented resolution and multiplexing power to standard microscopes at very low cost, aiming to transform biomedical discovery and digital pathology.
The new startup seeks to bring unprecedented resolution and multiplexing power to standard microscopes at very low cost, aiming to transform biomedical discovery and digital pathology.
Oct 13th, 2015
Read more
 Researchers will produce a new research methodology that, on atomistic level, will enable customisation of the next generation of catalysts, which may become the cornerstones of future energy systems.
Researchers will produce a new research methodology that, on atomistic level, will enable customisation of the next generation of catalysts, which may become the cornerstones of future energy systems.
Oct 13th, 2015
Read more
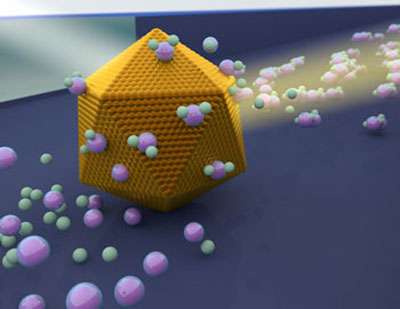 Studying catalytic processes on one single nanoparticle at a time, instead of on several billion simultaneously as has previously been the case, will create unique and more in-depth understanding of catalytic reactions on nanoparticles than previously possible - and it will at the same time lay the foundation for a new and sustainable energy technology and chemical synthesis.
Studying catalytic processes on one single nanoparticle at a time, instead of on several billion simultaneously as has previously been the case, will create unique and more in-depth understanding of catalytic reactions on nanoparticles than previously possible - and it will at the same time lay the foundation for a new and sustainable energy technology and chemical synthesis.
Oct 13th, 2015
Read more
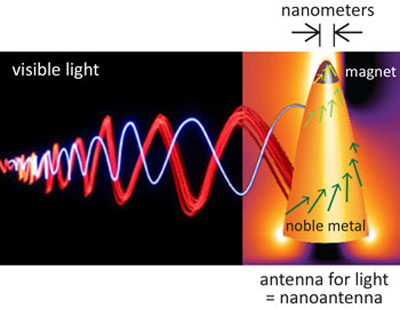 Researchers will take on a task that until now has been deemed impossible: creating strong interaction between light and magnetic fields and determining ways to control light with magnetism on the nanoscale.
Researchers will take on a task that until now has been deemed impossible: creating strong interaction between light and magnetic fields and determining ways to control light with magnetism on the nanoscale.
Oct 13th, 2015
Read more
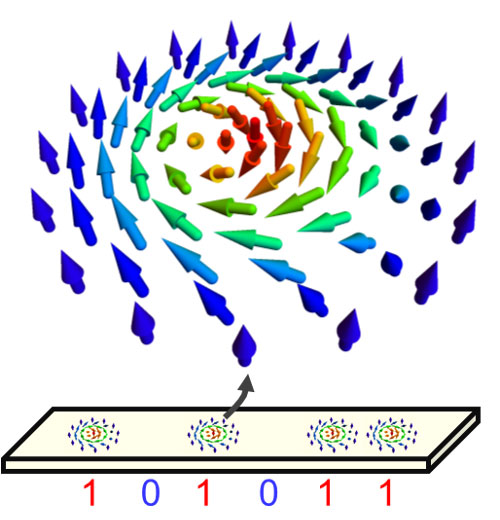 Researchers have found a way to manipulate skyrmions - tiny nanometer-sized magnetic vortices found at the surface of magnetic materials - using mechanical energy.
Researchers have found a way to manipulate skyrmions - tiny nanometer-sized magnetic vortices found at the surface of magnetic materials - using mechanical energy.
Oct 13th, 2015
Read more
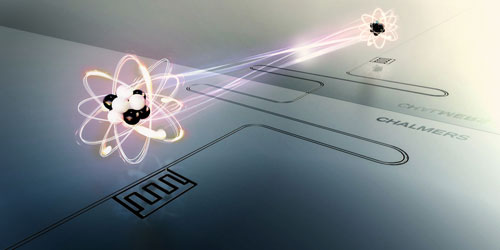 Researchers have succeeded in an experiment where they get an artificial atom to survive ten times longer than normal by positioning the atom in front of a mirror.
