| Nov 24, 2021 |
4D-printed dual stimulus responsive alginate hydrogel
|
|
(Nanowerk News) Stimuli-responsive hydrogels not only express excellent biocompatibility, but also can respond when exposed to external stimulation, enabling a wider range of applications in biomedicine. However, at present, stimuli-responsive hydrogel shows poor mechanical properties and limited response to a single stimulus.
|
|
There is a great need for stimuli-responsive hydrogels with excellent mechanical properties and capability to respond to multiple stimuli.
|
|
A team led by WANG Qihua and WANG Tingmei from the Lanzhou Institute of Chemical Physics (LICP) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences recently has issued a report on four dimensional (4D) printing of dual-stimuli response alginate hydrogel.
|
 |
| The deformation mechanism of alginate hydrogel. (Image: Lanzhou Institute of Chemical Physics)
|
|
The findings were reported in ACS Applied Polymer Materials ("4D Printing of a Sodium Alginate Hydrogel with Step-Wise Shape Deformation Based on Variation of Crosslinking Density").
|
|
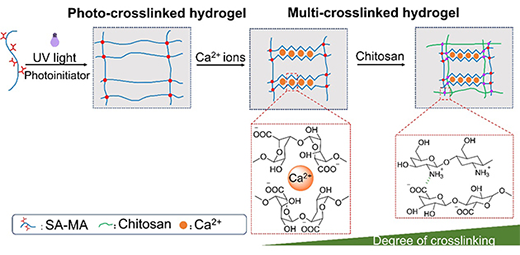
According to the researchers, these hydrogel structures were directly printed with high structural accuracy, following which the hydrogels were immersed in Ca2+ solution and chitosan solution respectively. The 4D printed hydrogels were able to perform step-wise volume contraction.
|
|
The soaking strategy adopted was able to not only achieve step-wise volume contraction of the sodium alginate structure, but also continuous enhancement of the mechanical properties of alginate hydrogel with continuous immersion in two solutions.
|
|
The printed structures were able to be used for loading-unloading experiments five times and support an object which weighs 361 times its own weight.
|

