| Aug 03, 2020 | |
Atoms at the photo shoot(Nanowerk News) The first photograph of a single trapped atom represented a milestone for quantum research. This breakthrough was made possible because the atom was captured in a vacuum using electric fields and held far from surfaces whose scattered light could blind the camera. |
|
| Scientists at Humboldt University of Berlin (HU) and Technical University of Vienna (TU) have now succeeded for the first time in taking photos of individual atoms floating less than a thousandth of a millimeter above a light-conducting glass fiber (Phys. Rev. Lett., "Imaging and localizing individual atoms interfaced with a nanophotonic waveguide"). | |
| This allows effects such as the absorption and emission of light to be studied in the laboratory in a much more controlled way than before. | |
| In addition, the knowledge gained will help to develop components for a new generation of optical fiber networks. | |
 |
|
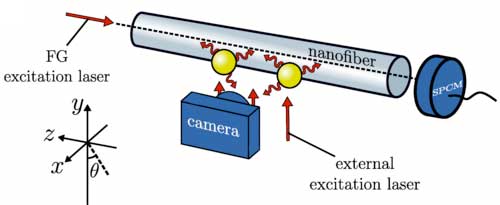
| A few cesium atoms are trapped ∼270 nm away from the surface of an optical nanofiber. They are exposed to a near-resonant excitation laser field that freely propagates along the +y direction. The atoms scatter this light and are imaged using a camera. A fraction of the scattered photons also couples to the nanofiber-guided mode. The atoms can also be excited or probed with light launched into the nanofiber. The light exiting the nanofiber can be detected with a single photon counting module (SPCM). (© Physical Review Letters) | |
| About ten years ago, Prof. Dr. Arno Rauschenbeutel's research group realized for the first time a novel atom-light interface in which several thousand atoms are trapped in the vicinity of special glass fibers. These are so-called optical nanofibers, which are 100 times thinner than a human hair. The atoms are captured with tweezers created by laser light only 0.2 micrometers away from the glass fiber surface. At the same time, they are cooled with laser light to a temperature of about one millionth of a degree above absolute zero. | |
| Despite these extreme conditions, the researchers have recently even been able to carry out experiments with single fiber-coupled atoms. They took photographs of the atoms and made short films of a few seconds duration (see link). To do this, they used an ultra-sensitive camera and had to rigorously shield any ambient light. Thanks to the permanent cooling, the atoms remained so steady that the images could be exposed for almost half a second. | |
| "Based on these results, we will be able to study the interaction of light and matter extremely precisely, atom by atom", says Dr. Philipp Schneeweiss, a member of Rauschenbeutel’s team. Possible applications of this research include more efficient light sources and photosensitive elements, using individual atoms as probes to study the properties of surfaces, and the optical processing of quantum information. |
| Source: Humboldt-Universität zu Berlin | |
|
Subscribe to a free copy of one of our daily Nanowerk Newsletter Email Digests with a compilation of all of the day's news. |
