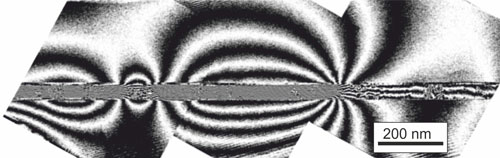
 Miniaturization is the magic word when it comes to nanomagnetic devices intended for use in new types of electronic components. Scientists now have proposed the use of ion beams for their fabrication. An ultra-fine beam consisting of around 10 neon ions suffices to bring several hundred atoms of an iron-aluminum alloy into disarray and thereby generate a nanomagnet embedded directly in the material.
Miniaturization is the magic word when it comes to nanomagnetic devices intended for use in new types of electronic components. Scientists now have proposed the use of ion beams for their fabrication. An ultra-fine beam consisting of around 10 neon ions suffices to bring several hundred atoms of an iron-aluminum alloy into disarray and thereby generate a nanomagnet embedded directly in the material.
Nov 23rd, 2015
Read more
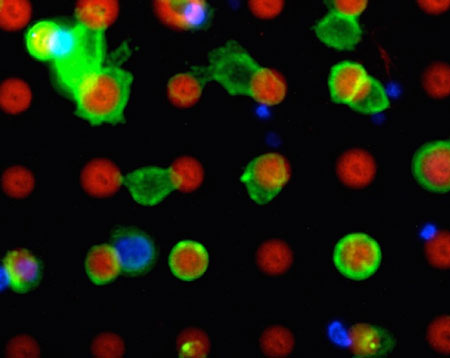 Researchers develop a new method to detect cancer cells in the blood before they settle in the tissue and form a new tumor.
Researchers develop a new method to detect cancer cells in the blood before they settle in the tissue and form a new tumor.
Nov 23rd, 2015
Read more
An interdisciplinary research team has found a way of accessing the interior of transistors. The researchers have manipulated the electron gas contained within by applying resonators to generate rhythmic oscillation in the terahertz range inside.
Nov 23rd, 2015
Read more
Physicists have discovered novel behaviours of materials that could enhance telecommunications technology.
Nov 23rd, 2015
Read more
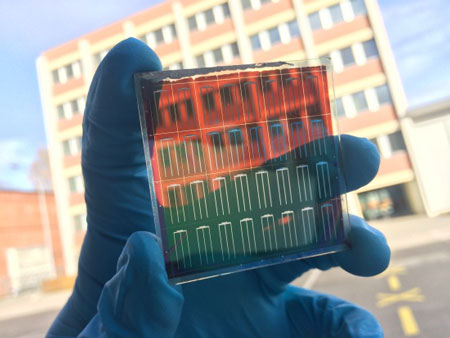 Researchers have come up with a procedure that makes it possible to produce thin film tandem solar cells in which a thin perovskite layer is used. The processing of peroveskite takes place at just 50 degrees Celsius and such a process is potentially applicable for low cost roll-to-roll production in future.
Researchers have come up with a procedure that makes it possible to produce thin film tandem solar cells in which a thin perovskite layer is used. The processing of peroveskite takes place at just 50 degrees Celsius and such a process is potentially applicable for low cost roll-to-roll production in future.
Nov 23rd, 2015
Read more
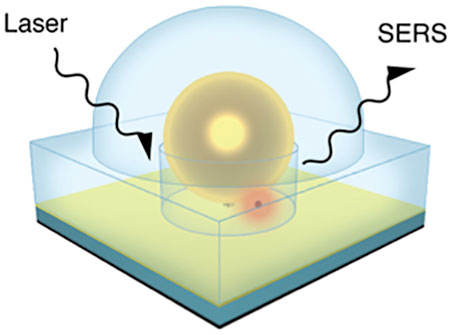 Researchers have developed a smart sensor that can detect single molecules in chemical and biological compounds - a highly valued function in medicine, security and defence.
Researchers have developed a smart sensor that can detect single molecules in chemical and biological compounds - a highly valued function in medicine, security and defence.
Nov 23rd, 2015
Read more
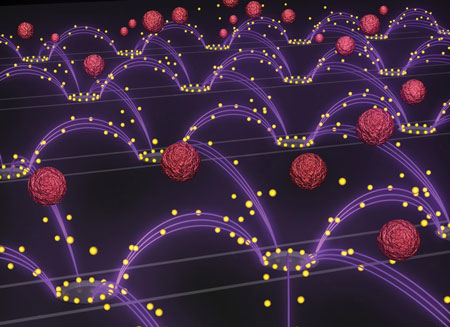 Engineers have developed a new technology that uses an oscillating electric field to easily and quickly isolate drug-delivery nanoparticles from blood. The technology could serve as a general tool to separate and recover nanoparticles from other complex fluids for medical, environmental, and industrial applications.
Engineers have developed a new technology that uses an oscillating electric field to easily and quickly isolate drug-delivery nanoparticles from blood. The technology could serve as a general tool to separate and recover nanoparticles from other complex fluids for medical, environmental, and industrial applications.
Nov 23rd, 2015
Read more
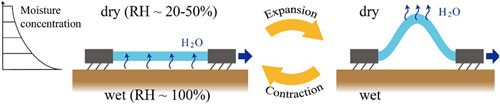 Here come futuristic, plant-inspired microrobots that are powered simply through changes in environmental humidity - no batteries or electrical components at all.
Here come futuristic, plant-inspired microrobots that are powered simply through changes in environmental humidity - no batteries or electrical components at all.
