| Posted: Aug 13, 2017 | |
Fabricating hexagonal boron nitride foam for CO2 absorption(Nanowerk News) In ACS Nano ("Lightweight Hexagonal Boron Nitride Foam for CO2 Absorption"), scientists report a technique to fabricate lightweight 3D macroscopic porous structures formed from hexagonal boron nitride (h-BN) nanosheets. |
|
| With its naturally occurring layered structure, hexagonal boron nitride (h-BN) has emerged as an important 2D material, possessing excellent properties such as high temperature stability, high thermal conductivity, as well as mechanical strength. | |
| The fabrication of three-dimensional porous nanostructures from interconnected two-dimensional (2D) materials such as graphene, clays, metal dichalcogenides, etc. has proven to be a promising technique to exploit their properties for several applications including catalysis, energy storage, biological and environmental applications, mechanical damping, and gas sequestration. | |
 |
|
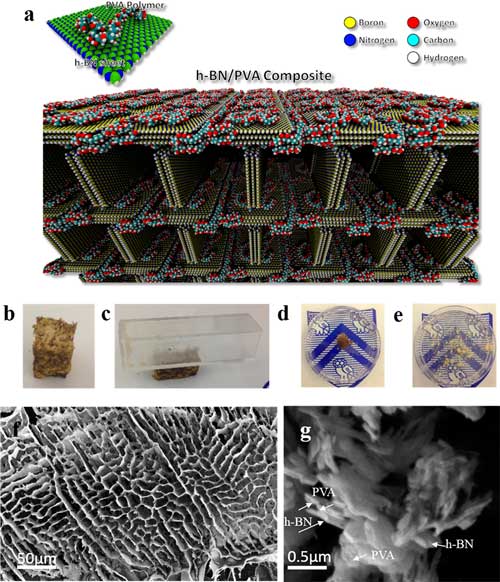
| Characterization and morphology of h-BN/PVA foams. (a) Schematic representation depicting the h-BN nanosheets connected by poly(vinyl alcohol) (PVA) molecules. Typical chains contain 30 monomers (∼6.2 nm chain length). The PVA molecules act like a glue to link the nanosheets through van der Waals interactions between the hydroxyl groups in the PVA and boron/nitrogen atoms in the nanosheets. (b) Structural stability of the h-BN/PVA foam. (c) Mechanical stability of the lightweight foam carrying a vial without any visible degradation. (d) Stable structure of the foam when subjected to liquids. (e) Pristine foam disintegrates in the presence of water, whereas h-BN/PVA maintains its stable interconnected morphology (Rice University owns the copyright for the logo displayed and is used with permission). (f,g) Lowmagnification and high-magnification image of the foam. (© ACS) (click on image to enlarge) | |
| In this new work, the researchers first liquid-phase-exfoliated h-BN in water to separate the layers, and then poly(vinyl alcohol) (PVA) was added (1-1.5 wt %), followed by in situ freeze-drying. | |
| The hybrid structure exhibits enhanced mechanical properties, large surface area, and increased porosity. | |
| According to the team, their fabrication method allows for the creation of intermolecular bonding between h-BN layers, where PVA acts like a bridge to link the individual layers, thus forming a network structure at the nanoscale. | |
| Unlike pristine h-BN foams, which normally disintegrate immediately once removed from a freeze-drier, h-BN/PVA foams show a robust freestanding structure with favorable mechanical stability. | |
| A detailed molecular dynamics study further verified and provided insights on the origins of such interconnections in improving the mechanical integrity. | |
| The foam also exhibits excellent CO2 absorption of 340% and storage under varying pressure values, mainly due to nitrogen functional groups and an increased surface area. | |
| Furthermore, when coated with polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS), the foam shows superior laser shielding properties by withstanding a varied amount of laser energy with minimal structural degradation. |
 By
Michael
Berger
– Michael is author of three books by the Royal Society of Chemistry:
Nano-Society: Pushing the Boundaries of Technology,
Nanotechnology: The Future is Tiny, and
Nanoengineering: The Skills and Tools Making Technology Invisible
Copyright ©
Nanowerk LLC
By
Michael
Berger
– Michael is author of three books by the Royal Society of Chemistry:
Nano-Society: Pushing the Boundaries of Technology,
Nanotechnology: The Future is Tiny, and
Nanoengineering: The Skills and Tools Making Technology Invisible
Copyright ©
Nanowerk LLC
|
|
|
Subscribe to a free copy of one of our daily Nanowerk Newsletter Email Digests with a compilation of all of the day's news. |
