Electronic Tattoos: The Future of Wearable Technology
What are Electronic Tattoos?
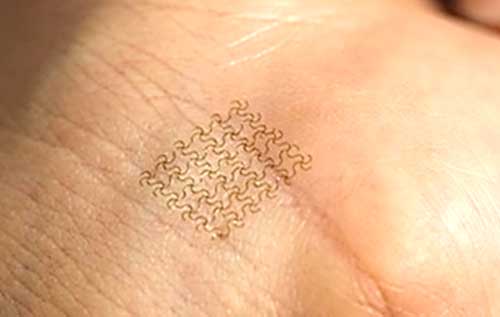
Electronic tattoos, also known as epidermal electronics or e-tattoos, are a groundbreaking development in wearable technology. Electronic tattoos are a specialized subset of electronic skin technologies. Designed to be ultra-thin, lightweight, and directly worn on the skin, e-tattoos conform closely to the body's contours and movements, making them virtually imperceptible yet highly functional. They primarily focus on medical and health-monitoring applications, offering capabilities such as physiological monitoring and transdermal drug delivery, distinguishing them from broader e-skin applications.
Electronic Skin (E-skin)
Electronic skin generally refers to a broader category of flexible, stretchable electronic devices that mimic the properties of human skin. E-skin can be used for various applications, such as:
- Prosthetics and robotics: Providing tactile sensing and feedback to enhance the functionality and control of artificial limbs and robotic systems.
- Large-area sensor networks: Covering large surfaces, such as walls or vehicles, with sensor arrays for environmental monitoring, structural health monitoring, or interactive interfaces.
- Wearable devices: Integrating sensors, displays, and other electronic components into clothing, patches, or accessories for health monitoring, fitness tracking, or personal electronics.
Electronic Tattoos (E-tattoos)
Electronic tattoos are a specific subset of electronic skin that are designed to be worn directly on the skin, conforming to the body's contours and movements. E-tattoos are typically thinner, more lightweight, and more intimately integrated with the skin compared to other types of e-skin. Key characteristics and applications of e-tattoos include:
- Ultra-thin and conformal: E-tattoos are often less than 100 micrometers thick, allowing them to seamlessly adhere to the skin without causing discomfort or irritation.
- Biocompatibility: The materials used in e-tattoos are carefully selected to ensure compatibility with the skin and minimize any adverse reactions.
- Physiological monitoring: E-tattoos are primarily used for continuous, non-invasive monitoring of vital signs, such as heart rate, blood pressure, temperature, and respiration.
- Transdermal drug delivery: Some e-tattoos are designed to deliver medications through the skin, providing targeted and controlled drug release.
Key Features of Electronic Tattoos
Electronic tattoos possess several unique features that distinguish them from traditional wearable devices:
- Ultra-thin and Lightweight: E-tattoos are typically less than 100 micrometers thick, making them incredibly lightweight and virtually imperceptible when worn on the skin.
- Flexibility and Stretchability: The materials used in electronic tattoos, such as polymers and nanomaterials, allow them to conform to the skin's surface and accommodate the body's natural movements without compromising functionality.
- Wireless Operation: E-tattoos can be powered wirelessly through various methods, such as near-field communication (NFC), radio-frequency identification (RFID), or energy harvesting from body heat or motion.
- Biocompatibility: The materials used in electronic tattoos are carefully selected to ensure biocompatibility and minimize any potential irritation or adverse reactions to the skin.
Applications of Electronic Tattoos
Electronic tattoos have a wide range of potential applications across various fields:
Healthcare Monitoring
E-tattoos can continuously monitor vital signs such as heart rate, blood pressure, temperature, and respiration. They can also track brain activity, detect seizures, and monitor wound healing. This real-time, non-invasive monitoring can revolutionize patient care and early disease detection.
Fitness and Sports
Electronic tattoos can provide athletes and fitness enthusiasts with valuable data on their performance, such as muscle activity, hydration levels, and electrolyte balance. This information can help optimize training, prevent injuries, and enhance overall performance.
Drug Delivery
E-tattoos can be designed to deliver drugs transdermally, providing a controlled and targeted release of medications. This can improve patient compliance, reduce side effects, and enable personalized treatment plans.
Human-Machine Interfaces
Electronic tattoos can serve as a natural and intuitive interface between humans and machines. They can detect gestures, translate sign language, or even provide haptic feedback, enabling new forms of communication and control.
Challenges and Future Perspectives
Despite the promising potential of electronic tattoos, several challenges need to be addressed for their widespread adoption. One of the main challenges is the durability and longevity of e-tattoos, as they need to withstand the wear and tear of daily use, as well as exposure to sweat, moisture, and other environmental factors.
Another challenge is the integration of advanced sensing capabilities and wireless communication in such thin and flexible form factors. Researchers are exploring novel materials, fabrication techniques, and power management strategies to overcome these hurdles.
Future research in electronic tattoos will focus on expanding their functionality, improving their reliability, and exploring new application domains. The integration of machine learning and artificial intelligence algorithms can enable smart and adaptive e-tattoos that can learn from user behavior and provide personalized insights and recommendations.
As electronic tattoos continue to evolve, they have the potential to transform the way we monitor our health, interact with technology, and enhance our daily lives. The fusion of nanotechnology, materials science, and electronics will drive the development of ever more sophisticated and capable e-tattoos, ushering in a new era of wearable technology.
Further Reading
Science, Epidermal Electronics
Journal of Dermatology and Skin Science, Electronic Tattoos: A Promising Approach to Real-time Theragnostics