Nov 22nd, 2015
Read more
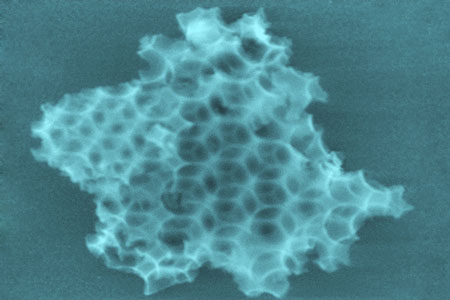 Researchers designed a novel bottom-up scalable process, using low cost chemical ingredients, to create three dimensional porous architectures from silica - with a complexity rivalling that found in nature.
Researchers designed a novel bottom-up scalable process, using low cost chemical ingredients, to create three dimensional porous architectures from silica - with a complexity rivalling that found in nature.
Nov 20th, 2015
Read more
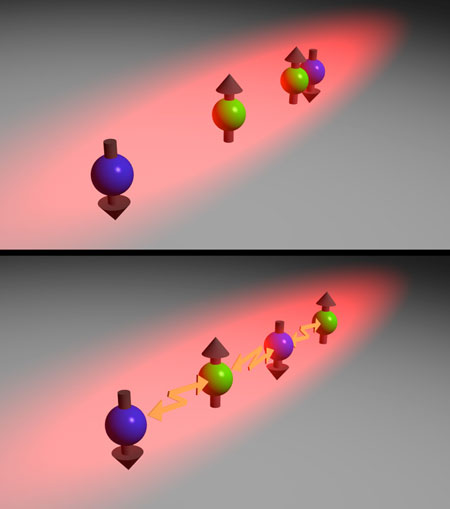 Physicists use ultracold atoms to imitate the behaviour of electrons in a solid.
Physicists use ultracold atoms to imitate the behaviour of electrons in a solid.
Nov 20th, 2015
Read more
New method builds on Nobel Prize-winning technique, with exciting implications for understanding the inner workings of cells and neurons.
Nov 20th, 2015
Read more
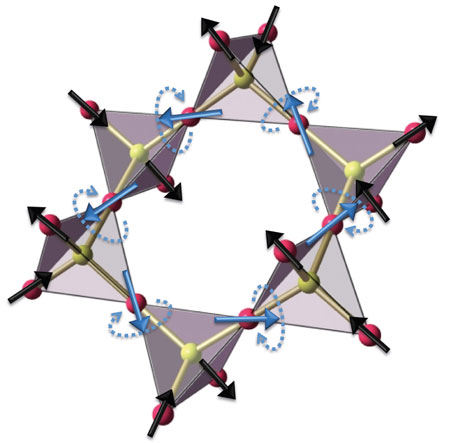 Computations reveal how quantum interactions can break a deadlock in magnetic spin ice oxides.
Computations reveal how quantum interactions can break a deadlock in magnetic spin ice oxides.
Nov 20th, 2015
Read more
 A brand-new competition, awarding finalists the opportunity to present their entries at the 2016 USA Science and Engineering Festival and compete for cash prizes, opens today for high school students interested in science, engineering and superpowers.
A brand-new competition, awarding finalists the opportunity to present their entries at the 2016 USA Science and Engineering Festival and compete for cash prizes, opens today for high school students interested in science, engineering and superpowers.
Nov 20th, 2015
Read more
 Affordable graphene production could lead to a wide range of new technologies reaching the market, including synthetic skin capable of providing sensory feedback to people with limb prostheses.
Affordable graphene production could lead to a wide range of new technologies reaching the market, including synthetic skin capable of providing sensory feedback to people with limb prostheses.
Nov 20th, 2015
Read more
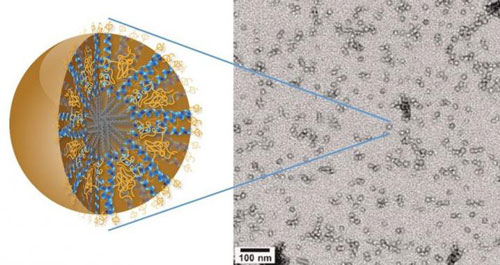 Researchers have developed a new family of nanocarriers, called 3HM, that meets all the size and stability requirements for effectively delivering therapeutic drugs to the brain for the treatment of a deadly form of cancer known as glioblastoma multiforme.
Researchers have developed a new family of nanocarriers, called 3HM, that meets all the size and stability requirements for effectively delivering therapeutic drugs to the brain for the treatment of a deadly form of cancer known as glioblastoma multiforme.
Nov 19th, 2015
Read more
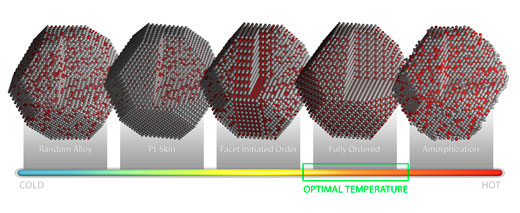 Atomic-level imaging of catalysts could help manufacturers lower the cost and improve the performance of emission-free fuel cell technologies.
Atomic-level imaging of catalysts could help manufacturers lower the cost and improve the performance of emission-free fuel cell technologies.
Nov 19th, 2015
Read more
 Miniaturization is the magic word when it comes to nanomagnetic devices intended for use in new types of electronic components. Scientists now have proposed the use of ion beams for their fabrication. An ultra-fine beam consisting of around 10 neon ions suffices to bring several hundred atoms of an iron-aluminum alloy into disarray and thereby generate a nanomagnet embedded directly in the material.
Miniaturization is the magic word when it comes to nanomagnetic devices intended for use in new types of electronic components. Scientists now have proposed the use of ion beams for their fabrication. An ultra-fine beam consisting of around 10 neon ions suffices to bring several hundred atoms of an iron-aluminum alloy into disarray and thereby generate a nanomagnet embedded directly in the material.












 Subscribe to our Nanotechnology News feed
Subscribe to our Nanotechnology News feed