| Feb 20, 2022 |
Pine needles inspire MOF-based solar steam generation
(Nanowerk News) Solar steam generation has become a promising renewable energy technology for water harvesting, desalination, and purification, that could benefit people who need it most in remote communities, disaster-relief areas, and developing nations.
|
|
Solar steam generation turns solar energy into heat, which evaporates water, and the steam is then condensed into drinking water.
|
|
Inspired by drying clothes outside under solar irradiation, researchers have now demonstrated a novel biface evaporator using an ultrablack copper-based metal−organic framework (MOF) foam with pine needle-like hierarchical structures as the photothermal material.
|
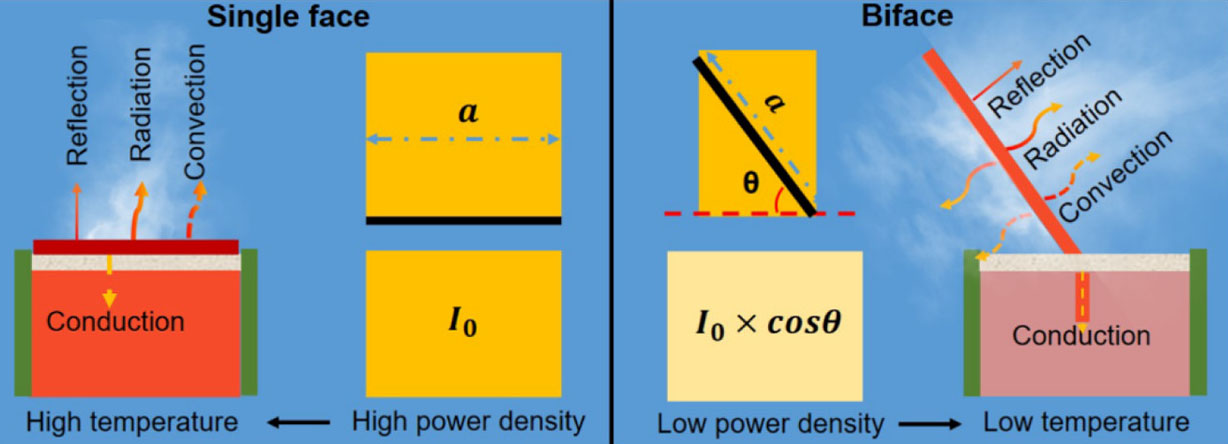 |
| Concept of single-face and biface evaporators. Compared with the single-face evaporator, the biface evaporator has a low power density and low contact area with bulk water, which leads to its low evaporation surface temperature and low energy losses by radiation, convection, and conduction. (Reprinted with permission by American Chemical Society)
|
|
As the researchers point out, the simple spatial change from lying flat on the water to being mostly exposed to the air, greatly improves the evaporation performances and application value of the biface evaporator.
|
|
The findings have been reported in ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces("Over 11 kg m−2 h−1 Evaporation Rate Achieved by Cooling Metal−Organic Framework Foam with Pine Needle-Like Hierarchical Structures to Subambient Temperature")
|
|
The researchers fabricated their ultrablack Cu−Cu(OH)2-MOF foam with interconnected pores and pine needle-like hierarchical structures by vertically growing Cu(OH)2 nanowires on Cu foam and then radially growing Cu-MOF nanowhiskers around the Cu(OH)2 nanowires.
|
|
The pine needle-like hierarchical structures of the MOF foam lead to multiple absorption and enhanced scattering of the incident light, which result in its excellent light absorption of 99.01% across 250−2000 nm. Besides, the pine needle-like hierarchical structures also contribute to enhancing the capillary force of the foam and thereby supplying adequate water.
