| Mar 22, 2021 |
A novel nanofiltration membrane for highly-efficient dye/salt separation
(Nanowerk News) A research group led by Prof. WAN Yinhua from the Institute of Process Engineering (IPE) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences developed a robust dually charged loose nanofiltration (NF) membrane for highly efficient dye/salt separation.
|
|
The study was published in Journal of Membrane Science ("A robust dually charged membrane prepared via catechol-amine chemistry for highly efficient dye/salt separation").
|
|
NF is an effective method for treating textile wastewater. However, most commercially available NF membranes exhibit low selectivity in dye/salts separation due to their negatively charged dense separation layer.
|
 |
| Diagram of the dually charged membrane fabricated via catechol-amine chemistry surface engineering. (Image: CAO Yang)
|
|
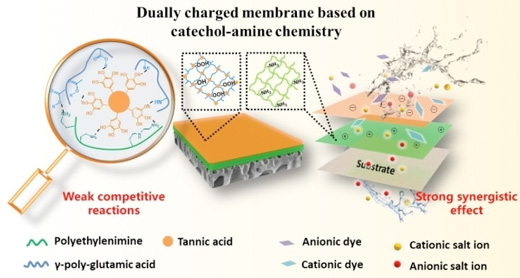
The researchers prepared a NF membrane with a loose and dually charged separation layer based on a simple catechol-amine chemistry surface engineering strategy.
|
|
In the strategy, polyethyleneimine (PEI) was coated on a hydrolyzed polyacrylonitrile substrate to construct a positively charged intermediate layer, followed by codeposition of tannic acid (TA) and poly-γ-glutamic acid (γ-PGA) to engineer a negatively charged top layer.
|
|
The loose separation layer structure was attributed to the competitive reaction induced by polyphenols, which means the covalent interactions, hydrogen bonding and electrostatic adsorption among TA, γ-PGA and PEI hindered the rapid and non-uniform self-polymerization of TA.
|
|
The pre-reaction between TA and γ-PGA could further weaken those competitive reactions, tuning the pore size and charging property, and thus improving the separation performance.
|
|
Due to the synergy between size exclusion and electrostatic interaction of the loose dual-charged separation layer, the prepared membrane exhibited outstanding water permeability (36.9 Lm-2h-1bar-1) with low salt rejections (11.1% for Na2SO4) and high rejection to both positively and negatively charged dyes.
|
|
Moreover, this dually charged membrane also showed excellent acid resistance as well as satisfactory antifouling performance and long-term stability.
"This work provides a novel dimension toward the environmental-friendly approach for preparing highly selective separation membrane, and such versatile coating strategy can be employed to fabricate/modify the membrane with controllable properties for various separation applications," said Prof. LUO Jianquan from IPE.
|