Researchers have succeeded in an experiment where they get an artificial atom to survive ten times longer than normal by positioning the atom in front of a mirror.
Oct 13th, 2015
Read more
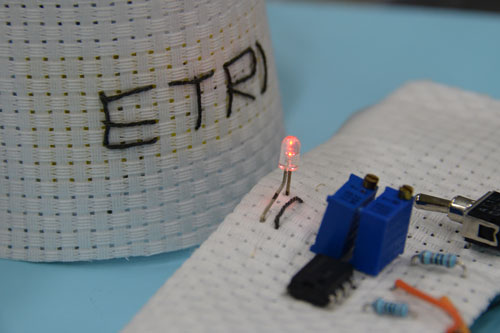 Scientists have developed wearable, graphene-coated fabrics that can detect dangerous gases present in the air, alerting the wearer by turning on an LED light.
Scientists have developed wearable, graphene-coated fabrics that can detect dangerous gases present in the air, alerting the wearer by turning on an LED light.
Oct 13th, 2015
Read more
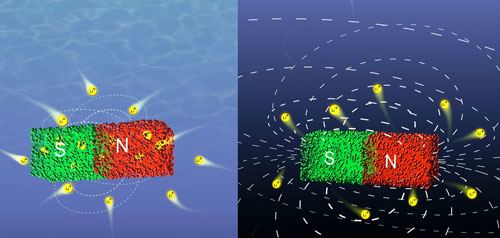 Magnets are well-known from the physics lessons at school, but they are hardly covered in chemistry lectures; and it is still a chemical process by means of which researchers have succeeded in controlling magnetic properties in bulk ferromagnets.
Magnets are well-known from the physics lessons at school, but they are hardly covered in chemistry lectures; and it is still a chemical process by means of which researchers have succeeded in controlling magnetic properties in bulk ferromagnets.
Oct 12th, 2015
Read more
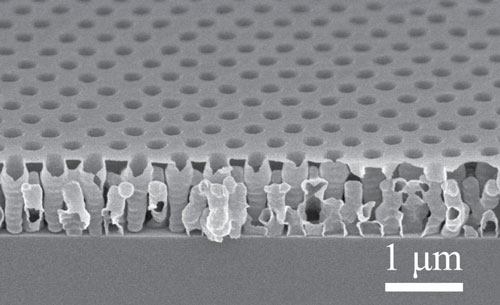 Researchers have developed a dielectric film that has optical and electrical properties similar to air, but is strong enough to be incorporated into electronic and photonic devices - making them both more efficient and more mechanically stable.
Researchers have developed a dielectric film that has optical and electrical properties similar to air, but is strong enough to be incorporated into electronic and photonic devices - making them both more efficient and more mechanically stable.
Oct 12th, 2015
Read more
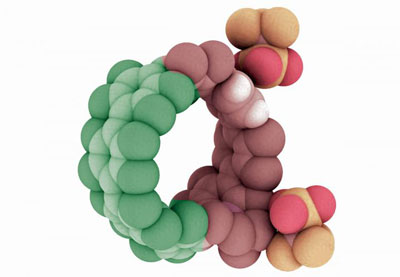 While application is down the road, these tiny organic circular structures could be used in solar cells, light-emitting diodes and medical diagnostics.
While application is down the road, these tiny organic circular structures could be used in solar cells, light-emitting diodes and medical diagnostics.
Oct 12th, 2015
Read more
 A new, all-optical method for compressing narrow electron pulses to a billionth of a billionth of a second could improve real-time movies of chemical reactions and other ultrafast processes.
A new, all-optical method for compressing narrow electron pulses to a billionth of a billionth of a second could improve real-time movies of chemical reactions and other ultrafast processes.














 Subscribe to our Nanotechnology News feed
Subscribe to our Nanotechnology News feed