|
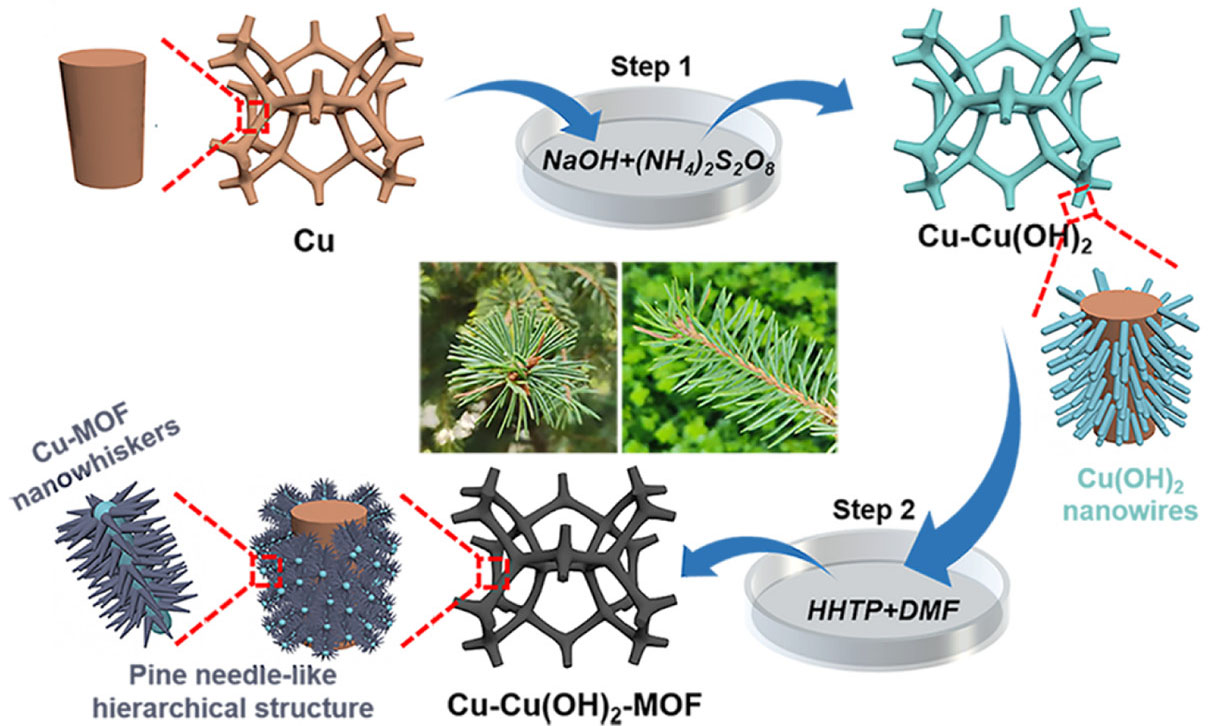 |
| Schematic diagram of the fabrication process of Cu−Cu(OH)2-MOF foam with pine needle-like hierarchical structures. Cu−Cu(OH)2-MOF foam with pine needle-like hierarchical structures was fabricated using a simple two-step solvent method. (Reprinted with permission by American Chemical Society)
|
|
The team's biface evaporator achieved a high evaporation rate of 3.27 kg m−2 h−1, which was 9.62 and 2.80 times that of pure water and a single-face evaporator, respectively, under one sun illumination.
|
|
Furthermore, when cooled in seawater to subambient temperature by coupling with an air flow of 5.8 m s−1, the biface evaporator achieved an ultrahigh evaporation rate of 11.58 kg m−2 h−1 with an efficiency of 160%, which according to the authors, are the highest data among the up-to-date evaporators. The biface evaporator showed a high evaporation rate of 7.76 kg m−2 h−1 in an outdoor test, showing its great application prospect to be used in drinking water production and seawater desalination.
|


 By
Michael
Berger
– Michael is author of three books by the Royal Society of Chemistry:
Nano-Society: Pushing the Boundaries of Technology,
Nanotechnology: The Future is Tiny, and
Nanoengineering: The Skills and Tools Making Technology Invisible
Copyright ©
Nanowerk LLC
By
Michael
Berger
– Michael is author of three books by the Royal Society of Chemistry:
Nano-Society: Pushing the Boundaries of Technology,
Nanotechnology: The Future is Tiny, and
Nanoengineering: The Skills and Tools Making Technology Invisible
Copyright ©
Nanowerk LLC
