| May 22, 2019 | |
Data science helps engineers discover new materials for solar cells and LEDs(Nanowerk News) Engineers at the University of California San Diego have developed a high-throughput computational method to design new materials for next generation solar cells and LEDs. Their approach generated 13 new material candidates for solar cells and 23 new candidates for LEDs. Calculations predicted that these materials, called hybrid halide semiconductors, would be stable and exhibit excellent optoelectronic properties. |
|
| The team published their findings in the journal Energy & Environmental Science ("High-throughput computational design of organic–inorganic hybrid halide semiconductors beyond perovskites for optoelectronics "). | |
| Hybrid halide semiconductors are materials that consist of an inorganic framework housing organic cations. They show unique material properties that are not found in organic or inorganic materials alone. | |
| A subclass of these materials, called hybrid halide perovskites, have attracted a lot of attention as promising materials for next generation solar cells and LED devices because of their exceptional optoelectronic properties and inexpensive fabrication costs. However, hybrid perovskites are not very stable and contain lead, making them unsuitable for commercial devices. | |
 |
|
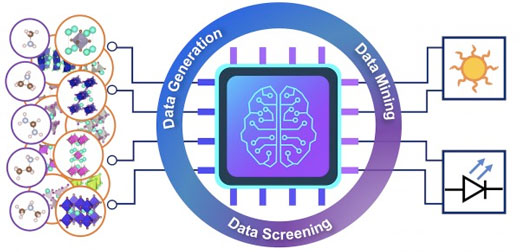
| Schematic illustration of the workflow for the high-throughput design of organic-inorganic hybrid halide semiconductors for solar cells and light emitting diodes. (Image: Yang lab) | |
| Seeking alternatives to perovskites, a team of researchers led by Kesong Yang, a nanoengineering professor at the UC San Diego Jacobs School of Engineering, used computational tools, data mining and data screening techniques to discover new hybrid halide materials beyond perovskites that are stable and lead-free. “We are looking past perovskite structures to find a new space to design hybrid semiconductor materials for optoelectronics.” Yang said. | |
| Yang’s team started by going through the two largest quantum materials databases, AFLOW and The Materials Project, and analyzing all compounds that were similar in chemical composition to lead halide perovskites. Then they extracted 24 prototype structures to use as templates for generating hybrid organic-inorganic materials structures. | |
| Next, they performed high-throughput quantum mechanics calculations on the prototype structures to build a comprehensive quantum materials repository containing 4,507 hypothetical hybrid halide compounds. Using efficient data mining and data screening algorithms, Yang’s team rapidly identified 13 candidates for solar cell materials and 23 candidates for LEDs out of all the hypothetical compounds. | |
 |
|
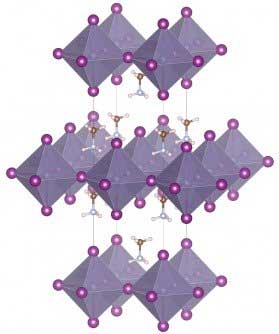
| One representative candidate material, (MA)2GeI4, with a Pearson symbol tI14. (Image: Yang lab) | |
| “A high-throughput study of organic-inorganic hybrid materials is not trivial,” Yang said. It took several years to develop a complete software framework equipped with data generation, data mining and data screening algorithms for hybrid halide materials. It also took his team a great deal of effort to make the software framework work seamlessly with the software they used for high-throughput calculations. | |
| “Compared to other computational design approaches, we have explored a significantly large structural and chemical space to identify novel halide semiconductor materials,” said Yuheng Li, a nanoengineering PhD candidate in Yang’s group and the first author of the study. This work could also inspire a new wave of experimental efforts to validate computationally predicted materials, Li said. | |
| Moving forward, Yang and his team are using their high-throughput approach to discover new solar cell and LED materials from other types of crystal structures. They are also developing new data mining modules to discover other types of functional materials for energy conversion, optoelectronic and spintronic applications. |
| Source: UC San Diego | |
|
Subscribe to a free copy of one of our daily Nanowerk Newsletter Email Digests with a compilation of all of the day's news. |
